Need clear, concise information about Zithromax? This article provides practical guidance on its usage, focusing on key aspects to help you understand your treatment. We’ll explore common uses, potential side effects, and crucial precautions.
Zithromax, also known as azithromycin, is a macrolide antibiotic effective against various bacterial infections. It’s frequently prescribed for respiratory infections like bronchitis and pneumonia, as well as certain sexually transmitted infections. However, remember this medication treats bacterial, not viral infections. A proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional is vital before starting any treatment.
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and stomach upset. More serious, though less frequent, reactions can occur. Always report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately. Furthermore, interact with your physician about potential drug interactions, particularly with other medications you’re currently taking. This ensures safe and effective treatment.
Proper dosage and treatment duration are critical for successful outcomes and preventing antibiotic resistance. Strictly adhere to your doctor’s prescribed regimen. Do not stop taking the medication prematurely, even if you feel better. Completing the full course is key to eradicating the infection. Your healthcare provider will answer any questions you have regarding dosage and potential risks.
- Zithromax (Azithromycin) Information: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Zithromax
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- Drug Interactions
- Storage and Disposal
- What is Zithromax (Azithromycin)?
- Common Uses
- Dosage and Administration
- Possible Side Effects
- Precautions
- Note:
- Alternatives
- Common Uses of Zithromax
- How to Take Zithromax: Dosage and Administration
- Potential Side Effects of Zithromax
- Drug Interactions with Zithromax
- Antacids and Zithromax
- Drugs Affected by Zithromax
- Specific Medication Interactions
- Other Considerations
- Reporting Adverse Effects
- Precautions and Warnings Regarding Zithromax Use
- Zithromax and Pregnancy/Breastfeeding
- Pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
- Important Note:
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Zithromax
- Signs Requiring Medical Attention
- Zithromax Alternatives and Treatment Options
Zithromax (Azithromycin) Information: A Comprehensive Guide
Always consult your doctor before starting any medication, including Zithromax. This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice.
Understanding Zithromax
Zithromax, containing azithromycin, is a macrolide antibiotic. It fights bacterial infections by stopping bacteria from producing proteins necessary for their survival. This medication targets a wide range of bacterial infections.
- Common Uses: Zithromax treats various infections, including bronchitis, pneumonia (certain types), sinusitis, ear infections (otitis media), and some sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea.
- Dosage: Your doctor determines the correct dosage based on your specific infection and health. Typical regimens involve taking a single daily dose for several days. Strictly follow your prescribed dosage and duration.
- Administration: Zithromax is usually taken orally, as tablets or suspension.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Like all medications, Zithromax can cause side effects. These vary in severity and frequency.
- Common Side Effects: Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain are possible. These are usually mild and temporary.
- Less Common, but Serious Side Effects: Allergic reactions (rash, hives, swelling), heart rhythm problems, liver problems, and severe diarrhea (pseudomembranous colitis) can occur. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any serious side effect.
- Precautions: Inform your doctor of any existing health conditions, especially liver or heart problems, before taking Zithromax. Also disclose any allergies to medications. Pregnancy and breastfeeding should be discussed with your doctor before initiating treatment.
Drug Interactions
- Zithromax can interact with certain medications. Always inform your physician about all the medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking.
- Some interactions may increase the risk of side effects or reduce the effectiveness of Zithromax.
- Your doctor can assess potential interactions and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
Storage and Disposal
Store Zithromax as directed on the label, usually at room temperature, away from moisture and heat. Properly dispose of any unused medication following your pharmacist’s or doctor’s instructions. Never flush medication down the toilet.
What is Zithromax (Azithromycin)?
Zithromax is an antibiotic containing azithromycin, a macrolide. It fights bacterial infections by stopping bacterial protein synthesis, thus preventing bacterial growth.
Common Uses
- Respiratory tract infections like bronchitis and pneumonia.
- Skin infections such as cellulitis and impetigo.
- Ear infections (otitis media).
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia and gonorrhea.
Doctors frequently prescribe it for these conditions due to its effectiveness and convenient dosage schedule.
Dosage and Administration
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Dosage varies depending on the infection being treated and your individual health. Typical regimens involve a few days of medication, often just once daily.
Possible Side Effects
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling)
Serious side effects are rare but require immediate medical attention. Inform your doctor about any health concerns or medications you are currently taking before starting Zithromax.
Precautions
- Inform your doctor about any allergies, especially to antibiotics.
- Let your doctor know about any liver or kidney problems.
- Discuss potential interactions with other medications.
- Avoid alcohol consumption during treatment.
