When your healthcare provider prescribes amoxicillin, they’re targeting bacterial infections with a reliable antibiotic. This medication is part of the penicillin family and works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, helping your body to fight off infections effectively.
Follow the prescribed dosage carefully; typically, adults may take 500 mg every 8 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours, depending on the infection’s severity. For children, the dosage is based on weight, so it’s crucial to measure out the correct amount. Always consult your physician for adjustments if you experience side effects or if your condition does not improve.
Completing the full course of amoxicillin is essential, even if you start to feel better before finishing the medication. Stopping early can lead to the bacteria becoming resistant, making future infections harder to treat. Stay hydrated and consider taking the medication with food to minimize any potential stomach upset.
If any allergic reactions occur, such as rashes or difficulty breathing, seek medical attention immediately. Knowing the signs to watch for can make a significant difference in your recovery. Remember, while amoxicillin is effective against many infections, it doesn’t treat viral infections like the common cold or flu.
Prescriptions for Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for various bacterial infections, including pneumonia, bronchitis, and infections of the ear, nose, throat, skin, and urinary tract. A typical adult dose ranges from 250 mg to 500 mg every 8 hours or 500 mg to 875 mg every 12 hours, depending on the severity of the infection. For children, the dosage is usually determined by weight, often calculated as 20 to 40 mg per kg per day, split into two or three doses.
To ensure optimal results, take amoxicillin on an empty stomach, either one hour before a meal or two hours after. Adhere to the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve before completion. Skipping doses or stopping early may lead to antibiotic resistance.
Monitor for side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. If any severe reactions occur, including difficulty breathing or swelling, seek immediate medical attention. Discuss any pre-existing conditions or medications with a healthcare provider to avoid potential interactions.
Refills on a prescription for amoxicillin may be necessary for ongoing treatment. Always consult the prescribing doctor if symptoms persist or worsen despite following the medication regimen.
Understanding Amoxicillin: Uses and Indications
Amoxicillin treats a variety of bacterial infections. It belongs to the penicillin class of antibiotics, targeting a range of pathogens effectively.
- Respiratory Tract Infections: Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis. It’s effective against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae.
- Ear Infections: Acute otitis media in children often responds well to amoxicillin, particularly when caused by specific bacteria.
- Skin Infections: This antibiotic can treat skin conditions like cellulitis, administered to combat infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Amoxicillin may be used for uncomplicated UTIs, especially when the causative organisms are sensitive to this antibiotic.
- Dental Conditions: Dentists often prescribe amoxicillin to prevent or manage infections after dental procedures.
Amoxicillin is also used in combination therapies, such as for treating Helicobacter pylori infections in peptic ulcer disease. It’s important to finish the prescribed course to minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Consult a healthcare provider for appropriate dosage and duration based on specific health conditions. Regular monitoring may be necessary to watch for side effects such as gastrointestinal disturbances or allergic reactions.
Proper Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Amoxicillin
Adults typically receive a dosage of 250 mg to 500 mg every eight hours or 500 mg to 875 mg every twelve hours, depending on the severity of the infection. For more serious infections, higher dosages may be necessary.
Children usually take 20 mg to 40 mg per kg of body weight per day, divided into two or three doses for mild to moderate infections. For more severe cases, the dosage can increase to 80 mg to 90 mg per kg per day.
Amoxicillin can be taken with or without food. However, taking it with food may reduce the potential for stomach upset. Always shake the liquid formulation well before use to ensure proper dosing.
Maintain regular dosing intervals to keep a consistent level of the medication in the bloodstream. If a dose is missed, take it as soon as remembered unless it’s close to the time for the next dose. Do not double up on doses.
Course duration often ranges from 5 to 14 days, based on the infection type and response to treatment. Complete the entire prescribed course, even if symptoms improve, to prevent resistance.
Consult your healthcare provider for any adjustments in cases of renal impairment, as dosage may need modification. Always report any adverse reactions, including rash or gastrointestinal disturbances, to a healthcare professional immediately.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions of