Recognizing severe hives caused by amoxicillin is crucial for immediate action. If you experience widespread welts, itching, or swelling after taking this antibiotic, stop the medication and consult a healthcare professional right away. An allergic reaction can escalate quickly, and timely intervention can prevent complications.
Monitor your symptoms closely; hives may appear suddenly, sometimes within minutes of ingestion. Document any additional symptoms such as difficulty breathing or swelling of the face, as these may indicate a more serious reaction known as anaphylaxis. Always inform your doctor about your full medical history, including any previous adverse reactions to medications.
If diagnosed with hives induced by amoxicillin, your doctor may recommend antihistamines or corticosteroids to alleviate symptoms. Follow their treatment plan diligently and avoid re-exposure to the antibiotic unless cleared by a healthcare provider. Safe alternatives for treating infections will be discussed, ensuring future treatments do not trigger similar reactions.
- Severe Hives from Amoxicillin
- Understanding Severe Hives: Definition and Symptoms
- Symptoms Overview
- When to Seek Help
- How Amoxicillin Triggers Severe Hives Reactions
- Identifying Symptoms
- Managing Reactions
- Risk Factors for Developing Hives from Amoxicillin
- Age and Health Conditions
- Environmental Factors
- Diagnosing Severe Hives After Amoxicillin Use
- Symptom Evaluation
- Allergy Testing
- Immediate Actions to Take When Experiencing Hives
- Monitor Symptoms Closely
- Relieve Discomfort
- Long-Term Management Strategies for Amoxicillin-Induced Hives
- Alternative Antibiotics: Safe Options for Allergic Patients
- Consulting Healthcare Professionals: When and Why
Severe Hives from Amoxicillin
If you experience severe hives after taking amoxicillin, seek immediate medical attention. Hives can signify an allergic reaction that may require urgent care. Discontinue use of the medication right away to prevent worsening symptoms.
Identify the reactions promptly. Look for raised, itchy welts on the skin, which can vary in size and often appear in clusters. Severe hives can lead to swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, which may cause further breathing difficulties.
Inform your healthcare provider about your reaction to amoxicillin. Discuss alternative antibiotics if you need treatment for an infection. Your provider might recommend medications like diphenhydramine or corticosteroids to mitigate symptoms and manage the allergic response.
Follow up with an allergist for testing if hives persist. A comprehensive allergy assessment can determine sensitivities to amoxicillin and similar antibiotics. Keeping a detailed record of any medications taken and reactions observed will assist in future medical decisions.
Consider wearing a medical alert bracelet if you have a known antibiotic allergy. This can provide crucial information to first responders in case of emergencies.
Understanding Severe Hives: Definition and Symptoms
Severe hives, also known as urticaria, occur as a response to allergens, including medications like amoxicillin. This condition manifests as large, itchy welts on the skin that may appear suddenly and can lead to significant discomfort.
Symptoms of severe hives include:
Symptoms Overview
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Itching | Intense itching often accompanies welts, making it hard to resist scratching. |
| Welts | Raised, red or skin-colored bumps can vary in size, appearing anywhere on the body. |
| Swelling | Swelling may occur in the affected areas, sometimes including the face, lips, or throat. |
| Duration | Hives may last from a few hours to several days; persistent symptoms require medical attention. |
When to Seek Help
If you experience difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, or other severe reactions alongside hives, seek medical attention immediately. These symptoms may indicate anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition that requires urgent care.
How Amoxicillin Triggers Severe Hives Reactions
Amoxicillin can provoke severe hives due to its role as a beta-lactam antibiotic. The body may recognize amoxicillin as a foreign substance, leading to an immune response. This response involves IgE antibodies binding to the drug, which triggers mast cells to release histamines. The release of histamines causes blood vessels to dilate, resulting in the characteristic welts and redness associated with hives.
Identifying Symptoms
Recognizing hives is key to managing this reaction. Symptoms typically include raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size. These welts can appear suddenly and change location. In some cases, hives can be accompanied by additional symptoms such as swelling of the face, lips, or throat, and difficulty breathing. If these symptoms arise after taking amoxicillin, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Managing Reactions
If hives develop following amoxicillin use, discontinue the medication promptly. Antihistamines may provide relief from itching and swelling. In cases of severe reactions, such as anaphylaxis, an epinephrine injection is necessary. Always consult a healthcare provider for alternative treatment options and to discuss any history of antibiotic allergies.
Risk Factors for Developing Hives from Amoxicillin
Individuals with a history of allergies, particularly to penicillin or related antibiotics, should be cautious when using amoxicillin. Such a background significantly increases the likelihood of experiencing hives as an adverse reaction. Genetic predisposition also plays a role; those with a family history of allergic reactions may be more susceptible to developing hives from this medication.
Age and Health Conditions
Age influences the risk as well. Children tend to manifest skin reactions more often than adults after taking amoxicillin. Additionally, individuals with compromised immune systems or existing skin conditions like eczema are at heightened risk. Chronic health issues, particularly those related to the respiratory system or autoimmune conditions, can complicate the body’s response to medications, including amoxicillin.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors may also contribute to the risk of hives. Exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, or certain foods can lead to a heightened sensitivity when amoxicillin is introduced into the system. Maintaining awareness of these factors can aid in anticipating potential allergic reactions and managing them effectively.
