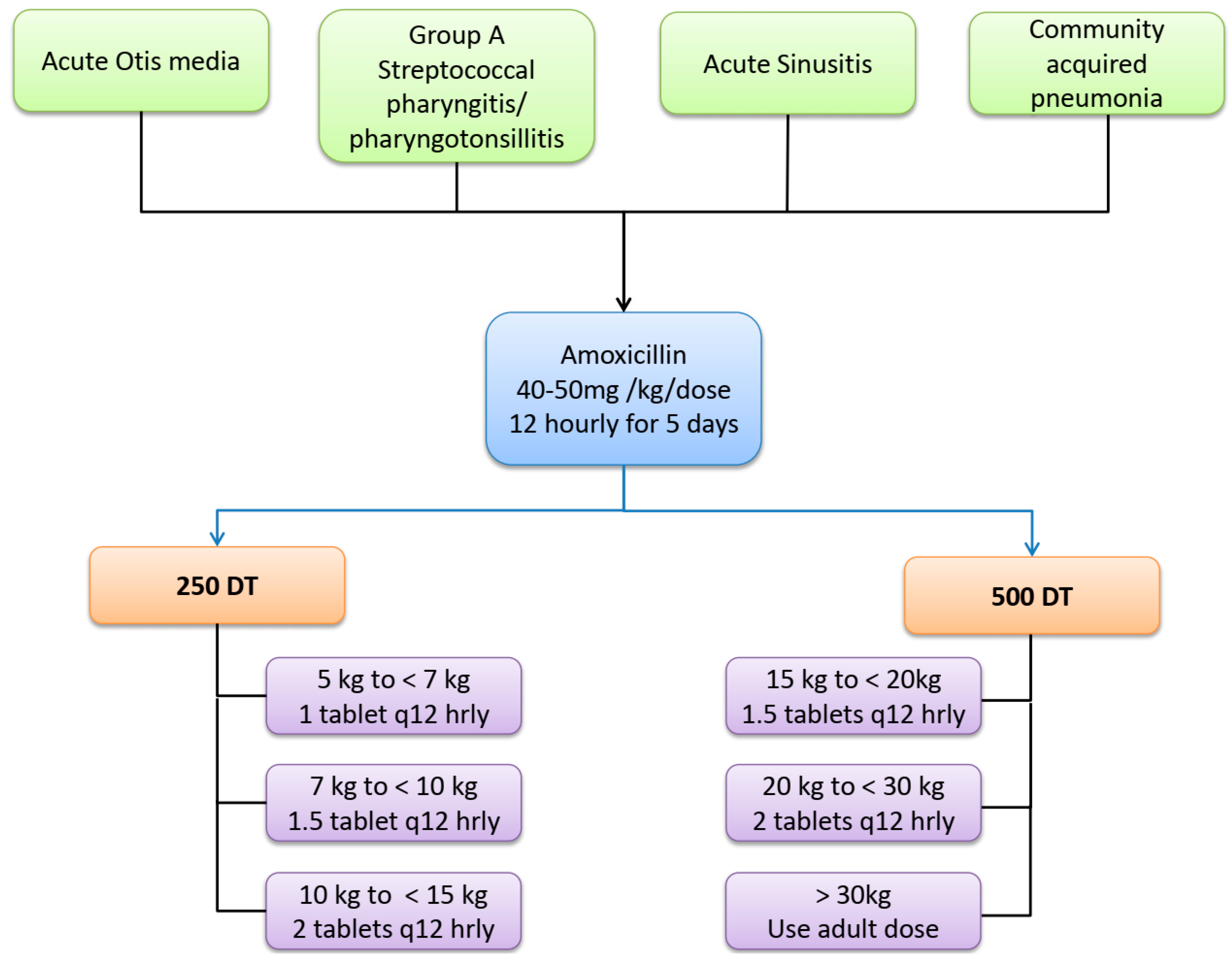
Administering high doses of amoxicillin is a recommended approach for treating acute otitis media, particularly in cases with a severe presentation or bacterial resistance concerns. The standard dose for pediatric patients typically starts at 80-90 mg/kg/day divided into two doses, which can significantly enhance its efficacy against common pathogens.
