When used correctly, amoxicillin is generally safe for treating bacterial infections. However, like any medication, it carries potential risks and side effects. Be aware that allergic reactions can occur, especially among individuals with a history of penicillin allergies. Symptoms may include skin rashes, itching, and, in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
It’s vital to take amoxicillin as prescribed by a healthcare professional. Misuse, such as not completing the course or using it for viral infections, can contribute to antibiotic resistance and other health issues. Pay close attention to dosing recommendations to minimize risks and enhance treatment effectiveness.
Monitor any side effects during the course of treatment. Common reactions include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, which can be uncomfortable but are often manageable. Consult your doctor if these symptoms persist or worsen. For some, probiotics may help restore digestive balance during and after a course of antibiotics.
In summary, while amoxicillin serves as a valuable tool in combating bacterial infections, understanding its potential dangers ensures a safer experience. Stay informed, communicate with your healthcare provider, and adhere to their advice for optimal results.
Is Amoxicillin Dangerous?
Amoxicillin is generally safe for most individuals when taken as prescribed. It effectively treats various bacterial infections, but it can pose risks in specific situations.
Some patients may experience allergic reactions, ranging from mild skin rashes to severe anaphylaxis. If you have a history of penicillin allergies, avoid using amoxicillin without consulting your doctor.
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and stomach upset. These are typically mild, but they can lead to dehydration if severe. Staying hydrated can help manage these symptoms.
It’s essential to complete the full course of treatment to prevent antibiotic resistance. Stopping early, even if symptoms improve, could lead to a resurgence of infection.
Drug interactions can also occur. Inform your healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and herbal products you use to avoid potential complications.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should discuss the use of amoxicillin with their healthcare provider, as it can affect both mother and child.
Always follow medical advice regarding dosage and duration. Self-medicating or altering the prescribed regimen can increase the risk of unwanted effects.
In conclusion, while amoxicillin is safe for many, awareness of potential risks and proper usage will enhance its benefits while minimizing dangers.
Understanding Amoxicillin: Uses and Benefits
Amoxicillin serves as a powerful antibiotic, primarily used to treat bacterial infections. It effectively targets infections in the respiratory tract, ear, nose, throat, skin, and urinary tract. This medication belongs to the penicillin group, which makes it particularly effective against certain strains of bacteria.
Common Uses
Patients often receive amoxicillin for treating conditions such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis. It helps eliminate bacteria causing these infections, leading to faster recovery. Physicians frequently prescribe amoxicillin for strep throat and to prevent bacterial endocarditis in individuals with specific heart conditions. Its effectiveness in treating Helicobacter pylori, a bacteria associated with ulcers, enhances its versatility in medical treatment.
Benefits of Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin offers a range of advantages. It has a favorable safety profile, making it suitable for children and pregnant women under medical supervision. The oral form ensures easy administration, whether as capsules, tablets, or liquid suspension. Treatment typically involves a short course, which increases adherence and minimizes side effects. Additionally, amoxicillin’s capacity to treat a variety of infections reduces the need for multiple medications, streamlining therapy.
Possible Side Effects and Risks Associated with Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin may cause side effects that range from mild to severe. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and rashes. These symptoms often resolve as your body adjusts to the medication. However, if these do not improve or worsen, consult your healthcare provider.
Allergic reactions, although rare, can occur. Signs include hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face and throat. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience these symptoms. It’s crucial to inform your doctor about any known allergies before starting treatment.
Some individuals may develop antibiotic-associated colitis due to disruptions in gut flora. If you notice persistent diarrhea, especially with blood or mucus, contact your physician promptly. They may recommend specific tests to evaluate your condition.
In rare instances, amoxicillin can affect liver function. Symptoms such as jaundice, dark urine, or persistent fatigue signal the need for urgent medical evaluation. Regular blood tests may be required if you have pre-existing liver issues.
Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should discuss risks and benefits with their healthcare provider. While amoxicillin is generally considered safe, individual circumstances can vary significantly.
Always disclose your complete medical history and any concurrent medications to your doctor. Drug interactions can amplify side effects or reduce effectiveness. Being informed about your treatment ensures you receive safe and effective care.
Who Should Avoid Amoxicillin: Contraindications and Precautions
Individuals with a known allergy to amoxicillin or other penicillins must avoid this antibiotic to prevent severe allergic reactions. Symptoms of an allergy may include rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
Patients with a history of liver disease should approach amoxicillin with caution, as it may impact liver function. Consulting a healthcare provider is essential before use.
Those with mononucleosis should avoid amoxicillin. This antibiotic can cause a widespread rash in patients with this viral infection, which may be mistaken for an allergy.
Individuals with kidney problems might need a dosage adjustment or should consider alternative treatments. Renal impairment affects how the body processes drugs, making careful monitoring necessary.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should discuss the use of amoxicillin with their healthcare provider to assess potential risks and benefits.
The following groups should be particularly cautious:
- People with asthma, as they may be more likely to have an allergic reaction.
- Patients taking anticoagulants or blood thinners, as amoxicillin can interact with these medications.
- Those with gastrointestinal diseases like colitis, as antibiotics can exacerbate certain symptoms.
Always consult a healthcare professional to understand personal risks and determine the appropriateness of amoxicillin for your specific health conditions.
Safe Usage: Guidelines for Amoxicillin Prescription and Administration
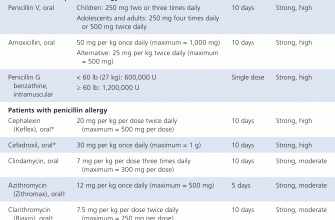
Prescribe amoxicillin only for bacterial infections confirmed by lab tests, avoiding its use for viral illnesses. Administer the medication at evenly spaced intervals to maintain consistent blood levels. For adults, a typical dosage ranges from 250 mg to 500 mg every 8 hours, while children’s doses are calculated based on weight, usually around 20-40 mg/kg per day.
Monitor for allergies. Inquire about previous allergic reactions to penicillins or cephalosporins before starting treatment. Advise patients to report any signs of allergic reactions, such as rashes or swelling, immediately.
Educate on completing the course. Encourage patients to finish the entire course, even if symptoms improve. This practice prevents antibiotic resistance and ensures full eradication of the infection.
Discuss potential interactions. Ask about other medications patients are taking. Certain drugs, like anticoagulants and methotrexate, can interact negatively with amoxicillin. Adjustments may be necessary based on the patient’s medication regimen.
Address side effects. Inform patients about common side effects like diarrhea, nausea, or skin rash. If severe gastrointestinal symptoms occur, recommend discontinuing the medication and consulting a healthcare provider.
Advise on storage. Store amoxicillin in a cool, dry place, away from sunlight. Reconstituted liquids should be refrigerated and used within 7 to 14 days.
Review medical history. Check for liver or kidney issues, as these conditions may necessitate dosage adjustments. Frequent monitoring may be required for patients with existing health concerns.
By following these guidelines, healthcare providers ensure the safe and effective use of amoxicillin, optimizing patient outcomes and minimizing risks.