Never take Zithromax and Prilosec together without consulting your doctor. This combination can affect how your body processes both medications, potentially reducing Zithromax’s effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects from Prilosec. Always prioritize a conversation with your healthcare provider before altering your medication regimen.
Prilosec, a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), reduces stomach acid. Zithromax, an antibiotic, requires sufficient stomach acid for optimal absorption. Lowering stomach acid with Prilosec might decrease the amount of Zithromax your body absorbs, potentially hindering its ability to fight infection. This interaction is a significant consideration.
Specific concerns include a less effective treatment of your infection, requiring a longer treatment duration or a higher dosage of Zithromax. Discuss any pre-existing conditions with your doctor, as certain health issues may make this interaction even more problematic. Your doctor can assess your individual situation and offer appropriate advice.
Your physician might adjust your dosage or recommend alternative medications. Open communication with your doctor is key to managing these medications safely and effectively. Always be proactive in disclosing all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking to ensure safe medication management.
- Zithromax and Prilosec: Understanding Potential Interactions
- What is Zithromax (Azithromycin)?
- What is Prilosec (Omeprazole)?
- How Does Prilosec Work?
- Prilosec Dosage and Forms
- Potential Side Effects
- Prilosec and Zithromax Interaction
- How Zithromax Works in the Body
- How Prilosec Works in the Body
- Potential Drug Interactions Between Zithromax and Prilosec
- Absorption Considerations
- Recommendations
- Effects of Combined Use: What to Expect
- Gastrointestinal Effects
- Other Potential Interactions
- Important Considerations
- Precautions and Considerations When Taking Both Medications
- Potential Interactions
- Monitoring Side Effects
- Medication Timing
- Other Medications
- Specific Conditions
- Reporting Issues
- Always Consult a Doctor
- When to Consult a Doctor About Zithromax and Prilosec
- Drug Interactions and Allergies
- Unusual Side Effects
Zithromax and Prilosec: Understanding Potential Interactions
While generally safe to take together, Zithromax (azithromycin) and Prilosec (omeprazole) can interact. Prilosec reduces stomach acid, potentially affecting Zithromax absorption. This might slightly lower Zithromax effectiveness, especially for high doses.
The effect is usually minor, but individuals sensitive to Zithromax should monitor for reduced effectiveness. This might manifest as persistent infection symptoms. If you experience this, consult your doctor.
Taking Zithromax and Prilosec at different times of day may help maximize Zithromax absorption. For example, take Zithromax in the morning and Prilosec in the evening. However, always follow your doctor’s specific instructions.
Inform your physician about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This allows them to assess potential interactions and adjust your treatment plan as needed, ensuring optimal outcomes.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always discuss potential drug interactions with your doctor or pharmacist before starting or changing any medication.
What is Zithromax (Azithromycin)?
Zithromax is an antibiotic containing azithromycin, a macrolide antibiotic. It fights bacterial infections by stopping bacteria from growing and multiplying.
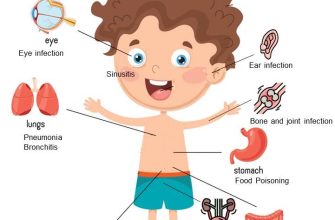
Doctors prescribe Zithromax for various bacterial infections, including:
- Respiratory tract infections like bronchitis and pneumonia.
- Skin and skin structure infections.
- Ear infections (otitis media).
- Certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Zithromax is typically taken as a short course of treatment, often only for three to five days. This is a key benefit, as it reduces the duration of treatment compared to other antibiotics.
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and stomach pain. More serious side effects are rare but possible. Always talk to your doctor if you experience any concerning symptoms.
Here’s what you should know before taking Zithromax:
- Dosage: Your doctor determines the appropriate dose based on your infection and overall health.
- Allergies: Tell your doctor about any known allergies, particularly to antibiotics.