Diagnosing Severe Hives After Amoxicillin Use
To diagnose severe hives following amoxicillin administration, healthcare providers should conduct a thorough patient history and physical examination. Focus on the timeline of symptoms, as hives typically develop within hours to days after drug intake.
Symptom Evaluation
Assess the characteristics of the hives. Look for raised, itchy welts that vary in size and may appear alongside other symptoms, such as swelling or difficulty breathing. Document the duration and frequency of episodes, as well as any accompanying symptoms like fever or gastrointestinal distress.
Allergy Testing
Consider referral for allergy testing if hives persist or are severe. Skin prick tests or specific IgE blood tests can confirm sensitivity to amoxicillin. Ensure to review any other medications taken concurrently, as polypharmacy can complicate the diagnosis.
| Symptom | Timeframe | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Itchy welts | Hours to Days | Typical reaction to amoxicillin |
| Swelling | Immediate to 3 days | Monitor for anaphylaxis |
| Respiratory issues | Minutes to Days | Urgent intervention required |
Monitor patients closely post-diagnosis. If an allergy is confirmed, discuss alternative antibiotics and management strategies to ensure safety in future treatments.
Immediate Actions to Take When Experiencing Hives
Remove the triggering substance as soon as you notice hives. If you suspect amoxicillin is the cause, stop taking it immediately. Contact your healthcare provider for further guidance on alternative medications.
Monitor Symptoms Closely
Keep track of any additional symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or rapid heart rate. These signs may indicate a more serious allergic reaction, requiring emergency assistance. If these symptoms occur, seek help right away.
Relieve Discomfort
For mild hives, consider taking an over-the-counter antihistamine, such as diphenhydramine or loratadine. Follow the dosage instructions on the package. Applying cool compresses to the affected areas can help soothe itching and reduce inflammation.
Long-Term Management Strategies for Amoxicillin-Induced Hives
Identify alternative antibiotics with a lower risk of allergic reactions. Work closely with your healthcare provider to find suitable options that maintain efficacy against your infections.
Implement an allergy action plan. This should include emergency medications such as antihistamines or corticosteroids to manage severe reactions and guidelines on when to seek medical help.
Schedule regular follow-ups with an allergist. These appointments can help monitor your condition and allow timely adjustments to your management strategy as needed.
Maintain accurate documentation of your reactions. Record the onset, duration, and severity of hives, including any other symptoms. This information serves as a valuable resource for your healthcare team.
Engage in education about allergenic triggers. Understand common allergens and their avoidance techniques, contributing to overall well-being and reduced incidents of severe hives.
Incorporate lifestyle modifications. Adopt a balanced diet and include regular physical activity to enhance immune function and overall health, possibly reducing allergy severity.
Utilize support groups for individuals dealing with allergies. Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide emotional support and helpful insights into managing hives effectively.
Stay informed about new treatments and therapies. Advances in allergy management may offer promising solutions that can improve your long-term care.
Alternative Antibiotics: Safe Options for Allergic Patients
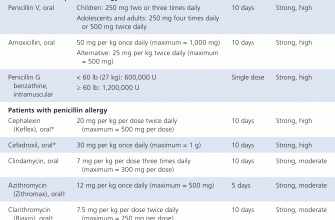
For patients who experience severe hives or allergic reactions to amoxicillin, several alternative antibiotics can effectively treat bacterial infections without triggering allergies. Here are some recommended options:
- Cefdinir: This cephalosporin antibiotic is often tolerated well by individuals with a penicillin allergy. It covers a broad range of infections, including respiratory tract infections.
- Doxycycline: A tetracycline antibiotic suitable for many infections, including skin and respiratory infections. Ensure that no history of allergic reactions exists prior to administration.
- Azithromycin: Commonly used for respiratory infections and certain types of skin infections. Azithromycin has a different structure than penicillin and is a good alternative for those with allergies.
- Clindamycin: Effective against a range of bacterial infections, particularly skin and soft tissue infections. This antibiotic is an excellent choice for patients allergic to beta-lactams.
- Levofloxacin: A fluoroquinolone antibiotic effective against a variety of pathogens, useful for respiratory tract infections and urinary tract infections.
Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate alternative based on the specific infection type and patient history. Always disclose previous allergic reactions to ensure safe treatment options.
Staying informed about alternatives can enhance treatment efficacy while minimizing allergy risks. Explore these options and discuss them with your doctor to maintain your health without compromising safety.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals: When and Why
Seek guidance from healthcare professionals immediately if you experience severe hives after taking amoxicillin. Early intervention can prevent complications and manage symptoms effectively.
Consider these specific situations for consulting a healthcare provider:
- Severe Reactions: If hives are accompanied by difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or rapid heartbeat, go to the emergency room without delay.
- Persistent Symptoms: If hives last more than a few days despite over-the-counter antihistamines, a healthcare professional may need to adjust your treatment plan.
- History of Allergies: Consult a doctor if you have a history of allergic reactions to antibiotics or other medications. They can evaluate your allergy profile and suggest safe alternatives.
- Concurrent Medications: If you are on other medications, talk to your doctor. Interactions may exacerbate allergic reactions or lead to new issues.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Individuals with compromised immune systems or chronic conditions should consult a healthcare provider sooner rather than later to determine appropriate care.
Healthcare professionals can offer tailored advice based on your health history and current medications. Rely on their expertise to ensure safe and effective management of your symptoms. They may recommend allergy testing or prescribe alternative antibiotics to avoid similar issues in the future.