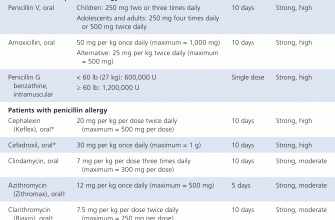
For those looking to tackle bacterial infections effectively, amoxicillin-pot clavulanate stands out as a valuable option. This combination antibiotic not only combats a wide range of bacteria but also fortifies its efficacy against resistant strains. Consideration of its uses and dosage is crucial to maximize benefits while minimizing risks.
Typically prescribed for conditions like sinusitis, pneumonia, and urinary tract infections, this medication targets both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, leading to cell death. Patients often find it beneficial for its dual action–amoxicillin treats the infection, while clavulanate prevents bacteria from breaking down amoxicillin, thus enhancing its antibacterial effect.
A recommended dosage usually ranges from 500 mg/125 mg to 875 mg/125 mg, taken every 12 hours, depending on the severity of the infection. It’s important to adhere to the complete course, generally lasting 7 to 14 days, to prevent relapse and resistance. Hydration and regular monitoring for potential side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort, can also contribute to a smoother treatment experience.
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting treatment to ensure this antibiotic is suitable for your specific condition, especially for individuals with a history of liver issues or allergies to penicillins. By carefully following these guidelines, you can harness the full potential of amoxicillin-pot clavulanate in your fight against infections.
- Amoxicillin-Potassium Clavulanate: A Comprehensive Overview
- Understanding Amoxicillin and Potassium Clavulanate Components
- Common Indications for Amoxicillin-Potassium Clavulanate Use
- Dosage Guidelines and Administration Techniques
- Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- Allergic Reactions
- Other Possible Effects
- Drug Interactions and Contraindications to Consider
- Contraindications
- Monitoring Recommendations
- Patient Care and Counseling Tips for Safe Usage
- Medication Administration
- Side Effects and Management
- Drug Interactions
Amoxicillin-Potassium Clavulanate: A Comprehensive Overview
Amoxicillin-potassium clavulanate, commonly known as Augmentin, combines two potent agents to combat bacterial infections. Amoxicillin, a penicillin derivative, inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis, leading to cell death. Clavulanate potassium, a beta-lactamase inhibitor, enhances amoxicillin’s efficacy against resistant bacteria by preventing the breakdown of antibiotics by beta-lactamases.
Healthcare professionals often prescribe this combination for respiratory and urinary tract infections, skin infections, and sinusitis. It offers a broad spectrum of activity against common pathogens, including Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae.
Dosage varies depending on age, weight, and severity of infection. Adults typically receive 500 mg/125 mg or 875 mg/125 mg every 12 hours. For pediatric patients, dosing is often determined by weight, generally ranging from 20 to 40 mg/kg/day. Follow the prescribing physician’s guidance for specific situations.
Common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea and diarrhea. Monitoring for allergic reactions or liver dysfunction is essential, especially in patients with a history of penicillin allergy. Adjustments to dosing may be necessary for individuals with renal impairment to prevent accumulation and toxicity.
| Indication | Typical Dosage | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Respiratory Tract Infections | 500 mg/125 mg every 12 hours | Nausea, Diarrhea |
| Urinary Tract Infections | 875 mg/125 mg every 12 hours | Rash, Abdominal Pain |
| Skin Infections | 500 mg/125 mg every 12 hours | Allergic Reactions, Headache |
This combination antibiotic effectively addresses many bacterial infections. Ensure adherence to prescribed regimens to reduce the risk of resistance development. Consult with a healthcare provider for any concerns regarding side effects or interactions with other medications.
Understanding Amoxicillin and Potassium Clavulanate Components
Amoxicillin, a penicillin derivative, combats various bacterial infections by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. This action effectively halts the growth of susceptible bacteria. It’s widely prescribed for conditions like pneumonia, bronchitis, and infections affecting the ear, nose, and throat.
Potassium clavulanate complements amoxicillin by countering bacterial resistance. Some bacteria produce beta-lactamase enzymes that impede amoxicillin’s effectiveness. Clavulanate inhibits these enzymes, allowing amoxicillin to work unhindered. Together, these components form a synergistic relationship that enhances antibacterial activity.
- Amoxicillin: Targets a broad range of gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria.
- Potassium Clavulanate: Designed to overcome specific resistance mechanisms in bacteria.
This combination is available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and oral suspensions. Adhere to prescribed dosages to ensure optimal results and minimize potential side effects. Common side effects may include gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea and nausea.
Be aware of allergic reactions, which can include rashes, itching, or swelling. Inform healthcare professionals about any known allergies to penicillin or other medications before starting treatment. Regular follow-ups can help monitor effectiveness and adjust dosages if necessary.
The combination therapy of amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate is a powerful option against resistant bacterial infections. Maintaining adherence to treatment guidelines remains crucial for positive health outcomes.
Common Indications for Amoxicillin-Potassium Clavulanate Use
Amoxicillin-potassium clavulanate is prescribed for various bacterial infections. It effectively treats acute bacterial sinusitis, particularly when caused by resistant strains. This combination is often the preferred choice for managing moderate to severe cases of otitis media, especially in children.
