For treating urinary tract infections (UTIs), amoxicillin often serves as a reliable option. This antibiotic targets a broad spectrum of bacteria, effectively combating the pathogens responsible for UTIs. If you’ve been diagnosed with a UTI, you might find that your healthcare provider prescribes this medication to help alleviate your symptoms and clear the infection.
Amoxicillin works by interfering with the bacterial cell wall synthesis, ultimately leading to cell lysis and death. This mechanism makes it particularly effective against bacteria such as Escherichia coli, which is a common culprit in urinary infections. When used appropriately, it can effectively reduce discomfort and promote a speedy recovery.
While amoxicillin can be an effective choice, it’s essential to adhere to the prescribed dosage and complete the full course of treatment. Stopping the medication early may lead to antibiotic resistance or a recurrence of the infection. Always consult your healthcare provider if you have concerns about side effects or if symptoms persist after treatment.
- Understanding UTI and Amoxicillin: A Practical Guide
- When to Consider Amoxicillin
- Managing Side Effects and Precautions
- Overview of Urinary Tract Infections and Their Symptoms
- Recognizing the Symptoms
- When to Seek Medical Help
- Mechanism of Action: How Amoxicillin Works Against UTI
- Administration and Dosage
- Considerations and Resistance
- Dosage Guidelines and Treatment Duration for UTI with Amoxicillin
- Dosage Adjustments
- Monitoring Treatment Progress
- Potential Side Effects and Interactions of Amoxicillin in UTI Treatment
- Common Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
Understanding UTI and Amoxicillin: A Practical Guide
For treating a urinary tract infection (UTI), healthcare professionals often prescribe amoxicillin. This antibiotic works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria that cause infections in the urinary system. Characterized by symptoms such as frequent urination, burning sensation while urinating, and cloudy urine, UTIs require prompt attention to prevent complications.
When to Consider Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is particularly effective against certain strains of bacteria, including E. coli, which is a common culprit in UTIs. If your healthcare provider identifies a bacterial infection susceptible to amoxicillin through urinalysis or culture tests, they may recommend it as a first-line treatment. Always follow the prescribed dosage and complete the full course to eliminate the infection effectively.
Managing Side Effects and Precautions
Common side effects of amoxicillin include nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. Stay hydrated and consider probiotics to maintain gut health during treatment. Inform your healthcare provider of any allergies or preexisting conditions since these factors can influence your treatment strategy. Regularly monitor your symptoms; if they worsen or persist, consult your doctor promptly.
Overview of Urinary Tract Infections and Their Symptoms
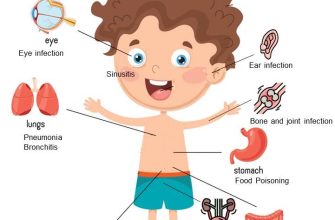
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) commonly occur when bacteria enter the urinary system, causing irritation and inflammation. The most frequent symptoms include a persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine. If you experience these signs, seek medical advice promptly.
Recognizing the Symptoms
UTIs manifest through various symptoms that can vary in intensity. Frequent urination, even if little urine is produced, is typical. Discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvic area might also occur. Blood in urine, known as hematuria, can signal a more severe infection and requires immediate attention.
When to Seek Medical Help
If symptoms persist for more than a day or escalate in severity, consulting a healthcare provider is essential. Delaying treatment can lead to complications, such as kidney infections. Maintaining hydration and practicing good hygiene can aid in prevention and management of UTIs.
Mechanism of Action: How Amoxicillin Works Against UTI
Amoxicillin fights urinary tract infections (UTIs) by targeting bacterial cell wall synthesis. It inhibits the enzyme transpeptidase, essential for cross-linking peptidoglycan layers in the bacterial cell wall. Without proper cross-linking, the cell wall becomes weak and eventually bursts, leading to bacterial death.
This antibiotic is effective against various gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria, making it a versatile option for treating UTIs caused by susceptible organisms, such as E. coli. Amoxicillin, when absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract, reaches high concentrations in urine, optimizing its bactericidal effects in urinary tissues.
Administration and Dosage
For uncomplicated UTIs, healthcare providers typically recommend amoxicillin at a dose of 500 mg every 12 hours for a duration of 3 to 7 days. It’s crucial to complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve, to prevent resistance development.
Considerations and Resistance
Some bacterial strains may produce beta-lactamase, an enzyme that renders amoxicillin ineffective. In such cases, a combination with a beta-lactamase inhibitor, like clavulanic acid, may be necessary. Regular sensitivity testing helps ensure the chosen antibiotic remains effective against the specific bacterial pathogen.
Dosage Guidelines and Treatment Duration for UTI with Amoxicillin
For uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs), the recommended dosage of amoxicillin is typically 500 mg every 12 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours for a duration of 3 to 7 days. Adjustments may be necessary based on the severity of the infection and individual patient factors.
Dosage Adjustments
Patients with renal impairment may require dosage adjustment. It is vital to assess kidney function before starting treatment. In cases of creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min, dosing intervals should be extended to avoid toxicity. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Monitoring Treatment Progress
Monitor symptoms during the treatment period. Improvement should occur within 48 to 72 hours. If no improvement or worsening symptoms are observed, reevaluation of the treatment plan is necessary, which may include switching to a different antibiotic.
Always adhere to the prescribed dosage schedule for optimal results and follow-up with your healthcare provider to ensure effective treatment of the infection.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions of Amoxicillin in UTI Treatment
Amoxicillin, while generally well-tolerated, may lead to several side effects during UTI treatment. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and skin rashes. If these symptoms occur, consider discussing them with your healthcare provider for possible management strategies.
Common Side Effects
- Nausea: Sometimes, taking the medication with food can help alleviate this symptom.
- Diarrhea: Staying hydrated is important. If diarrhea persists, consult your doctor.
- Skin Rash: This may indicate an allergic reaction. Seek medical advice if it develops.
- Headache: Over-the-counter pain relievers may provide relief.
Drug Interactions
Amoxicillin may interact with other medications. Awareness of these interactions can prevent complications.
- Anticoagulants: Amoxicillin may enhance the effect of blood thinners, increasing the risk of bleeding. Regular monitoring is crucial.
- Oral Contraceptives: While generally safe, some studies suggest a potential reduction in effectiveness. Consider using additional contraceptive measures.
- Probenecid: This medication can increase the levels of amoxicillin in the blood, which may heighten the risk of side effects.
Always inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements you are taking to avoid potential interactions. Observing side effects and keeping an open line of communication will aid in a safe and effective treatment experience.