For a tooth abscess, your doctor will likely prescribe amoxicillin. A common dosage is 500mg every eight hours. This schedule ensures consistent antibiotic levels to fight the infection effectively.
However, the precise dosage depends on several factors, including your weight, overall health, and the severity of the abscess. Children require lower doses adjusted for their weight. Always follow your doctor’s instructions meticulously; never self-adjust your medication.
Remember, amoxicillin treats the infection, but you’ll also need professional dental care to address the underlying cause of the abscess. Ignoring the abscess may lead to serious complications, including spread of infection. Schedule a dental appointment as soon as possible.
Caution: Amoxicillin can have side effects. Report any unusual symptoms, such as allergic reactions (rash, swelling), nausea, or diarrhea, to your doctor immediately. Do not stop taking amoxicillin without consulting your doctor, even if you feel better. Completing the full course of antibiotics is vital to ensuring the infection is completely eradicated.
- Amoxicillin Dosage for Tooth Abscess
- Factors Influencing Dosage
- Important Considerations
- Understanding Tooth Abscesses and Their Severity
- Why Amoxicillin is Often Prescribed
- Excellent Penetration & Affordability
- Alternative Options for Allergies
- Dosage Considerations
- Beyond Amoxicillin
- Standard Amoxicillin Dosage for Adults
- Amoxicillin Dosage Adjustments for Children and Special Populations
- Children
- Special Populations
- Monitoring
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Allergic Reactions
- Other Potential Side Effects
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Other Warning Signs Requiring Prompt Medical Help
- Alternative Antibiotics and Treatment Options
Amoxicillin Dosage for Tooth Abscess
For a tooth abscess, your doctor typically prescribes amoxicillin at a dosage of 500mg every 8 hours or 250mg every 12 hours for adults. Children’s dosages vary significantly based on weight and age; consult your pediatrician for precise instructions. The treatment duration usually lasts for 5 to 10 days. Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions precisely.
Factors Influencing Dosage
Several factors influence the appropriate amoxicillin dose. These include the severity of the infection, the patient’s overall health, potential allergies, and the presence of other medical conditions. Kidney or liver problems, for example, may require dosage adjustments. Your physician will consider these aspects when determining the correct dosage and treatment plan.
Important Considerations
Complete the entire course of amoxicillin, even if you feel better before finishing. Stopping early can lead to a relapse. If symptoms worsen or don’t improve after a few days, contact your dentist or doctor immediately. Amoxicillin can cause side effects, such as diarrhea or nausea. Report any significant side effects to your healthcare provider.
Understanding Tooth Abscesses and Their Severity
Tooth abscesses are serious infections requiring immediate dental attention. Their severity depends on several factors, including the abscess location, size, and the presence of spreading infection.
A periapical abscess forms at the root tip of a tooth, often due to untreated decay or a cracked tooth. These can cause intense pain, swelling, and sensitivity to pressure. They may also lead to bone loss if left untreated.
A periodontal abscess, on the other hand, develops in the gums surrounding a tooth, usually due to gum disease. These abscesses may cause less intense pain initially, but they can quickly become severe, leading to significant gum damage and potential tooth loss.
Symptoms vary, but can include throbbing pain, swelling of the face or gum, fever, difficulty swallowing, and foul-tasting pus. Severe cases can result in spread of the infection to other parts of the body, including the brain, a life-threatening complication. Therefore, prompt diagnosis and treatment are critical.
Your dentist will determine the severity through a clinical examination, X-rays, and potentially additional tests. Treatment options range from drainage of the abscess to root canal therapy or tooth extraction depending on the extent of the damage.
Delaying treatment can worsen the infection, increasing the risk of complications and requiring more extensive procedures. Seek immediate dental care at the first sign of a tooth abscess.
Why Amoxicillin is Often Prescribed
Amoxicillin’s widespread use for tooth abscesses stems from its potent broad-spectrum activity against many common bacterial culprits. It effectively targets Streptococcus species, frequently involved in dental infections. This makes it a reliable first-line treatment option for most patients.
Excellent Penetration & Affordability
Amoxicillin readily penetrates oral tissues, ensuring it reaches the infection site effectively. This high tissue concentration is crucial for eradicating bacteria within the abscess. Furthermore, its relatively low cost makes it an accessible treatment option for many.
Alternative Options for Allergies
However, amoxicillin isn’t suitable for everyone. Allergic reactions are possible. If you have a penicillin allergy, alternatives like clindamycin or azithromycin are available. Always discuss your medical history with your dentist or doctor.
Dosage Considerations
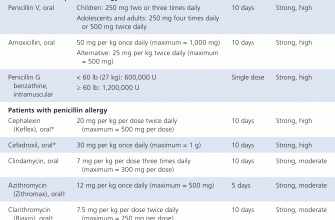
| Patient Group | Typical Dosage (mg) | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Adults | 500 | Every 8 hours |
| Children (weight-based) | Consult your doctor | As directed |
Remember, this table provides general information. A healthcare professional will determine the appropriate dosage based on individual needs, considering factors like age, weight, and the severity of the infection. Always follow prescribed instructions carefully.
Beyond Amoxicillin
While amoxicillin frequently provides effective treatment, severe cases or those unresponsive to initial treatment may require stronger antibiotics or additional procedures like drainage. Your dentist can guide you.
