If you suspect strep throat, it’s crucial to consult your healthcare provider for appropriate testing. The rise of amoxicillin-resistant strains of Streptococcus pyogenes challenges the effectiveness of this common antibiotic. Recognizing the symptoms early ensures timely intervention, which is vital for preventing complications.
Typical symptoms of strep throat include a sudden sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. Weakness and headache may accompany these symptoms. Testing, often a rapid strep test or throat culture, confirms the diagnosis, guiding treatment decisions. If initial tests reveal resistance to amoxicillin, your doctor may recommend alternative antibiotics such as cephalexin or clindamycin.
Prevention plays an integral role in reducing the spread of resistant strains. Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and avoiding close contact with infected individuals, helps mitigate risks. Educating yourself and your community about antibiotic resistance fosters a healthier environment.
- Amoxicillin Resistant Strep Throat: Understanding the Issue
- Signs of Resistance
- Treatment Alternatives
- What Is Amoxicillin Resistant Strep Throat?
- Causes of Resistance
- Signs and Symptoms
- How to Identify Symptoms and Get Proper Diagnosis?
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- Understanding Treatment Options
- Treatment Options for Amoxicillin Resistant Infections
- Preventive Measures to Avoid Resistance Development
Amoxicillin Resistant Strep Throat: Understanding the Issue
For patients experiencing strep throat symptoms, testing and treatment should focus on the presence of antimicrobial resistance. In cases where amoxicillin is ineffective, understanding the underlying reasons becomes vital. A significant contributor to antibiotic resistance is the overuse and misuse of antibiotics, which creates an environment where bacteria evolve and adapt, leading to challenges in treatment.
Signs of Resistance
Monitoring symptom duration and severity is key. If a sore throat persists beyond 48 hours despite amoxicillin treatment, this may indicate resistance. Additional symptoms, such as fever, swollen glands, or rash, should prompt consultation with a healthcare provider. Testing for streptococcus via a rapid strep test or throat culture can confirm the diagnosis and guide effective treatment.
Treatment Alternatives
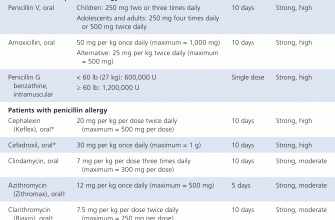
If resistance is confirmed, alternative antibiotics such as cephalexin or clindamycin may be prescribed. It’s essential to complete any prescribed course, even if symptoms improve, to prevent the development of further resistance. Always discuss antibiotic options with a healthcare provider, who can tailor treatment based on individual health and local resistance patterns.
What Is Amoxicillin Resistant Strep Throat?
Amoxicillin resistant strep throat occurs when the bacteria causing the infection, typically Streptococcus pyogenes, do not respond to treatment with amoxicillin. This resistance can result from several factors, including the overuse of antibiotics, incomplete courses of treatment, and natural variations within bacterial populations.
Causes of Resistance
- Antibiotic Overuse: Excessive or inappropriate prescribing of amoxicillin contributes to the development of resistant strains.
- Incomplete Treatment: Stopping antibiotic treatment prematurely can allow bacteria to survive and evolve resistance.
- Bacterial Mutation: Natural genetic changes can lead to some bacteria becoming resistant to antibiotics.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of amoxicillin resistant strep throat may mirror those of a typical strep infection:
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Red and swollen tonsils
- Difficulty swallowing
If standard treatment does not improve the condition within a few days, it may indicate resistance.
Consult a healthcare provider for alternative antibiotics, or potential testing of bacterial cultures to determine the most effective treatment for resistant strep throat.
How to Identify Symptoms and Get Proper Diagnosis?
Recognize the common symptoms of strep throat, which include a sudden sore throat, difficulty swallowing, red and swollen tonsils, white patches on the tonsils, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. Pay attention to accompanying symptoms like headache, stomach pain, or rash, as these may indicate a higher likelihood of strep throat rather than a viral infection.
If you suspect strep throat, visit a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis. They usually perform a rapid antigen test or throat culture to confirm the presence of streptococcal bacteria. It’s essential to share all symptoms and any recent illnesses with your provider for the best assessment.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention if you experience severe pain, difficulty breathing, rash, or if symptoms persist beyond 48 hours despite home care. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications, especially regarding amoxicillin resistance.
Understanding Treatment Options
If strep throat is diagnosed, your healthcare provider may prescribe an antibiotic. Follow the prescribed treatment regimen and complete the course, even if symptoms improve early. This helps reduce antibiotic resistance, ensuring effective treatment for future infections.
Treatment Options for Amoxicillin Resistant Infections
If a throat infection shows resistance to amoxicillin, clinicians often turn to alternative antibiotics. Options like cephalexin or clindamycin can be effective against resistant strains of streptococcus. Cephalexin, a cephalosporin antibiotic, is typically well-tolerated and is effective in treating various bacterial infections. Clindamycin, also an option, works particularly well for patients who may have a penicillin allergy.
For patients with more severe infections, intravenous antibiotics might be necessary. Options include ceftriaxone or vancomycin, both of which cover a broader range of bacteria. These choices depend on the severity of the infection and potential allergies. A culture and sensitivity test can guide the appropriate choice of antibiotic.
In cases where bacterial resistance is high, discussing adjunctive therapies is prudent. Corticosteroids can help reduce throat inflammation and improve symptoms alongside antibiotic treatment. Always consult a healthcare professional before making treatment decisions.
For individuals who frequently experience recurrent strep throat, a prophylactic antibiotic regimen may be recommended. Options might include daily penicillin or amoxicillin, depending on individual patient factors and bacterial susceptibility.
Finally, preventive measures play a significant role. Encourage good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing and avoiding close contact with infected individuals, to minimize the risk of infections. Staying hydrated and resting also supports the immune system during recovery.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Resistance Development
Limit the use of antibiotics to cases where they’re truly necessary, such as severe or persistent infections. Consult your healthcare provider before taking any medication.
Always complete the prescribed antibiotic course. This ensures that all bacteria are killed, reducing the likelihood of resistance development.
Practice good hygiene to prevent the spread of infections. Wash your hands regularly, especially before meals and after using the restroom. This simple step can minimize your chances of falling ill.
Stay updated with vaccinations. Vaccines can prevent many bacterial infections, reducing the reliance on antibiotics and helping to curb resistance.
Avoid sharing antibiotics or taking leftover medications. Each prescription is tailored to individual needs, and misuse can lead to ineffective treatment and resistance.
Engage in regular communication with your healthcare provider about any concerns regarding antibiotics. This dialogue can lead to appropriate alternatives or preventive strategies.
| Preventive Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Limit Antibiotic Use | Use antibiotics only when necessary and prescribed by a healthcare provider. |
| Complete Prescriptions | Finish the full course of antibiotics as directed, even if symptoms improve. |
| Good Hygiene Practices | Wash hands frequently and maintain cleanliness to prevent infections. |
| Stay Vaccinated | Keep vaccinations up to date to prevent bacterial infections. |
| Avoid Sharing | Never share antibiotics or use leftover medications from others. |
| Communicate with Healthcare Providers | Discuss any concerns about antibiotic use with your doctor. |