Using amoxicillin for sinusitis without a prescription can be a viable option for some individuals experiencing mild symptoms. It’s important to understand that this antibiotic works effectively against bacterial infections, and many sinusitis cases may be caused by bacteria. However, self-medication should be approached with caution; understanding your symptoms and their duration is crucial.
Before considering amoxicillin, assess your condition. If symptoms persist beyond ten days or worsen significantly, seeking medical advice is wise. In cases where a doctor has diagnosed a bacterial sinus infection, they often prescribe a course of amoxicillin. For those familiar with their medical history and past responses to antibiotics, discussing options with a pharmacist can provide valuable insights.
While amoxicillin is typically well tolerated, potential side effects include gastrointestinal discomfort and allergic reactions. It’s best to take this medication with plenty of water and food to minimize any stomach upset. Monitoring symptoms during treatment allows for any necessary adjustments or consultations with healthcare professionals.
Choosing to manage sinusitis with amoxicillin requires careful consideration and self-awareness. Stay informed about your health, recognize warning signs, and seek professional guidance when necessary to ensure optimal results.
- Amoxicillin for Sinusitis Without a Prescription
- Dosage Guidelines
- Potential Side Effects
- Understanding Sinusitis and Its Symptoms
- Diagnosing Sinusitis
- Managing Symptoms
- When to Consider Amoxicillin for Sinusitis
- Chronic Symptoms
- Underlying Health Conditions
- Risks of Using Amoxicillin Without Medical Guidance
- Potential Side Effects
- Interactions with Other Medications
- How to Safely Use Amoxicillin for Sinusitis
- Alternatives to Amoxicillin for Sinusitis Treatment
- Consulting a Healthcare Professional: Why It Matters
- Accurate Diagnosis
- Individual Health Considerations
Amoxicillin for Sinusitis Without a Prescription
Amoxicillin is a common antibiotic that can effectively treat bacterial sinusitis. While it is often prescribed by healthcare professionals, obtaining it without a prescription raises important considerations. It’s crucial to understand proper usage and potential risks associated with self-medicating.
Dosage Guidelines
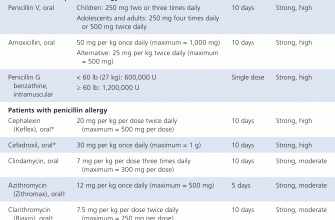
The typical dosage for adults is 500 mg to 875 mg every 12 hours, depending on the severity of the infection. For children, the dosage should be based on weight, usually around 20 to 40 mg per kg per day divided into two or three doses. Always adhere to the instructions provided with the medication.
Potential Side Effects
Although amoxicillin is generally well-tolerated, side effects can occur. Common issues include nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. If you experience difficulty breathing, swelling, or severe rash, seek medical attention immediately. It’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen.
| Side Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Nausea | Stomach discomfort and potential vomiting. |
| Diarrhea | Increased frequency of loose or watery stools. |
| Allergic Reaction | Symptoms may include hives, rash, or difficulty breathing. |
Using amoxicillin without professional guidance carries risks. Ensure you are aware of the specific bacteria causing the sinusitis, as amoxicillin will not treat viral infections. Consider seeking help from a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan.
Understanding Sinusitis and Its Symptoms
Sinusitis results from inflamed sinuses, often triggered by infections or allergies. Identifying symptoms quickly can lead to effective management. Common signs include:
- Facial pain or pressure, especially around the nose, eyes, or forehead
- Blockage or congestion, making it difficult to breathe through your nose
- Thick nasal discharge, which may be yellow or green
- Reduced sense of smell or taste
- Fever and chills in some cases
- Bad breath resulting from nasal congestion
Diagnosing Sinusitis
Healthcare professionals diagnose sinusitis through medical history and physical examination. Sometimes, imaging tests like X-rays or CT scans are necessary for confirmation. Knowing the type–acute or chronic–helps tailor treatment.
Managing Symptoms
Management strategies include:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers to ease discomfort
- Saline nasal sprays to relieve congestion
- Steam inhalation to keep sinuses moist
- Staying hydrated to thin mucus
Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to better outcomes and faster recovery from sinusitis.
When to Consider Amoxicillin for Sinusitis
Amoxicillin is a common antibiotic used for sinusitis, particularly when symptoms persist for 10 days or more. If nasal congestion, facial pain, or thick yellow or green mucus are present, this may indicate a bacterial infection that benefits from antibiotic treatment.
Chronic Symptoms
In cases where sinusitis symptoms last longer than a week or worsen after an initial improvement, consider consulting a healthcare provider for a potential prescription. These chronic symptoms include persistent headaches, facial pressure, or a declining sense of smell.
