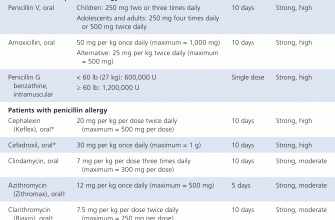
For uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs), a common Ciprofloxacin dosage is 250mg twice daily for 3-7 days. This is a guideline, and your doctor will determine the best course of treatment based on your specific needs and the severity of your infection.
Factors influencing dosage include your age, kidney function, and the type of bacteria causing the infection. Always consult your physician; they’ll consider these factors and may adjust the dosage or treatment duration. Never self-medicate or alter your prescribed dosage without their explicit approval.
Important Note: Ciprofloxacin is a powerful antibiotic. Potential side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and photosensitivity. Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately. Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern; complete your entire course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better before the prescription ends.
This information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. For accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment, schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider. They can conduct tests to confirm the infection and ensure Ciprofloxacin is the appropriate antibiotic for your specific case.
- Bladder Infection Cipro Dosage: A Comprehensive Guide
- Factors Influencing Cipro Dosage
- Alternative Treatments
- Understanding Ciprofloxacin for Urinary Tract Infections
- Dosage and Administration
- Possible Side Effects
- Standard Cipro Dosage for Bladder Infections
- Factors Affecting Dosage
- Possible Dosage Adjustments
- Factors Affecting Cipro Dosage and Treatment Duration
- Potential Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Monitoring for Side Effects
- When to Contact Your Doctor
- Alternative Treatments for Bladder Infections
- Dietary Changes
- Herbal Remedies
- Lifestyle Adjustments
- When to See a Doctor
- Disclaimer
- When to Seek Medical Attention
Bladder Infection Cipro Dosage: A Comprehensive Guide
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) dosage for a bladder infection typically involves a 250mg or 500mg tablet twice daily for seven to ten days. Your doctor will determine the precise dosage and duration based on your specific condition and medical history. Always follow their instructions carefully.
Factors Influencing Cipro Dosage
Several factors influence the prescribed dosage. Kidney function plays a significant role; individuals with impaired kidney function may require a lower dose or less frequent administration to prevent drug accumulation. Age is another factor; older adults might need a modified dosage. Severity of the infection also dictates the duration of treatment, with more severe cases requiring a longer course of antibiotics.
Never adjust your dosage without consulting your doctor. Stopping the medication prematurely can lead to treatment failure and the potential development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. If you experience any side effects, report them to your physician immediately. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and headache. Severe side effects are rare but require immediate medical attention.
Alternative Treatments
In cases of allergy or resistance to Cipro, alternative antibiotics, such as nitrofurantoin or sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (Bactrim), are available. Your doctor will choose the most appropriate antibiotic based on your individual needs and the specific bacteria causing your infection. This decision is crucial for effective treatment.
Understanding Ciprofloxacin for Urinary Tract Infections
Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, effectively treats many urinary tract infections (UTIs). Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage based on your specific condition and medical history. Typical regimens involve taking one or two tablets daily for 7-14 days. Precise instructions are crucial; follow them diligently.
Dosage and Administration
Dosage varies significantly depending on the severity of the infection and your individual health. Common dosages range from 250mg to 750mg twice daily. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your doctor. Administration is usually oral, with tablets taken with a full glass of water. Avoid taking Ciprofloxacin with dairy products or antacids, as these can interfere with absorption.
Possible Side Effects
While generally safe and effective, Ciprofloxacin can cause side effects. Common ones include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. More serious, though less frequent, side effects include tendonitis, peripheral neuropathy, and allergic reactions. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately. If you experience severe allergic reaction (difficulty breathing, swelling), seek immediate medical attention.
Standard Cipro Dosage for Bladder Infections
For uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs), a common Ciprofloxacin dosage is 250 mg twice daily for 3-7 days. Your doctor will determine the exact duration based on your individual needs and response to treatment.
Factors Affecting Dosage
The prescribed dosage may vary depending on several factors. These include the severity of the infection, your kidney function, and your overall health. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
Possible Dosage Adjustments
In some cases, a higher dosage–500 mg twice daily–might be prescribed, particularly for more severe infections. Conversely, for individuals with impaired kidney function, a lower dose or less frequent administration may be recommended. Your doctor will perform necessary tests to determine the most appropriate dosage for your specific circumstances.
Factors Affecting Cipro Dosage and Treatment Duration
Your doctor determines the precise Cipro dosage and treatment length based on several key factors. Let’s explore them.
