For adults treating infections, the typical dosage of amoxicillin is 500 mg every 12 hours or 250 mg every 8 hours. This regimen effectively combats various bacterial infections, including respiratory and urinary tract infections. For more severe infections, healthcare providers may recommend increasing the dosage to 875 mg every 12 hours.
Children’s dosages are based on weight, usually ranging from 20 to 40 mg/kg/day divided into two or three doses. A common guideline is 25 mg/kg/day for mild infections, and for more serious cases, the dosage may increase to 45 mg/kg/day. It’s important to ensure the prescription aligns with the child’s current health status.
Regardless of age, completing the full course of antibiotics is critical even if symptoms improve early. Stopping medication prematurely can lead to resistant bacteria, making future infections harder to treat. If side effects or allergic reactions occur, consulting a healthcare provider immediately is essential for safe management.
- Amoxicillin Dosage for Infection
- Dosage Adjustments
- Duration of Treatment
- Understanding Amoxicillin and Its Use in Infections
- Recommended Dosage Guidelines for Adult Patients
- Amoxicillin Dosage for Children: Key Considerations
- Adjusting Amoxicillin Dosage for Kidney Impairment
- How to Take Amoxicillin: Important Administration Tips
- Potential Side Effects and Dosage Adjustments
- Common Side Effects
- Serious Side Effects
- Consulting Healthcare Professionals: When to Seek Advice
Amoxicillin Dosage for Infection
The typical dosage of Amoxicillin for adults treating infections ranges from 250 mg to 500 mg every 8 hours or 500 mg to 875 mg every 12 hours. For pediatric patients, the dosage generally depends on the child’s weight and specific infection type, with a common range of 20 to 40 mg per kilogram of body weight per day, divided into two or three doses.
Dosage Adjustments
For individuals with kidney impairment, it’s crucial to modify the dosage based on the severity of the condition. In cases of mild to moderate renal dysfunction, reduce the dose or extend the time between doses. For severe impairment, dosages may need more significant adjustments.
Duration of Treatment
Treatment duration typically lasts 7 to 14 days, depending on the infection being treated. Acute infections may resolve within a week, while more persistent conditions could require extended therapy. Always follow the prescribed regimen until completion, even if symptoms improve early.
Consult your healthcare provider for personalized dosages and recommendations tailored to your health condition. Accuracy in dosing fosters better recovery and reduces the risk of resistance.
Understanding Amoxicillin and Its Use in Infections
Amoxicillin plays a key role in treating various bacterial infections. Recommended dosages typically range from 250 mg to 500 mg every 8 hours or 500 mg to 875 mg every 12 hours. Important factors include the type of infection, patient’s age, weight, and any other medical conditions. Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential for a tailored dosage plan.
Common uses of Amoxicillin include:
- Treatment of ear, nose, and throat infections.
- Management of urinary tract infections.
- Control of skin infections.
- Treatment of pneumonia and bronchitis.
Amoxicillin works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, making it effective against many strains of bacteria. When prescribed, antibiotics like Amoxicillin should be taken for the complete course, even if symptoms improve. Stopping early can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Possible side effects may include:
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Diarrhea.
- Rash or allergic reactions.
In case of severe side effects or allergic reactions, seek immediate medical attention. It is vital to inform your healthcare provider about any other medications you are taking, as interactions can alter effectiveness or increase risk. Regular follow-ups help monitor the treatment’s success and adjust dosages if necessary.
Recommended Dosage Guidelines for Adult Patients
The standard dose of amoxicillin for adults treating most infections is typically 500 mg every 12 hours or 250 mg every 8 hours. For more severe infections, the dose may be increased to 875 mg every 12 hours.
In cases of community-acquired pneumonia or acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, dose adjustments might be necessary. A recommended guideline is 500 mg every 8 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours for these scenarios.
For urinary tract infections, a common dosage is 500 mg every 12 hours for 3 to 7 days, depending on the severity of the infection. Healthcare providers often prescribe a higher dose of 1 gram every 12 hours for uncomplicated gonorrhea, usually combined with other antibiotics for enhanced effect.
Consider renal function when determining dosage. In patients with renal impairment, the dosage may require adjustment. Typically, it’s advisable to reduce the dose or extend the interval between doses to avoid toxicity, especially in cases of severe renal dysfunction.
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting amoxicillin to confirm the appropriate dosage for your specific situation and to discuss potential interactions with other medications.
Amoxicillin Dosage for Children: Key Considerations
The typical dosage of amoxicillin for children depends on their weight and the specific infection being treated. Generally, doctors recommend a dosage of 20 to 40 mg/kg/day for mild to moderate infections, divided into two or three doses. For severe infections, this can increase to up to 90 mg/kg/day.
It’s crucial to accurately weigh the child before determining the dosage. For example, if a child weighs 20 kg and is being treated for an ear infection, the daily dosage could range from 400 mg to 800 mg, depending on the infection’s severity.
Administering amoxicillin with food may improve absorption and reduce stomach upset. Liquid formulations are available, making it easier to give the medication to younger children. Always use the dosing syringe or cup provided with the medication for accuracy.
