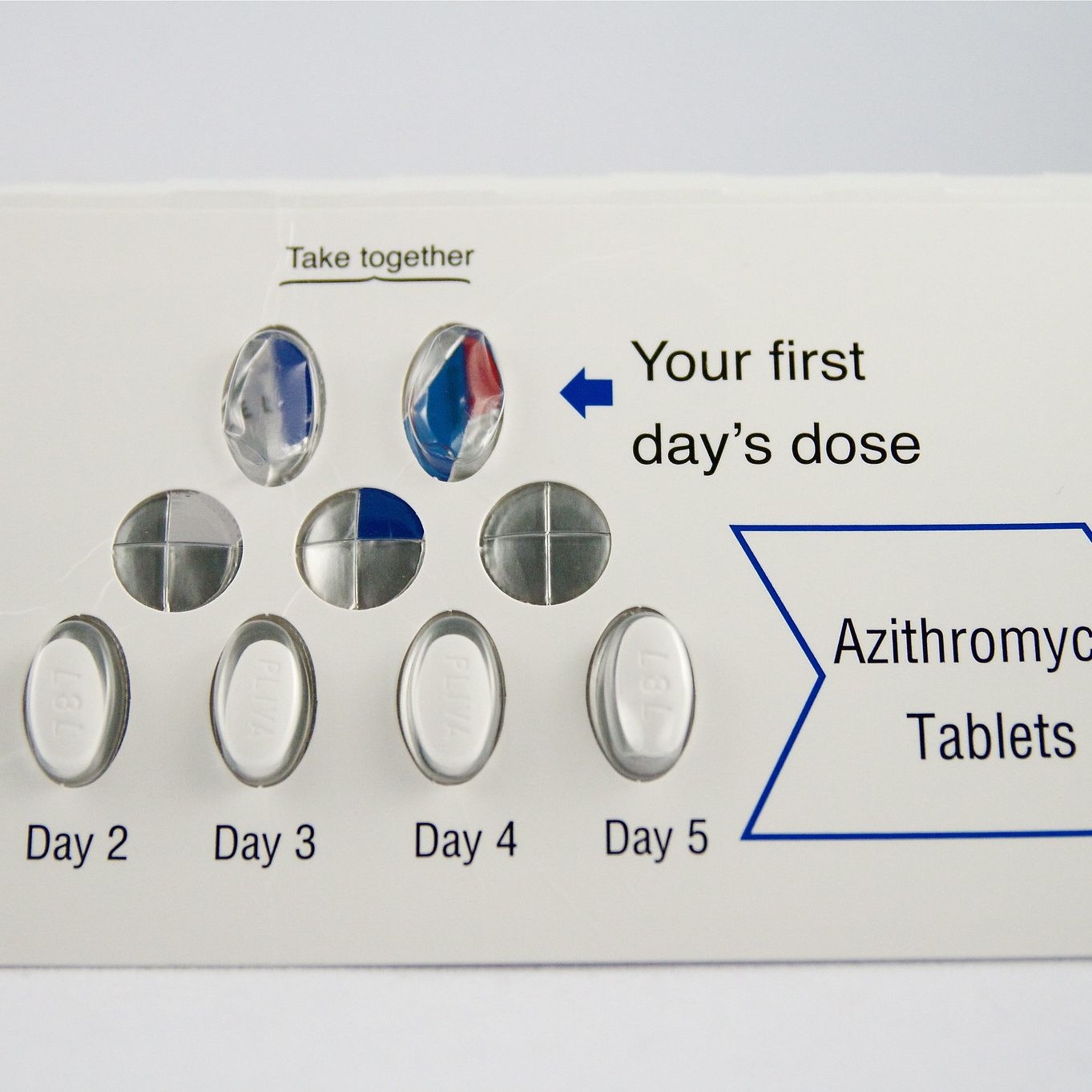
For adults treating common bacterial infections, the typical Zithromax (azithromycin) dosage is 500 mg on the first day, followed by 250 mg daily for four days. This equates to a total of 1500 mg over five days. This regimen is often prescribed for conditions like bronchitis and pneumonia, but always consult your doctor for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.
Children’s dosages vary significantly based on weight and specific infection. A doctor will determine the appropriate dose, usually a lower daily amount spread over a similar five-day course. Never administer adult medication to children; incorrect dosage can be harmful.
Remember, Z-pack is only effective against bacterial infections. Viral infections, like the common cold or flu, will not respond to this antibiotic. Taking antibiotics unnecessarily contributes to antibiotic resistance, a growing public health concern. Always seek professional medical advice before starting any antibiotic treatment. Your physician will conduct a thorough examination to ensure Z-pack is the right medication for your specific infection.
While generally well-tolerated, potential side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Rarely, more serious reactions occur. Report any unexpected symptoms or side effects to your doctor immediately. Proper storage is also crucial; follow the instructions provided on your prescription label for optimal medication efficacy and safety.
Understanding Z-Pack (Azithromycin) Dosage for Adults
The typical adult dosage for Z-Pack (azithromycin) is 500 mg on the first day, followed by 250 mg daily for four more days. This amounts to a total of 1500 mg over five days. This is a common regimen, but your doctor might prescribe a different dosage depending on your specific infection and health.
Variations in Dosage
Sometimes, a different dosage is needed. For example, a doctor may prescribe a higher initial dose, such as 1000 mg, followed by 500 mg daily. Or they might adjust the total treatment duration. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely; never alter your medication schedule yourself.
Important Considerations
Certain medical conditions, such as liver problems, can affect how your body processes azithromycin. Your doctor will adjust the dosage accordingly if needed. Never take more azithromycin than prescribed. Report any side effects, such as stomach upset or allergic reactions, to your healthcare provider immediately. Azithromycin can interact with other medications, so inform your doctor about all medications you’re currently taking.
Z-Pack (Azithromycin) Dosage for Children: A Cautious Approach
Never administer Z-Pack to a child without first consulting your pediatrician. Dosage depends heavily on the child’s weight and the specific infection. A doctor will determine the appropriate amount of azithromycin based on these factors and your child’s overall health. Self-treating can be dangerous and lead to complications.
Typical Pediatric Dosage Guidelines (Consult a Doctor Before Use)
While general guidelines exist, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice. These guidelines illustrate the range of dosages: A common regimen might involve a loading dose on the first day, followed by lower daily doses. For example, a 250mg/5ml suspension might have a loading dose of 10ml, followed by 5ml for the next four days. However, weight-based calculations are crucial. Your doctor will perform this calculation and provide a precise prescription. Always follow the doctor’s instructions strictly; never deviate from the prescribed dosage or duration.
Potential Side Effects in Children
Children may experience side effects like diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain, or allergic reactions. Immediate medical attention is necessary for severe reactions. Inform your doctor about any pre-existing conditions or allergies your child has before starting treatment. Closely monitor your child for any unusual symptoms during and after treatment.