- Severity of Infection: A more severe infection generally requires a higher dose and longer treatment period. Mild cases may be treated with a lower dose for a shorter duration.
- Type of Bacteria: Ciprofloxacin’s effectiveness varies depending on the specific bacteria causing the infection. Some strains are more resistant, necessitating higher doses or alternative antibiotics.
- Patient’s Age and Weight: Dosage adjustments are often necessary for children, the elderly, or individuals with significantly low or high body weight to ensure safety and efficacy. Dosage is typically calculated based on weight.
- Kidney Function: If you have impaired kidney function, your doctor will likely reduce the dosage or extend the time between doses to prevent medication buildup and potential side effects. Creatinine clearance is often used to guide these adjustments.
- Liver Function: Similar to kidney function, liver problems may require dosage modification to avoid complications. Your doctor will assess your liver function before prescribing.
- Other Medications: Some medications interact with Ciprofloxacin, potentially affecting its effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. Always inform your doctor about all medications you are currently taking.
- Patient’s Medical History: Pre-existing conditions, such as allergies or certain genetic predispositions, might influence the choice of dosage and treatment strategy. Full disclosure of your medical history is crucial.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your physician for accurate diagnosis and treatment recommendations. They will consider your individual circumstances to determine the optimal Cipro dosage and treatment duration for your specific bladder infection.
Potential Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin, while effective against bladder infections, can cause side effects. These vary in severity and frequency. Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Less common, but still possible, are headaches and dizziness.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Gastrointestinal upset is a frequent concern. Severe diarrhea, potentially indicating Clostridium difficile infection, requires immediate medical attention. This serious complication necessitates contacting your doctor without delay. Consider taking probiotics to support gut health during treatment. Drink plenty of fluids to help prevent dehydration, which can worsen nausea and diarrhea.
Other Potential Side Effects
Beyond digestive problems, Ciprofloxacin can sometimes affect your nervous system. This might manifest as insomnia, restlessness, confusion, or even seizures, although these are rare. Skin reactions, like rash or itching, are also possible. In rare cases, more serious side effects like tendonitis (inflammation of tendons) or peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage) can occur. These require immediate medical attention.
Monitoring for Side Effects
| Side Effect | Severity | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Diarrhea | Common | Increase fluid intake; consider probiotics. |
| Severe Diarrhea | Serious | Contact your doctor immediately. |
| Headache/Dizziness | Common | Rest; avoid activities requiring alertness. |
| Rash/Itching | Variable | Contact your doctor; may require discontinuation of Ciprofloxacin. |
| Tendon Pain/Swelling | Serious | Seek immediate medical attention. Stop taking the medication. |
When to Contact Your Doctor
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe or persistent side effects. Early intervention can prevent complications. They can assess your symptoms and determine the best course of action, which may include adjusting your dosage or switching to an alternative antibiotic.
Alternative Treatments for Bladder Infections
Drink plenty of water! This simple step helps flush out bacteria.
Dietary Changes
- Reduce or eliminate caffeine and alcohol, as they can irritate the bladder.
- Increase your intake of cranberry juice or cranberry supplements. While effectiveness varies, some studies suggest they may help prevent bacteria from adhering to the bladder wall.
- Consume foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt with live cultures. These can support gut health, which indirectly influences urinary tract health.
Consider over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) to manage discomfort. Always follow dosage instructions.
Herbal Remedies
Some people find relief with herbal remedies like D-mannose. However, remember to consult your doctor before using any herbal supplements, especially if you are taking other medications.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Urinate frequently and completely to prevent bacteria buildup.
- Always wipe from front to back after using the toilet.
- Wear loose-fitting cotton underwear to allow for better air circulation.
When to See a Doctor
If symptoms persist or worsen despite trying these alternative treatments, seek medical attention immediately. Delaying treatment can lead to complications.
Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe abdominal pain, high fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C), or chills accompanying your bladder infection symptoms. These could indicate a more serious complication.
Seek medical advice if your symptoms don’t improve within 72 hours of starting Cipro, or if they worsen. This includes persistent pain, frequent urination, or blood in your urine.
If you experience nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea that is severe or persistent, contact your physician. These could be side effects of Cipro requiring attention.
Allergic reactions, such as hives, rash, or difficulty breathing, require immediate medical care. Stop taking Cipro and seek help immediately.
If you develop new symptoms, such as back pain or pain during urination that is significantly different from your initial symptoms, schedule a doctor’s visit.
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid potential interactions.