Note:
This information is for general knowledge and should not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your physician or pharmacist for diagnosis and treatment of any health issue.
Alternatives
If azithromycin isn’t suitable, your doctor can discuss other antibiotic options appropriate for your specific infection.
Common Uses of Zithromax
Zithromax, the brand name for azithromycin, effectively treats various bacterial infections. Its widespread use stems from its broad spectrum of activity and convenient dosing schedule.
Respiratory infections frequently respond well to Zithromax. This includes bronchitis, pneumonia (certain types), and sinusitis. The medication targets bacteria commonly responsible for these ailments, offering relief from symptoms like coughing and congestion.
Skin infections are another common application. Zithromax is often prescribed for cellulitis, an infection of the deeper layers of skin, and erysipelas, a superficial skin infection. It effectively combats the bacteria causing these conditions, promoting healing.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) also benefit from Zithromax treatment. It’s commonly used to treat chlamydia and gonorrhea, significantly reducing the spread of these infections. However, always follow your doctor’s guidance and complete the entire course of antibiotics.
Beyond these key applications, Zithromax may be used for other infections depending on the specific bacterial cause and your physician’s assessment. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment options.
| Infection Type | Common Bacteria Targeted |
|---|---|
| Respiratory Infections (Bronchitis, Pneumonia, Sinusitis) | Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae |
| Skin Infections (Cellulitis, Erysipelas) | Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes |
| Sexually Transmitted Infections (Chlamydia, Gonorrhea) | Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
Remember, antibiotics, including Zithromax, should only be used as prescribed by a doctor. Misuse can lead to antibiotic resistance.
How to Take Zithromax: Dosage and Administration
Always follow your doctor’s prescription exactly. Dosage depends on your specific infection and your weight. Commonly, adults take a single dose of 1 gram or a 500mg dose for the first day followed by 250mg per day for four to five days. Children’s dosages are significantly lower and are always determined by the doctor based on their weight and condition.
Take Zithromax with a full glass of water. You can take it with or without food, but consistency is key. If you choose to take it with food, try to maintain a similar pattern every time. This helps to maintain consistent blood levels of the medication.
Complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if you feel better before finishing the medication. Stopping early can allow bacteria to survive and possibly return. This can lead to a more resistant infection.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it’s nearly time for your next dose. Do not take two doses at once to make up for a missed dose. If you have questions about missed doses, contact your doctor or pharmacist immediately.
Store Zithromax at room temperature, away from moisture and direct sunlight. Keep it out of reach of children.
Inform your doctor of any allergies, other medications you’re taking (including over-the-counter drugs), pregnancy, breastfeeding, or liver/kidney problems before starting treatment.
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Contact your doctor if you experience severe or persistent side effects.
Potential Side Effects of Zithromax
Zithromax, while generally safe and effective, can cause side effects. The most common are mild and usually resolve without treatment. These include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Some individuals experience vomiting or indigestion.
Less common but more serious side effects can occur. These include allergic reactions, such as skin rash, itching, or swelling. In rare cases, a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) may develop, requiring immediate medical attention. Contact your doctor immediately if you experience shortness of breath, hives, or swelling of your face, lips, or throat.
Changes in your hearing or dizziness are possible side effects. Report these symptoms promptly to your physician. Similarly, temporary changes in your sense of taste or smell have been reported. These usually subside once you finish the medication.
Severe side effects are infrequent but include liver problems (hepatitis) and inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis). Seek immediate medical advice if you experience persistent abdominal pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), or dark urine.
This information doesn’t cover all possible side effects. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for a complete list and to discuss any concerns you may have. Always follow your physician’s instructions for taking this medication.
Drug Interactions with Zithromax
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins, before starting Zithromax. This helps prevent potentially harmful interactions.
Antacids and Zithromax
Taking antacids containing aluminum or magnesium can reduce Zithromax absorption. Separate the administration of these medications by at least two hours for optimal efficacy.
Drugs Affected by Zithromax
Zithromax can interact with several medications, altering their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. This includes blood thinners like warfarin (Coumadin), certain heart medications, and some drugs used to treat seizures. Your doctor should monitor you closely if you’re taking these concurrently.
Specific Medication Interactions
| Medication Class | Specific Medications | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulants | Warfarin | Increased bleeding risk |
| Ergot alkaloids | Ergotamine, dihydroergotamine | Increased risk of ergotism |
| Statins | Simvastatin, lovastatin | Increased risk of muscle damage (rhabdomyolysis) |
| Digoxin | Digoxin | Increased digoxin levels |
Other Considerations
Zithromax may also interact with certain types of birth control pills, potentially decreasing their effectiveness. Discuss alternative contraception with your doctor during Zithromax treatment. Always check with your doctor or pharmacist before starting or stopping any medication while taking Zithromax.