- Interactions: Inform your doctor of all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as Zithromax may interact with some of them.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Discuss Zithromax use with your doctor if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or plan to become pregnant.
Remember, Zithromax treats bacterial infections, not viral infections like the common cold or flu. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment of any illness.
What is Prilosec (Omeprazole)?
Prilosec, containing the active ingredient omeprazole, is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI). It significantly reduces stomach acid production. This makes it highly effective for treating conditions like heartburn, acid reflux, and ulcers.
How Does Prilosec Work?
Omeprazole targets the proton pump, a crucial part of the cells lining your stomach that release acid. By inhibiting this pump, Prilosec lessens the amount of acid your stomach produces, providing relief from acid-related symptoms.
Prilosec Dosage and Forms
Prilosec comes in various forms: over-the-counter (OTC) options like Prilosec OTC and prescription-strength versions. Dosage depends on the specific condition and your doctor’s recommendation. Common forms include capsules and delayed-release tablets.
| Form | Typical Dosage (Consult your doctor for precise instructions) |
|---|---|
| Prilosec OTC | One 20mg tablet daily for 14 days |
| Prescription Prilosec | Varies depending on the condition; can range from 20mg to 80mg daily |
Potential Side Effects
While generally safe, Prilosec can cause side effects in some individuals. These may include headache, diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain. More serious, but rare, side effects may occur. Always discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
Prilosec and Zithromax Interaction
Taking Prilosec alongside Zithromax (azithromycin) usually doesn’t cause significant interactions. However, informing your doctor about all medications you’re taking ensures safe and effective treatment.
How Zithromax Works in the Body
Zithromax, or azithromycin, targets bacteria by binding to their ribosomes. This prevents them from synthesizing proteins, a process vital for bacterial survival and reproduction. The drug’s unique structure allows it to readily penetrate bacterial cells, maximizing its impact.
Specifically, azithromycin interferes with the bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit. This subunit plays a critical role in protein synthesis, and its disruption halts bacterial growth. The concentration of azithromycin needed to achieve this effect is relatively low, making it a potent antibiotic.
Azithromycin boasts excellent tissue penetration, reaching high concentrations in various tissues like the lungs, skin, and prostate. This characteristic makes it effective against infections in these areas. It’s also well-absorbed after oral administration, simplifying treatment.
The drug’s long half-life allows for a shorter treatment course compared to many other antibiotics. This reduces the likelihood of side effects and improves patient compliance. However, completing the entire prescribed course remains crucial, even if symptoms improve prematurely.
Note: This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult your physician before starting any medication, including Zithromax.
How Prilosec Works in the Body
Prilosec, or omeprazole, reduces stomach acid production by targeting specific cells in your stomach lining. These cells, called parietal cells, secrete acid through a complex process involving a proton pump.
Omeprazole acts as a proton pump inhibitor (PPI). It blocks this pump, preventing the parietal cells from releasing hydrochloric acid into your stomach. This leads to a significant decrease in stomach acidity.
The effect is not immediate; it usually takes a few days for Prilosec to reach its full effect. The medication is absorbed in the small intestine and then concentrates in the parietal cells, where it exerts its inhibitory action.
Your body eliminates omeprazole primarily through metabolism in the liver, with the resulting byproducts excreted in urine and feces. The duration of its effects depends on dosage and individual metabolism.
Remember to consult your doctor regarding the appropriate dosage and duration of Prilosec treatment, as individual needs vary considerably.
Potential Drug Interactions Between Zithromax and Prilosec
While generally considered safe to take together, Zithromax (azithromycin) and Prilosec (omeprazole) may interact in some individuals. Omeprazole, a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), increases stomach pH. This increased pH can slightly affect the absorption of some medications, though the impact with azithromycin is usually minimal.
Absorption Considerations
Studies show that the extent of azithromycin absorption might decrease slightly when co-administered with omeprazole. This usually isn’t clinically significant, meaning it’s unlikely to substantially reduce the effectiveness of your Zithromax treatment. However, individuals with compromised absorption capacity might experience a slightly reduced effect.