Adhere to the prescribed duration, even if symptoms improve before completing the course. Stopping early may lead to antibiotic resistance. Always consult a pediatrician before adjusting the dosage, especially in cases of underlying health conditions or other medications that may interact with amoxicillin.
Monitor for potential side effects, such as diarrhea or allergic reactions. Contact a healthcare provider if you notice any concerning symptoms or if the child’s condition does not improve after two to three days of treatment.
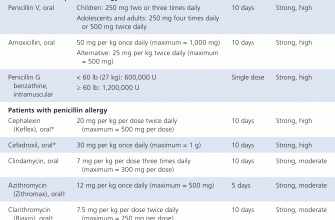
Adjusting Amoxicillin Dosage for Kidney Impairment
In patients with kidney impairment, reducing the amoxicillin dosage is crucial to avoid toxicity and ensure adequate treatment of infections. The dosage adjustment is primarily based on the severity of the renal impairment. Generally, for mild to moderate kidney disease, the standard dosing can be modified by decreasing the frequency rather than the amount of the dose. For severe impairment, significant adjustments are necessary.
A common approach involves the following guidelines:
| Creatinine Clearance (ml/min) | Adult Amoxicillin Dosage |
|---|---|
| >50 | Standard dosage |
| 30-49 | 500 mg every 12 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours |
| 10-29 | 250 mg every 12 hours or 500 mg every 24 hours |
| <10 | 250 mg every 24 hours or consider alternative treatment |
It’s essential to monitor renal function regularly during treatment. Dosage adjustments should be tailored not only to the creatinine clearance levels but also to individual patient factors like age, weight, and overall health. If a patient experiences any signs of nephrotoxicity, such as decreased urine output or elevated creatinine levels, reconsider the treatment plan.
Always consult a healthcare professional before making any changes to prescribed medications. Proper management greatly reduces the risk of complications associated with both infection and kidney impairment.
How to Take Amoxicillin: Important Administration Tips
Take amoxicillin exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Follow the dosage instructions carefully and do not skip doses. For most infections, it is common to take this antibiotic every 8 to 12 hours, depending on the severity of the infection and the specific prescription.
Swallow capsules and tablets whole with a full glass of water. If you’re using the liquid form, shake it well before measuring the dose. Always use a measuring device, such as a syringe or a measuring spoon, to ensure you take the correct amount. Do not use a household spoon.
For optimal effectiveness, consume amoxicillin with or without food, but be consistent. Taking it with food may reduce stomach upset but can slightly delay absorption. If you experience stomach discomfort, consider taking it with food.
Continue taking amoxicillin for the entire duration prescribed, even if symptoms improve. Stopping the medication too early can lead to a return of the infection and contribute to antibiotic resistance.
If you forget a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it’s almost time for your next dose, skip the missed one and resume your regular schedule. Do not double up.
Stay hydrated while taking amoxicillin. Drinking plenty of fluids will help your body absorb the medication effectively and flush out toxins.
Inform your doctor of any allergies, particularly to penicillin or cephalosporins, before starting treatment. This precaution helps avoid serious allergic reactions.
If you experience any unusual side effects, such as rash, difficulty breathing, or severe gastrointestinal symptoms, seek medical attention immediately. Always consult your healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns regarding your treatment with amoxicillin.
Potential Side Effects and Dosage Adjustments
Amoxicillin can cause side effects that vary in severity. Common reactions include diarrhea, nausea, and skin rashes. Monitor these symptoms closely to ensure they do not escalate. If diarrhea becomes severe or persistent, contact a healthcare provider.
Common Side Effects
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Skin rash
- Abdominal pain
Serious Side Effects
- Allergic reactions (swelling, breathing difficulties)
- Liver problems (jaundice, dark urine)
- Severe digestive issues (colitis)
If serious side effects arise, discontinue use and seek immediate medical attention. Adjusting the dosage may be necessary for patients with renal impairment. Typically, the dose is reduced in such cases to prevent drug accumulation and toxicity.
For mild to moderate infections, standard dosages vary based on age and weight. Always follow a doctor’s guidance and keep an open line of communication regarding your response to the medication.
- Adults: Generally prescribed 500 mg every 8 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours.
- Children: Dosages depend on weight, typically ranging from 20 mg to 40 mg per kg per day, divided into two or three doses.
Regularly reassess any ongoing symptoms during treatment. Adjustments to the plan can enhance therapeutic outcomes while minimizing risks.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals: When to Seek Advice
If you experience symptoms that persist despite taking amoxicillin, consult a healthcare professional. Increased symptoms or new reactions may indicate a need for reevaluation.
Seek medical advice if side effects occur, such as severe allergic reactions, persistent diarrhea, or any unusual symptoms. These may require immediate attention and possibly different treatment.
Consider contacting a healthcare provider if the infection does not show signs of improvement after 48 to 72 hours of starting amoxicillin. Early intervention can prevent potential complications.
If you have underlying health conditions or are pregnant, discuss amoxicillin use with your doctor. They can advise on the safest course of action tailored to your situation.
Always reach out for guidance if unsure about the dosage or any interactions with other medications you are taking. Clear communication with your healthcare provider ensures safe and effective treatment.