Reporting Adverse Effects
Report any unusual side effects or health changes to your healthcare provider immediately. This information allows them to make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan and ensure your safety.
Precautions and Warnings Regarding Zithromax Use
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This helps avoid potentially harmful interactions.
Zithromax can cause diarrhea. Severe diarrhea might indicate a serious condition called Clostridium difficile infection. Contact your doctor immediately if you experience persistent or bloody diarrhea.
Sun sensitivity is a possible side effect. Protect yourself from excessive sun exposure by wearing protective clothing and sunscreen while using Zithromax.
Liver problems are a rare but potential risk. Report any signs of liver trouble, like jaundice (yellowing of skin or eyes) or dark urine, to your doctor without delay.
Allergic reactions, ranging from mild rashes to severe anaphylaxis, can occur. Stop taking Zithromax and seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms like hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
Zithromax may prolong the QT interval, a measure of heart rhythm. This is a concern for people with heart conditions. Discuss your heart health with your doctor before starting Zithromax.
This medication can affect blood sugar levels. If you have diabetes, monitor your blood glucose closely.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding require careful consideration. Consult your physician about Zithromax use during these periods.
Follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage and duration precisely. Do not stop taking Zithromax prematurely, even if you feel better. Completing the course is vital for effective treatment.
Store Zithromax as directed on the label to maintain its effectiveness.
Zithromax and Pregnancy/Breastfeeding
Consult your doctor before using Zithromax during pregnancy or breastfeeding. The decision to use Zithromax depends on weighing potential benefits against potential risks.
Pregnancy
Zithromax is categorized as a Pregnancy Category B drug by the FDA. This means studies in animals have not shown risk to the fetus, but adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women are lacking. Your doctor will assess your individual circumstances and determine if the benefits of Zithromax outweigh potential risks to your pregnancy.
- Discuss your specific health condition and treatment options with your physician.
- Provide a complete medical history, including existing conditions and medications.
- Expect thorough monitoring throughout your pregnancy if Zithromax is prescribed.
Breastfeeding
Zithromax is excreted in breast milk. While the amount is generally considered low, it’s still recommended to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor. They may suggest alternative treatments or monitor your baby closely if you choose to use Zithromax while breastfeeding.
- Inform your doctor if you are breastfeeding.
- Consider the possible effects on your baby. Your doctor can advise on monitoring your child.
- Explore alternative treatment options if breastfeeding is a priority.
Important Note:
This information is for guidance only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider before making decisions regarding your health or medication use. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your unique situation.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Zithromax
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe allergic reactions like difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat, or hives. These are serious and require immediate medical attention.
Signs Requiring Medical Attention
Seek medical advice if you develop persistent diarrhea, significant abdominal pain, or bloody stools. These could indicate a serious side effect called Clostridium difficile colitis.
Also, contact your physician if you experience symptoms such as severe headache, confusion, unusual behavior, seizures, or changes in vision or hearing. These may indicate a less common, but serious, side effect.
If your symptoms don’t improve after completing the prescribed course of Zithromax, schedule a follow-up appointment with your doctor. They will assess your condition and determine the next steps.
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting Zithromax treatment. This helps avoid potential drug interactions.
Zithromax Alternatives and Treatment Options
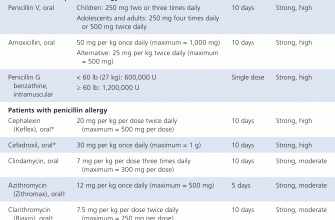
If Zithromax isn’t suitable, doctors often prescribe alternative antibiotics like azithromycin’s close relative, clarithromycin, or erythromycin. These target similar bacteria.
For specific infections, consider these options: Doxycycline effectively treats certain bacterial infections, including some respiratory and sexually transmitted infections. Amoxicillin is a common choice for various infections, particularly ear and respiratory ones. Cefuroxime, a cephalosporin, is another option for respiratory or skin infections.
Choosing the right alternative depends entirely on the infection’s type and severity, as well as individual factors like allergies and medical history. A doctor will consider these factors when making a treatment plan.
Beyond antibiotics, consider supportive care. This includes plenty of rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to manage symptoms.
Always consult a doctor before starting any new medication or treatment. They can accurately diagnose the infection and recommend the safest and most effective approach for your individual needs.