Amoxicillin 500mg is often prescribed for dental infections, but its effectiveness depends on the specific bacteria causing the infection. A dentist will diagnose the infection and determine the appropriate antibiotic. Self-treating can be risky, potentially leading to antibiotic resistance.
If your dentist prescribes Amoxicillin 500mg, take it precisely as directed. Complete the entire course, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. Stopping early increases the chance of the infection recurring, stronger and more resistant to treatment.
Important Considerations: Inform your dentist about any allergies, particularly penicillin allergies, as Amoxicillin is a penicillin-derived antibiotic. Report any side effects, such as rashes or digestive issues, immediately. Common side effects include nausea and diarrhea; if severe, seek medical attention.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your dentist or physician for diagnosis and treatment of dental infections.
- Amoxicillin 500mg for Dental Infections: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Amoxicillin’s Role in Treating Dental Infections
- Dosage and Administration of Amoxicillin 500mg for Dental Infections
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions When Using Amoxicillin 500mg
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Allergic Reactions
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Precautions
- When to Contact Your Doctor
- When to Seek Professional Help and Alternatives to Amoxicillin
- Amoxicillin Alternatives
- Considering Other Treatment Options
Amoxicillin 500mg for Dental Infections: A Comprehensive Guide
Amoxicillin 500mg is a common antibiotic prescribed for various dental infections. Always follow your dentist’s instructions precisely. The typical dosage is 500mg every 8 hours, but this can vary depending on the severity of the infection and your individual health.
Common dental infections treatable with Amoxicillin include abscesses, cellulitis, and periapical infections. However, Amoxicillin may not be effective against all bacterial infections, so your dentist will perform a proper diagnosis to confirm it’s the right choice.
Complete the full course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better. Stopping early can lead to recurring infections and antibiotic resistance. Side effects are possible and may include nausea, diarrhea, and stomach upset. Report any severe allergic reactions, such as difficulty breathing or swelling, immediately to your doctor.
Amoxicillin isn’t suitable for everyone. Inform your dentist about any allergies, current medications, or pregnancy. They will assess your suitability for Amoxicillin and may suggest alternative antibiotics if necessary. Proper oral hygiene is also critical in managing and preventing dental infections. Brush and floss regularly.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional dental advice. Always consult your dentist for diagnosis and treatment of dental infections.
Understanding Amoxicillin’s Role in Treating Dental Infections
Amoxicillin effectively combats many common bacteria causing dental infections, like Streptococcus and Prevotella species. It works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, preventing their growth and reproduction.
Your dentist prescribes Amoxicillin 500mg based on the severity and type of infection. Dosage and duration vary; always follow your dentist’s instructions precisely. Typical treatment involves taking the medication regularly for 5-10 days.
Amoxicillin targets bacteria, not viruses. If a viral infection contributes to your dental problem, the antibiotic won’t help with that aspect. Your dentist will determine the root cause and the appropriate treatment.
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and rash. Report any significant or persistent side effects immediately to your dentist or doctor. Allergic reactions, though rare, can be serious; seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms like swelling, difficulty breathing, or hives.
While Amoxicillin is usually successful, bacteria can develop resistance. Following the complete prescribed course, even if symptoms improve early, is key to preventing resistance and ensuring a full recovery. This prevents the infection from returning and spreading. Proper oral hygiene is also vital during and after treatment.
Remember, Amoxicillin is a prescription medication. Do not share it with others, even if they have similar symptoms. Always consult your dentist or doctor for diagnosis and treatment of dental infections.
Dosage and Administration of Amoxicillin 500mg for Dental Infections
Typically, your dentist will prescribe 500mg of amoxicillin every 8 hours for a dental infection. This means you’ll take three doses daily, spaced evenly throughout the day. Always follow your dentist’s specific instructions, as the dosage and duration may vary depending on the severity of your infection and your individual health.
Take amoxicillin with a full glass of water. You can take it with or without food, although taking it with food may reduce stomach upset. Avoid consuming alcohol while taking amoxicillin.
Complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if you feel better before finishing the prescription. Stopping early can allow the infection to return, potentially stronger. If side effects occur, such as diarrhea or rash, contact your dentist or doctor immediately.
Amoxicillin is an antibiotic; it fights bacterial infections, not viral ones. It’s crucial to understand that amoxicillin is only effective against bacterial dental infections. Your dentist will diagnose the cause of your infection and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Store amoxicillin at room temperature, away from moisture and direct sunlight. Keep it out of reach of children.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double up on doses.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions When Using Amoxicillin 500mg
Amoxicillin, while generally safe and effective, can cause side effects. Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. These usually are mild and resolve without intervention. However, severe allergic reactions are possible. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms such as hives, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, or difficulty breathing.
Gastrointestinal Issues
- Diarrhea is a common side effect. If it’s severe or persistent, contact your doctor.
- Nausea and vomiting can occur. Try taking the medication with food to minimize these effects.
- Avoid alcohol while taking amoxicillin, as it can worsen gastrointestinal upset.
Allergic Reactions
Amoxicillin is a penicillin antibiotic. If you have a penicillin allergy, you should not take this medication. Inform your dentist or doctor about any allergies before starting treatment.
Other Potential Side Effects
- Skin rashes
- Yeast infections (oral thrush)
- Headache
- Dizziness
Precautions
- Inform your doctor or dentist about all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, as interactions can occur.
- Complete the entire course of amoxicillin prescribed, even if you feel better before finishing it. Stopping early can lead to antibiotic resistance.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated. This aids in preventing some side effects.
- If you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or trying to conceive, discuss amoxicillin use with your doctor.
- Monitor yourself for any unusual symptoms and report them to your healthcare provider immediately.
When to Contact Your Doctor
Contact your doctor if you experience any severe or persistent side effects. This includes but is not limited to: severe diarrhea, persistent vomiting, significant skin rash, difficulty breathing, or swelling.
When to Seek Professional Help and Alternatives to Amoxicillin
Contact your dentist immediately if your dental infection worsens, symptoms like swelling, severe pain, or fever develop, or if you don’t see improvement within 48-72 hours of starting Amoxicillin. High fever (above 101°F or 38.3°C) requires immediate medical attention.
Amoxicillin Alternatives
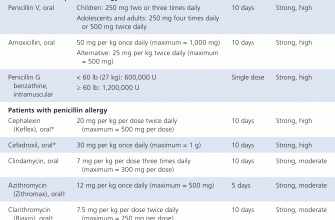
If you’re allergic to penicillin or Amoxicillin is ineffective, your dentist might prescribe an alternative antibiotic. Common alternatives include clindamycin, erythromycin, or azithromycin. Always inform your dentist about all allergies and medications you’re currently taking.
Considering Other Treatment Options
In some cases, antibiotics aren’t the sole solution. Your dentist may recommend additional treatments such as:
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Root Canal | Removes infected pulp from the tooth’s root. |
| Extraction | Removal of the severely infected tooth. |
| Dental Cleaning | Removes plaque and tartar contributing to infection. |
| Oral Surgery | Addresses complex infections or impacted teeth. |
Remember to follow your dentist’s instructions carefully, complete the prescribed antibiotic course, and maintain good oral hygiene to prevent future infections. Ignoring dental problems can lead to more serious health complications.