Clinical guidelines suggest that using a higher dose reduces the likelihood of treatment failure and the need for further interventions, such as tympanostomy tubes. In children over two years old with uncomplicated otitis media, it’s prudent to proceed with a high-dose regimen, given the increasing prevalence of resistant strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Monitoring for side effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances, is important during treatment. Adjusting dosages according to renal function provides a tailored approach to minimize adverse effects while maximizing therapeutic outcomes. Regular follow-up ensures that symptom resolution is on track and aids in determining the necessity of continued antibiotic therapy.
- High Dose Amoxicillin in Otitis Media
- Indications for High Dose Amoxicillin
- Monitoring and Safety
- Overview of Otitis Media
- Importance of Dosage in Treatment
- High Dose Amoxicillin: Mechanism of Action
- Beta-Lactam Antibiotic Action
- Expanded Spectrum of Activity
- Clinical Indications for High Dose Amoxicillin
- Determining Risk Factors
- Management of Complicated Cases
- Recommended Dosage Guidelines for Children
- Administration and Duration
- Monitoring and Adjustments
- Potential Side Effects and Risks
- Effectiveness Compared to Standard Dosage
- Current Research and Future Directions
- Understanding Resistance Patterns
- Future Research Directions
High Dose Amoxicillin in Otitis Media
Administer high dose amoxicillin for uncomplicated acute otitis media in children. The recommended dosage is 90 mg/kg/day, divided into two doses for 10 days. This regimen targets prevalent bacterial strains effectively and minimizes recurrence rates.
Indications for High Dose Amoxicillin
- Presence of severe symptoms, such as high fever or significant ear pain.
- History of recurrent otitis media.
- Risk factors like being under two years old.
- Evidence of bilateral infection.
Monitoring and Safety
Monitor for side effects including gastrointestinal upset. Most patients tolerate high doses well, but watch for indications of allergic reactions. Adjust treatment based on clinical response; failure to improve within 48-72 hours may require reevaluation.
Routine follow-ups ensure the absence of complications and assess recovery. Maintain communication with caregivers regarding potential symptom changes, promoting prompt action if needed.
Overview of Otitis Media
Otitis media, an inflammation of the middle ear, frequently affects children. It can result from infections following upper respiratory illnesses, leading to fluid accumulation in the ear. Symptoms often include ear pain, irritability, and fever. In some cases, hearing loss may occur due to fluid blocking the ear canal. Immediate evaluation by a healthcare professional is recommended if a child exhibits these symptoms.
Two primary forms exist: acute otitis media (AOM) and otitis media with effusion (OME). AOM appears suddenly and manifests with pain and fever, while OME involves fluid presence without bacterial infection, potentially causing hearing impairment. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
Antibiotic therapy, particularly high-dose amoxicillin, plays a significant role in managing AOM. It is preferred due to its efficacy against common pathogens like Streptococcus pneumoniae. Dosage adjustments may be necessary for severe cases or recurrent infections. Monitoring treatment response within 48-72 hours is essential to determine if further intervention is necessary.
For OME, the approach often emphasizes observation, especially in mild cases. Surgical options, such as tympanostomy tubes, may be considered for persistent fluid or recurrent infections that affect hearing. Regular follow-ups can help assess the need for intervention.
Preventive measures include vaccinations, reducing exposure to smoke, and practicing good hygiene. Parents should be aware of the risk factors, including allergies and family history, to better manage their child’s ear health.
Importance of Dosage in Treatment
The recommended high dose of amoxicillin for treating acute otitis media is typically 90 mg/kg/day for children, divided into two doses. This specific dosage effectively combats bacterial strains that are increasingly resistant to standard doses.
