Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) dosages vary significantly depending on the infection being treated and the patient’s individual factors. For uncomplicated urinary tract infections, a common adult dosage is 250mg twice daily for seven to ten days. Always follow your doctor’s prescribed regimen.
More severe infections, such as pneumonia or complicated UTIs, often require higher doses – possibly 500mg or even 750mg twice daily. The duration of treatment also extends for these conditions, sometimes reaching fourteen days or longer. Your physician will determine the appropriate dose and length of treatment based on your specific needs.
Children’s dosages are calculated based on weight and the specific infection. Never administer Cipro to a child without a doctor’s explicit instructions. Accurate weight-based calculations are critical for safe and effective treatment. Consult your pediatrician immediately for any concerns.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting or altering any medication. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your health history and the specifics of your condition. Ignoring prescribed dosages or durations can lead to treatment failure or the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
- Usual Dosage of Cipro
- Typical Adult Dosages
- Pediatric Dosages
- Important Considerations
- Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Specific Dosage Considerations
- Important Note:
- Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Respiratory Infections
- Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Other Infections
- Important Considerations and Warnings Regarding Ciprofloxacin Dosage
- Kidney Function and Ciprofloxacin
- Age and Ciprofloxacin Dosage
- Drug Interactions
- Potential Side Effects
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Usual Dosage of Cipro
Ciprofloxacin dosage depends heavily on the infection being treated and the patient’s condition. Always follow your doctor’s instructions. Self-medicating is dangerous. Never adjust your dosage without consulting a physician.
Typical Adult Dosages
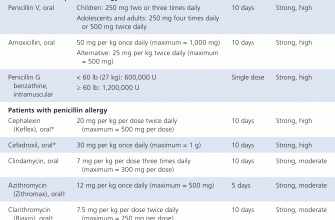
For uncomplicated urinary tract infections, a common dosage is 250 mg twice daily for 7-14 days. For more severe infections like pneumonia or complicated UTIs, higher doses (500 mg or 750 mg twice daily) may be prescribed for a longer duration, often two to four weeks. Doctors consider factors like your age, weight, and kidney function to determine the appropriate dosage.
Pediatric Dosages
Ciprofloxacin is generally not recommended for children and adolescents due to potential for cartilage damage. Alternatives are usually preferred. A doctor will carefully weigh the risks and benefits before considering Cipro for a child.
Important Considerations
Certain conditions, such as kidney or liver impairment, can influence the appropriate Cipro dosage. Always inform your doctor of all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions are possible. Report any side effects, such as nausea, diarrhea, or allergic reactions, to your doctor immediately.
Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
For uncomplicated UTIs, the typical adult dose is 250 mg twice daily for 3-7 days. Your doctor might adjust this based on your individual needs and the severity of your infection. Severe infections may require a higher dose, or a longer treatment duration. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
Specific Dosage Considerations
Children: Ciprofloxacin is generally not recommended for children due to potential cartilage damage. Your pediatrician will select an alternative antibiotic if a UTI is diagnosed.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Ciprofloxacin use during pregnancy and breastfeeding carries potential risks. Discuss alternatives with your doctor to ensure the safest approach for both you and your baby.
Important Note:
Never adjust your Ciprofloxacin dosage without consulting your healthcare provider. Incorrect dosage can lead to treatment failure and potential antibiotic resistance. Report any adverse effects immediately to your doctor. Always inform your doctor about other medications you are taking to avoid potential drug interactions.
Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Respiratory Infections
Treatment of respiratory infections with ciprofloxacin typically involves a dosage of 500 mg or 750 mg twice daily. The specific dosage depends on the severity of the infection and the patient’s overall health. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
For pneumonia, a common respiratory infection treated with ciprofloxacin, the usual course of treatment lasts 7-14 days. Your physician will determine the exact duration based on your individual response to the medication and the infection’s progress.
Acute bronchitis might be treated with a similar dosage regimen, though the duration could vary depending on symptoms. Your doctor will provide a tailored treatment plan.
Sinusitis, another respiratory infection potentially treated with ciprofloxacin, may require a slightly different approach. Your doctor will assess your specific needs and prescribe accordingly. The dosage remains usually within the 500-750 mg twice-daily range.
Note: Ciprofloxacin is a powerful antibiotic. Always discuss potential side effects and drug interactions with your doctor before starting treatment. This information should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Other Infections
For uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs), a typical course involves 250-500 mg twice daily for 3-7 days. For complicated UTIs or pyelonephritis, higher doses (up to 750 mg twice daily) and longer treatment durations (up to 14 days) may be necessary.
In treating acute bacterial prostatitis, 500 mg twice daily for 28 days is common. This duration is important for achieving complete eradication of the infection.
For acute sinusitis, a 500 mg twice-daily dosage for 7-10 days is usually prescribed. Chronic sinusitis may require longer treatment with physician supervision.
Treatment of pneumonia requires individualization based on the severity and causative organism. Generally, 400-750 mg twice daily for 7-14 days is administered, but adjustments are frequent.
In cases of skin and soft tissue infections, doses range from 250 mg to 750 mg twice daily for 7-14 days, contingent on the infection’s extent.
For intra-abdominal infections, higher doses and longer treatment are necessary. This decision is made in consultation with a physician.
Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance. Dosage adjustments may be needed based on your individual health status, the severity of your infection, and other factors such as age and kidney function.
Important Considerations and Warnings Regarding Ciprofloxacin Dosage
Always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage. Never adjust your Ciprofloxacin dose without consulting them. Incorrect dosage can lead to treatment failure or adverse effects.
Kidney Function and Ciprofloxacin
Reduced kidney function significantly impacts how your body processes Ciprofloxacin. Your doctor will likely adjust your dosage based on your creatinine clearance, a measure of kidney function. Higher creatinine clearance generally means higher dosages, while lower clearance means lower dosages.
- Regular blood tests may be necessary to monitor your kidney function during treatment.
- Inform your doctor of any pre-existing kidney conditions.
Age and Ciprofloxacin Dosage
Dosage adjustments are frequently needed for children, the elderly, and individuals with specific health conditions. Children may require lower doses per kilogram of body weight than adults. Elderly patients may also need dose reductions due to potential age-related changes in kidney function. Always discuss the appropriate dosage with your physician.
- Never give Ciprofloxacin to children without specific prescription from a pediatrician.
- Be especially cautious when administering Ciprofloxacin to elderly patients.
Drug Interactions
Ciprofloxacin can interact negatively with various medications. This interaction can either reduce Ciprofloxacin’s effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects. Examples include antacids, certain blood thinners, and some diuretics. A detailed discussion of all your current medications with your doctor is paramount before starting Ciprofloxacin.
- Provide a complete medication list to your physician.
- Be aware that even over-the-counter drugs can cause interactions.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Less frequent, but serious, side effects include tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, and severe allergic reactions. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any concerning symptoms.
- Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately.
- Be vigilant about potential side effects, especially tendon pain.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Ciprofloxacin use during pregnancy and breastfeeding needs careful evaluation by your doctor. The potential risks to the fetus or infant must be weighed against the benefits of treatment.
- Discuss with your doctor the risks and benefits of using Ciprofloxacin during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
- Explore alternative treatment options if possible.