Recommendations
If you’re prescribed both Zithromax and Prilosec, openly discuss this with your doctor or pharmacist. They can assess your individual health status and determine if any adjustments are necessary. Taking them at different times of the day (e.g., one in the morning, the other at night) can potentially minimize any potential interactions. Always inform your healthcare provider about all medications you’re taking to prevent unforeseen complications. Monitoring treatment response is also crucial.
Effects of Combined Use: What to Expect
Combining Zithromax (azithromycin) and Prilosec (omeprazole) generally doesn’t cause significant interactions, but you should be aware of potential side effects. Both medications can affect your stomach. Prilosec reduces stomach acid, while Zithromax, like many antibiotics, can sometimes cause nausea and stomach upset.
Gastrointestinal Effects
You might experience increased nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. These side effects are usually mild and temporary. Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated. If these symptoms become severe or persistent, contact your doctor.
Other Potential Interactions
While rare, Zithromax can slightly affect the way your body processes certain medications. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you take to ensure there are no unexpected interactions.
Important Considerations
Always follow your doctor’s prescription instructions precisely. Do not adjust dosages or stop taking either medication without consulting your doctor first. Report any unusual or concerning symptoms immediately. Regular monitoring by your physician is recommended, especially if you’re taking these medications for an extended period.
Precautions and Considerations When Taking Both Medications
Always inform your doctor you’re taking both Zithromax (azithromycin) and Prilosec (omeprazole). This allows them to monitor for potential interactions and adjust dosages as needed.
Potential Interactions
While generally considered safe when taken together, some interactions warrant attention. Azithromycin can slightly increase the levels of omeprazole in your blood. This doesn’t always cause problems, but increased omeprazole can lead to side effects like headaches or diarrhea. Your doctor might recommend a lower Prilosec dose.
Monitoring Side Effects
- Zithromax: Watch for diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, and allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling).
- Prilosec: Pay attention to headaches, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Long-term use can also increase the risk of bone fractures and nutrient deficiencies, so discuss this with your doctor.
Medication Timing
Take both medications as prescribed. There’s no specific timing recommendation for taking Zithromax and Prilosec together, but consistency is key. Consult your pharmacist or doctor if you have concerns.
Other Medications
Inform your doctor about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. Some can interact with either Zithromax or Prilosec, increasing the risk of adverse reactions.
Specific Conditions
- Liver disease: Both medications are metabolized by the liver. If you have liver problems, your doctor may need to adjust dosages or choose alternative medications.
- Kidney disease: Kidney function affects how your body eliminates these medications. Dosage adjustments may be necessary.
Reporting Issues
Report any unusual or concerning side effects to your doctor immediately. Don’t stop taking either medication without consulting your healthcare provider first.
Always Consult a Doctor
This information is for general guidance only. Individual needs vary, and your healthcare provider can provide personalized advice and monitor your progress while taking both Zithromax and Prilosec.
When to Consult a Doctor About Zithromax and Prilosec
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe diarrhea, persistent vomiting, or abdominal pain while taking Zithromax and Prilosec together. These could indicate a serious side effect. Also, report any new or worsening symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing, chest pain, or unusual bleeding.
Drug Interactions and Allergies
Inform your physician about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This helps prevent potentially dangerous drug interactions. If you have a known allergy to azithromycin (Zithromax) or omeprazole (Prilosec), or any other medication, you must tell your doctor before starting treatment. Allergic reactions can range from mild skin rashes to severe life-threatening events.
Unusual Side Effects
While common side effects like nausea and diarrhea are usually mild, any unexpected or concerning reaction warrants a call to your doctor. This includes but isn’t limited to: jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), severe dizziness, rapid heartbeat, or difficulty breathing. Your doctor can assess the situation and adjust your treatment plan if necessary.