Zithromax, or azithromycin, is a common antibiotic often prescribed for sinus infections. However, it’s not a guaranteed cure-all. Its effectiveness depends on the specific bacteria causing your infection. Your doctor will determine the appropriate course of treatment based on your individual needs and the results of any diagnostic tests.
Typically, a course of Zithromax involves a daily dose for 3-5 days, a shorter treatment period than some other antibiotics. This shorter duration can lead to quicker symptom relief, but it’s crucial to complete the entire course, even if you feel better sooner. Stopping early can increase the risk of the infection returning and developing antibiotic resistance.
While Zithromax can effectively treat many bacterial sinus infections, it’s ineffective against viral infections. A misdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary antibiotic use. Therefore, obtaining a proper diagnosis from your doctor is paramount. They’ll likely perform a physical exam and may order tests to identify the infection’s cause before recommending Zithromax or an alternative treatment.
Remember: Zithromax can cause side effects, ranging from mild (e.g., nausea, diarrhea) to more serious (e.g., allergic reactions). Always inform your doctor about any allergies or medical conditions you have before starting the medication. If you experience severe side effects, seek immediate medical attention.
- Zithromax and Sinus Infections
- What is Zithromax and How Does it Work?
- How Azithromycin Targets Bacteria
- Is Zithromax Effective Against Sinus Infections?
- When is Zithromax Prescribed for Sinus Infections?
- Potential Side Effects of Zithromax for Sinus Infections
- Alternatives to Zithromax for Treating Sinus Infections
- Other Antibiotic Options
Zithromax and Sinus Infections
Zithromax, or azithromycin, is a common antibiotic prescribed for various bacterial infections, including some sinus infections. However, it’s not effective against all sinus infections. A doctor diagnoses the specific cause–viral or bacterial–before prescribing antibiotics. Viral sinus infections don’t respond to antibiotics like Zithromax.
Bacterial sinus infections, if confirmed, might benefit from Zithromax. This antibiotic targets certain bacteria causing sinusitis. Your doctor weighs the benefits against potential side effects before prescribing.
Side effects can include nausea, diarrhea, and stomach upset. Less common but more serious side effects are possible. Discuss potential side effects with your physician.
Treatment duration typically involves a short course of Zithromax, usually 3-5 days. Complete the full course, even if you feel better sooner. Stopping early might lead to treatment failure and potential complications.
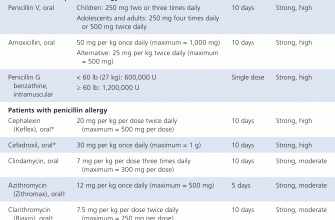
Alternatives to Zithromax exist for bacterial sinus infections. Amoxicillin is another common choice. Your doctor selects the best option based on your medical history, allergies, and the specific bacteria identified.
Home remedies for sinus infections, like saline nasal sprays and plenty of fluids, are often recommended alongside antibiotics. These can help alleviate symptoms. Always consult your doctor before starting any treatment.
Remember, Zithromax is a prescription medication. Self-treating a sinus infection is risky. Seek professional medical advice for diagnosis and treatment.
What is Zithromax and How Does it Work?
Zithromax is the brand name for azithromycin, a common antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections, including sinus infections. It’s a macrolide antibiotic, meaning it works by binding to bacterial ribosomes. This prevents the bacteria from making proteins necessary for their survival and reproduction, ultimately killing them.
How Azithromycin Targets Bacteria
Azithromycin specifically targets the 50S ribosomal subunit of bacteria. This differs from human ribosomes, allowing the drug to effectively kill bacteria without significantly harming human cells. However, like all antibiotics, it has the potential to cause side effects, which your doctor will discuss.
The medication is available in different forms, including tablets, capsules, and oral suspensions, making it convenient for many patients. Your doctor will prescribe the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment based on the severity of your infection and your individual health status. Always follow their instructions carefully and complete the full course of medication, even if you start feeling better sooner.
Is Zithromax Effective Against Sinus Infections?
Zithromax, or azithromycin, is a common antibiotic often prescribed for bacterial sinus infections. However, its success depends heavily on the cause of your infection.