Standard Amoxicillin Dosage for Adults
For most adult infections, including dental abscesses, the typical Amoxicillin dosage is 500 mg every 8 hours. This translates to three 500 mg tablets daily, taken with water.
A doctor might prescribe a higher dose, perhaps 875 mg twice daily, depending on the severity of the infection. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Do not adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
The duration of treatment usually ranges from 5 to 14 days. Complete the full course even if you feel better sooner; stopping early can lead to recurrence of the infection.
If you experience any side effects like rash, diarrhea, or severe allergic reaction (difficulty breathing, swelling), discontinue use and contact your healthcare provider immediately.
This information is for general knowledge only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or dentist for diagnosis and treatment of a tooth abscess.
Amoxicillin Dosage Adjustments for Children and Special Populations
Always follow your doctor’s prescription precisely. Never adjust dosage without consulting a medical professional.
Children
Amoxicillin dosage for children is determined by their weight, not age. A common dosage is 20-40 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three doses. For example, a 20 kg child might receive 400 mg twice daily. Your pediatrician will calculate the precise amount based on your child’s individual needs and the severity of the infection.
- Infants (under 3 months): Require careful monitoring and possibly a different antibiotic altogether due to immature kidney function.
- Premature infants: Dosage adjustments are necessary due to their underdeveloped organ systems. A physician will provide specific guidelines.
Special Populations
- Kidney disease: Reduced kidney function necessitates dosage reduction to prevent drug accumulation. Your doctor will adjust the dosage according to your creatinine clearance.
- Liver disease: While less common, liver problems may also require dosage modifications. Close monitoring is advised.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Amoxicillin is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but always inform your doctor about your pregnancy status or breastfeeding to ensure appropriate monitoring and dosage adjustments if necessary.
- Allergic reactions: If an allergy to penicillin or amoxicillin is suspected, seek alternative treatment immediately. Severe allergic reactions require immediate medical attention.
Monitoring
- Closely observe your child or patient for any adverse reactions, such as rash, diarrhea, or vomiting.
- Report any unusual symptoms or changes in condition to your doctor promptly.
- Complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve. Stopping early can lead to treatment failure and antibiotic resistance.
This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor or pharmacist before starting or changing any medication, especially concerning children or individuals with health conditions.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Amoxicillin, while effective against many bacterial infections, including those causing tooth abscesses, can cause side effects. Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Less common, but still possible, are allergic reactions ranging from skin rashes to more severe reactions like swelling of the face, lips, or tongue. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any signs of a serious allergic reaction.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Diarrhea is a frequent side effect. If you experience severe or persistent diarrhea, contact your doctor. This is particularly important if your stool appears bloody or contains mucus. Proper hydration is crucial during antibiotic treatment to mitigate this side effect. Consider taking probiotics to support gut health.
Allergic Reactions
Amoxicillin belongs to the penicillin family of antibiotics. If you have a known penicillin allergy, you should not take amoxicillin. Inform your dentist or doctor about any allergies before starting treatment. Monitor yourself for allergic reactions and seek immediate medical attention if necessary. A mild rash may be treated with antihistamines, but more severe reactions require immediate medical care.
Other Potential Side Effects
While less common, other potential side effects include yeast infections (candidiasis), particularly in women, and changes in blood cell counts which are usually monitored through regular blood tests. If you experience unusual bruising or bleeding, or signs of infection such as fever or chills, contact your healthcare provider immediately. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Go to the emergency room or call your doctor immediately if you experience severe symptoms. This includes a high fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C), difficulty breathing or swallowing, significant swelling of your face or neck, or spreading redness around the infection site. Severe pain unresponsive to over-the-counter pain relievers also warrants immediate attention.
Other Warning Signs Requiring Prompt Medical Help
Seek immediate medical care if your abscess shows signs of worsening despite taking amoxicillin. This means increased pain, swelling, or pus discharge. Also, contact your doctor if you develop an allergic reaction to the amoxicillin, such as hives, itching, or difficulty breathing. Don’t delay seeking professional help if you have any concerns about your condition.
Alternative Antibiotics and Treatment Options
If amoxicillin isn’t suitable or effective, your dentist might prescribe clindamycin or metronidazole. These are alternative antibiotics frequently used for tooth abscesses.
Beyond antibiotics, several other treatments address the root cause:
- Drainage: Your dentist will likely perform an incision and drainage procedure to release pus from the abscess. This relieves pressure and pain immediately.
- Root Canal: If the infection stems from a severely damaged tooth, a root canal is necessary. This procedure cleans and seals the infected tooth root, preventing further infection.
- Extraction: In severe cases where the tooth is beyond repair, extraction may be the best option. This removes the source of infection completely.
Pain management is crucial. Your dentist can prescribe stronger pain relievers if over-the-counter options prove insufficient. Consider these pain management strategies:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Saltwater rinses to soothe the affected area.
- Applying a cold compress to the cheek to reduce swelling.
Remember, a proper diagnosis is key. Always consult your dentist or a medical professional for personalized treatment recommendations. Self-treating a tooth abscess can lead to serious complications. They will assess your specific situation and suggest the most appropriate course of action.