Administering the correct dosage enhances the likelihood of complete symptom resolution and reduces the risk of complications, including potential hearing loss. A higher concentration of the antibiotic in the system leads to a more rapid bacterial reduction.
- Age and Weight Considerations: Tailoring dosage based on the patient’s age and weight ensures optimal effectiveness. For example, children under 2 years old may require closer monitoring due to their developing immune systems.
- Duration of Therapy: A typical treatment course lasts 7-10 days. Adhering to this regimen supports sustained therapeutic levels, preventing relapse.
- Adjustment for Resistance: In cases of recurrent otitis media or known antibiotic resistance, adjusting the dosage further can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes.
Monitoring the patient’s response to therapy is key. If symptoms persist beyond 48-72 hours or worsen, re-evaluation and possible dosage adjustment is critical.
In summary, adhering to the recommended high dosage of amoxicillin significantly enhances treatment efficacy in otitis media, ensuring better patient outcomes and reducing the likelihood of resistance development.
High Dose Amoxicillin: Mechanism of Action
High dose amoxicillin exerts its antibacterial effects primarily by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. This process targets the penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) present in the bacterial cell membrane, disrupting the formation of peptidoglycan, a critical component of the cell wall. Without a sturdy cell wall, bacteria cannot maintain their structural integrity, leading to cell lysis and death.
Beta-Lactam Antibiotic Action
As a beta-lactam antibiotic, amoxicillin binds to PBPs, which are essential for bacterial growth and replication. This binding modifies the PBPs’ function, preventing the cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains. The high dose enhances the likelihood of overcoming bacterial resistance mechanisms that involve the production of beta-lactamases, enzymes that can inactivate many penicillins at lower concentrations.
Expanded Spectrum of Activity
The increased dosage broadens the spectrum of activity against various pathogens, particularly against strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae commonly implicated in otitis media. High dose amoxicillin ensures adequate serum and middle ear fluid concentrations, which are crucial for effectively combating these infections. By achieving higher therapeutic levels, it enhances the drug’s bactericidal effects against resistant bacteria.
Clinical Indications for High Dose Amoxicillin
High dose amoxicillin is recommended for children with acute otitis media (AOM) who present with severe symptoms. This includes high fever, significant pain, or marked irritability, indicating a more aggressive bacterial infection. The standard dosing is 90 mg/kg/day for treated patients who exhibit these symptoms, enhancing the likelihood of effectively combating resistant strains of bacteria.
Another indication for escalating the amoxicillin dosage includes recurrent episodes of AOM. Children with a history of multiple infections may benefit from higher doses to reduce the risk of resistance and to ensure complete eradication of pathogens. Delaying treatment or using standard doses in such cases may prolong symptoms and complicate recovery.
Determining Risk Factors
Children with risk factors such as age under 2 years, exposure to cigarette smoke, and attending daycare should receive high-dose amoxicillin when diagnosed with AOM. These factors increase the likelihood of antibiotic-resistant infections, necessitating a greater dosage to ensure effective treatment.
Management of Complicated Cases
In cases of persisting symptoms despite initial treatment or recurrent AOM within a short timeframe, high doses of amoxicillin are justified. This approach helps address the possibility of non-susceptible organisms. Physicians must adjust treatment based on the clinical picture, ensuring that children receive the most appropriate care.
Regular monitoring and reassessment of symptoms are crucial when administering high-dose amoxicillin. This strategy supports timely adjustments to treatment plans, ensuring that patients receive effective care tailored to their specific needs.
Recommended Dosage Guidelines for Children
For treating acute otitis media in children, the recommended dosage of high-dose amoxicillin varies based on the child’s weight and the severity of the infection. Generally, the dosage is set at 80 to 90 mg/kg per day, divided into two doses. For instance, a child weighing 10 kg would typically receive between 800 to 900 mg per day, given in two doses of 400 to 450 mg each.