Underlying Health Conditions
Individuals with underlying health issues, such as asthma or compromised immune systems, should discuss the use of amoxicillin with their healthcare provider if they experience sinusitis symptoms. This ensures appropriate management and minimizes complications.
Risks of Using Amoxicillin Without Medical Guidance
Using Amoxicillin without consulting a healthcare professional can lead to several risks. Self-diagnosis can result in improper treatment. For instance, sinusitis may be caused by a viral infection, for which antibiotics like Amoxicillin are ineffective. This misuse can delay appropriate care and worsen symptoms.
Another significant concern is antibiotic resistance. When Amoxicillin is used unnecessarily, bacteria can adapt, making infections harder to treat in the future. This can lead to a cycle where stronger antibiotics are needed, increasing the chances of side effects and complications.
Potential Side Effects
Amoxicillin can cause side effects ranging from mild to severe. Common reactions include nausea, diarrhea, and skin rashes. Serious allergic reactions, though rare, can occur and may be life-threatening. Recognizing these risks is crucial, especially without professional oversight.
Interactions with Other Medications
Amoxicillin may interact with other medications you are taking, which can diminish effectiveness or enhance side effects. Without medical guidance, you may overlook these interactions, leading to unpredictable health outcomes that could have been avoided with proper advice.
How to Safely Use Amoxicillin for Sinusitis
Choose Amoxicillin only if you have a bacterial sinus infection. Viral infections do not require antibiotics. Consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis.
When using Amoxicillin for sinusitis, adhere to the following guidelines:
- Dosage: Follow the prescribed dose. Typically, adults may take 500 mg three times a day or 875 mg twice a day for 7 to 10 days. Always adhere to your doctor’s recommendations.
- Timing: Take the medication at evenly spaced intervals to maintain consistent levels in your bloodstream. A timer can help you remember doses.
- Food: Amoxicillin can be taken with or without food. However, taking it with food may help reduce stomach upset.
- Hydration: Stay hydrated. Drinking plenty of fluids can promote recovery and help thin mucus.
- Side Effects: Monitor for side effects like rash, nausea, or diarrhea. If any severe reactions occur, stop taking it and seek medical assistance.
- Complete Course: Always finish the entire prescribed course. Stopping early may lead to antibiotic resistance and recurrence of infection.
If symptoms persist or worsen after a few days of treatment, return to your healthcare provider. They may need to reassess your condition or adjust your treatment plan.
Keep stored Amoxicillin in its original container, away from moisture and heat, and out of reach of children. Dispose of any unused medication properly. Local pharmacies often have take-back programs for safe disposal.
By following these recommendations, you can use Amoxicillin safely and effectively when dealing with sinusitis.
Alternatives to Amoxicillin for Sinusitis Treatment
Consider using nasal corticosteroids, like fluticasone or mometasone, to reduce inflammation and mucus production. These sprays can relieve nasal congestion and enhance sinus drainage, delivering quicker relief.
Saline nasal irrigation is another effective option. By rinsing your nasal passages with a saline solution, you can help clear out mucus and allergens, promoting comfort and easier breathing.
For those seeking natural remedies, steam inhalation provides soothing relief. Inhaling steam from hot water helps to open up nasal passages and alleviate pressure. You can enhance this treatment with essential oils like eucalyptus, known for its decongestant properties.
Over-the-counter decongestants, such as pseudoephedrine, can also help in managing sinus pressure. These medications reduce swelling in the nasal passages, improving airflow and drainage.
Consider antihistamines if allergies contribute to your sinus issues. These medications can help manage allergic reactions, minimizing symptoms like runny nose and sneezing.
In some cases, mucolytics, like guaifenesin, may provide aid by thinning mucus. This makes it easier to expel, thereby relieving sinus pressure and congestion.
If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended to discuss further treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional: Why It Matters
Consult a healthcare professional before taking amoxicillin for sinusitis. A medical expert will assess your symptoms, provide an accurate diagnosis, and recommend the appropriate treatment. Taking antibiotics without guidance can lead to inappropriate use and resistance, rendering the medication less effective in the future.
Accurate Diagnosis
Sinusitis can result from various causes, including viral infections, bacterial infections, and allergies. A healthcare provider will differentiate between these causes, ensuring you receive the correct treatment. Misdiagnosis may lead to unnecessary antibiotic use or insufficient treatment for your condition.
Individual Health Considerations
Your health history plays a significant role in treatment decisions. Certain medical conditions or allergies might affect the choice of medication. A healthcare professional will evaluate your medical background and current medications to avoid harmful interactions and side effects, tailoring the treatment to your specific needs.