Many sinus infections are viral, and antibiotics, including Zithromax, are ineffective against viruses. A doctor needs to determine the cause–bacterial or viral–through a physical exam and potentially other tests. If the infection is bacterial, Zithromax can be a suitable treatment option.
Zithromax’s effectiveness against bacterial sinus infections stems from its ability to halt bacterial growth. However, it’s crucial to complete the prescribed course, even if you start feeling better sooner. Stopping early can lead to resistant bacteria.
| Factor | Impact on Zithromax Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Type of infection (bacterial vs. viral) | Ineffective against viral infections; effective against specific bacteria causing bacterial sinusitis. |
| Bacterial species | Zithromax targets certain bacteria, but not all. The specific bacteria causing the infection influences treatment success. |
| Adherence to treatment | Completing the full course of medication is critical for preventing recurrence and resistant strains. |
| Patient’s overall health | Underlying health conditions can affect how the body responds to medication. |
Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. They will assess your individual situation and determine the best course of action, which may or may not include Zithromax.
When is Zithromax Prescribed for Sinus Infections?
Zithromax, or azithromycin, is a common antibiotic prescribed for bacterial sinus infections (sinusitis). Your doctor will likely prescribe it if your symptoms suggest a bacterial infection and haven’t improved with over-the-counter treatments for at least 7-10 days.
Specific scenarios leading to Zithromax prescription include:
- Severe sinus pain and pressure.
- High fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C).
- Thick, discolored nasal discharge (green or yellow).
- Facial swelling.
- Symptoms lasting longer than 10 days without improvement after trying other treatments.
- A history of recurrent sinusitis.
- Symptoms suggesting complications, such as spreading infection to other areas of the face.
Important Note: Zithromax is not effective against viral sinus infections, which are much more common. A doctor will determine the cause of your sinusitis through examination and possibly further tests before prescribing antibiotics.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Do not stop taking the medication early, even if you feel better, to ensure complete eradication of the infection. Discuss any concerns or side effects with your doctor or pharmacist.
Potential Side Effects of Zithromax for Sinus Infections
While Zithromax effectively treats many sinus infections, it’s crucial to be aware of potential side effects. These vary in severity and frequency.
Common side effects often resolve without intervention. These include:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
- Vaginal yeast infection
Less common, but more serious side effects require immediate medical attention. These can include:
- Severe allergic reactions (difficulty breathing, swelling of face, lips, or tongue)
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin or eyes)
- Severe abdominal pain
- Unusual bruising or bleeding
- Signs of a new infection (fever, persistent cough)
- Hearing loss
- Changes in heart rhythm
Specific considerations:
- Medication Interactions: Zithromax can interact with other medications. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you take.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Discuss Zithromax use with your doctor if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning pregnancy.
- Liver and Kidney Function: Individuals with liver or kidney problems might need a dosage adjustment or alternative treatment. Your doctor will assess your suitability for this medication.
- Reporting Side Effects: Report any concerning side effects to your doctor or pharmacist immediately.
This information does not substitute professional medical advice. Consult your doctor before starting any medication. They can determine the best treatment plan based on your individual health needs.
Alternatives to Zithromax for Treating Sinus Infections
Consider amoxicillin as a first-line alternative. It’s a common antibiotic often effective against bacterial sinus infections. However, increasing antibiotic resistance necessitates a doctor’s assessment to determine its suitability.
Other Antibiotic Options
Augmentin (amoxicillin-clavulanate) combines amoxicillin with clavulanate potassium, broadening its effectiveness against bacteria resistant to amoxicillin alone. Doxycycline, a tetracycline antibiotic, offers another option, particularly effective against certain bacteria causing sinus infections. Your doctor will consider your medical history and the specific bacteria involved before prescribing any antibiotic.
Beyond antibiotics, saline nasal sprays help clear nasal passages, improving drainage and reducing congestion. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can manage pain and fever. A humidifier adds moisture to the air, which can soothe irritated sinuses.
Finally, remember that a doctor’s diagnosis is crucial. They can determine the cause of your sinus infection–bacterial, viral, or fungal–and recommend the most appropriate treatment. Self-treating can be risky, so always consult a healthcare professional for guidance.