Dental infections benefit from amoxicillin-potassium clavulanate, especially in cases of abscesses or periodontitis. The drug also targets respiratory tract infections, such as pneumonia and bronchitis, particularly when symptoms suggest secondary bacterial involvement.
Skin and soft tissue infections, including cellulitis and animal bites, respond well to this medication. It combats infections associated with various surgical procedures, particularly in preventing postoperative infections.
In urinary tract infections, the combination is effective when traditional treatments fail, especially in cases of complicated UTIs due to resistant organisms. Amoxicillin-potassium clavulanate also plays a role in treating infections caused by anaerobic bacteria.
Utilizing this medication can help achieve a broader spectrum of activity against resistant bacteria that may not respond to amoxicillin alone. Always consider susceptibility patterns in your local area before prescribing.
Dosage Guidelines and Administration Techniques
For adults and children aged 12 years and older, the typical dosage of amoxicillin-potassium clavulanate is 875 mg/125 mg taken every 12 hours or 500 mg/125 mg every 8 hours, depending on the severity of the infection. For children under 12, the dosage is calculated based on body weight: generally, 20-40 mg/kg/day divided into two or three doses.
Administer the medication with food to enhance absorption and reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects. This approach can also improve patient compliance, especially in younger populations. Ensure patients drink a full glass of water with each dose to help with intake and absorption.
Adjustments may be necessary for patients with renal impairment. Creatinine clearance levels guide these adjustments; mild impairment may require no change in dosage, while more significant reductions could necessitate a total dose reduction of 25-50% or extended dosing intervals. Always consult specific renal guidelines for confirmation.
For longer treatment courses, regularly monitor for potential allergic reactions or side effects. Educate patients on recognizing symptoms such as skin rash, persistent diarrhea, or unusual fatigue, which may indicate an adverse reaction.
Instruct patients not to skip doses. If a dose is missed, they should take it as soon as they remember. However, if it’s close to the time of their next dose, they should skip the missed dose and resume the regular schedule. Caution against doubling the dose to compensate for a missed one.
For optimal results, complete the full course of therapy as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. Stopping early can lead to bacterial resistance and recurrence of the infection.
Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Amoxicillin-pot clavulanate may cause various side effects. Common reactions include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These often arise from the antibiotic’s effect on gut flora. Staying hydrated and consuming a bland diet helps manage these issues.
Allergic Reactions
Severe allergic reactions can occur, manifesting as skin rashes, itching, or swelling, especially in sensitive individuals. If you experience difficulty breathing or swelling of the face and throat, seek immediate medical assistance. Inform healthcare providers of any known allergies to penicillin or related antibiotics.
Other Possible Effects
Some may experience headaches, dizziness, or fatigue. Liver enzyme elevations, though rare, can occur, particularly in those with existing liver conditions. Regular monitoring through blood tests is advisable if you plan long-term use. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor promptly for assessment and guidance.
Drug Interactions and Contraindications to Consider
Amoxicillin-potassium clavulanate may interact with several medications, which can affect their efficacy and safety. Always review your current medications before starting this combination antibiotic. Anticoagulants, particularly warfarin, may have increased anticoagulation effects, necessitating regular monitoring of INR levels. Concurrent use with probenecid can increase amoxicillin levels, leading to potential toxicity; consult your healthcare provider if both are necessary.
Contraindications
This antibiotic is contraindicated in patients with a known allergy to penicillin or cephalosporins. Patients with a history of cholestatic jaundice or hepatic dysfunction related to amoxicillin/clavulanate should avoid this medication. Discuss any liver problems with your healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Monitoring Recommendations
Monitor for signs of an allergic reaction, such as rash, itching, or difficulty breathing. Liver function tests may be warranted in long-term use or if symptoms of liver dysfunction arise. For diabetics, this medication can yield false-positive results on urine glucose tests; alternative testing methods should be considered.
Patient Care and Counseling Tips for Safe Usage
Take amoxicillin-potassium clavulanate exactly as prescribed. Follow the dosage instructions carefully to ensure optimal effectiveness and minimize side effects.
Medication Administration
- Administer the medication with food to enhance absorption and reduce stomach upset.
- Use a calibrated measuring device for liquid forms to ensure accurate dosing.
- Complete the entire course of treatment, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
Side Effects and Management
Be aware of potential side effects. Common reactions may include nausea, diarrhea, and skin rashes. Contact a healthcare provider if severe side effects occur:
- Severe allergic reactions such as difficulty breathing or swelling.
- Persistent or severe diarrhea, which may indicate a secondary infection.
Hydrate well during the treatment and consider dietary adjustments if experiencing gastrointestinal symptoms. Avoid alcohol, as it can increase the risk of stomach irritation.
Drug Interactions
Inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements being taken. Some drugs may interact negatively with amoxicillin-potassium clavulanate, including:
- Anticoagulants, which can increase bleeding risks.
- Other antibiotics that may alter effectiveness.
Store this medication at room temperature, away from moisture and heat. Always check expiration dates and discard any unused medication properly.
Engage in follow-up appointments to monitor your progress and address any concerns. Your health is a priority, so maintain open communication with your healthcare team.