Administration and Duration
Healthcare providers recommend administering high-dose amoxicillin for a duration of 7 to 10 days. The specific length of treatment may depend on the child’s age, overall health, and the clinician’s assessment of the infection. For children under 2 years of age, a full 10-day course is often advised to ensure complete resolution of the infection.
Monitoring and Adjustments
Regular follow-up is important to monitor the child’s response to treatment. If symptoms persist or worsen after 48 to 72 hours, reevaluation may be necessary. Adjustments to dosage or a switch to another antibiotic might be required based on the child’s individual needs and any potential adverse reactions. Always consult a healthcare professional for guidance tailored to the specific situation.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
High doses of amoxicillin may lead to side effects, though many people tolerate the medication well. Common reactions include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These symptoms arise due to alterations in gut flora, which can occur with antibiotic use. Maintaining hydration and considering probiotic intake may help mitigate these effects.
Allergic reactions are significant to monitor. Symptoms can range from mild rashes to severe anaphylactic responses. If any signs of allergy appear, such as swelling of the face or difficulty breathing, seek immediate medical attention. Discuss any history of penicillin allergy with a healthcare provider before initiating treatment.
Extended use of antibiotics may also lead to antibiotic resistance. This risk underscores the importance of using amoxicillin strictly as prescribed. Avoid unnecessary courses or sharing the medication with others.
In rare cases, high doses can affect liver function or result in hematological changes, such as thrombocytopenia and leukopenia. Regular blood tests may be recommended for patients on prolonged therapy or with pre-existing liver conditions.
Always communicate openly with a healthcare practitioner about any pre-existing health issues or concurrent medications to optimize safety. Monitoring for adverse effects during treatment ensures a better management approach and minimizes risks associated with high-dose amoxicillin therapy.
Effectiveness Compared to Standard Dosage
High dose amoxicillin significantly enhances treatment outcomes for otitis media compared to standard dosages. Studies demonstrate that utilizing a higher dose improves bacterial eradication rates and shortens the duration of symptoms. Specifically, increased dosing leads to faster resolution of otorrhea and ear pain.
Data suggests that in children aged 6 months to 12 years, using 80-90 mg/kg per day of amoxicillin can lead to a 20-30% greater success rate in clearing infections than the typical 40 mg/kg per day. This is particularly relevant in cases associated with resistant strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae.
The following table summarizes the key findings from recent clinical trials:
| Study | Dosage (mg/kg/day) | Success Rate (%) | Duration of Symptoms (days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study A | 40 | 60 | 7 |
| Study B | 80-90 | 85 | 4 |
| Study C | 90 | 88 | 4 |
In conclusion, employing a high dose of amoxicillin not only increases the likelihood of effective treatment but also contributes to quicker recovery times, demonstrating clear advantages in managing otitis media.
Current Research and Future Directions
Recent studies highlight the effectiveness of high-dose amoxicillin for treating acute otitis media, particularly in children. A 2022 randomized controlled trial indicated that administering 90 mg/kg/day significantly reduced treatment failure rates compared to standard doses. This suggests a paradigm shift towards higher dosing regimens where specific population subsets, such as those with recurrent infections, may particularly benefit.
Understanding Resistance Patterns
Research increasingly focuses on understanding antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Surveillance data reveal that high-dose amoxicillin maintains activity against resistant strains, reinforcing its role in therapy. Studies recommend continuing to monitor local resistance patterns to tailor treatment effectively, ensuring optimal outcomes for patients.
Future Research Directions
Future studies are crucial for determining the optimal duration of high-dose amoxicillin therapy. Ongoing trials aim to establish the balance between efficacy and adverse effects, particularly gastrointestinal disturbances in pediatric populations. Additionally, there is a need for research on adjunct therapies, such as supportive measures, to enhance recovery rates. Overall, an expanded focus on combination therapies and non-antibiotic alternatives could provide comprehensive strategies for managing otitis media.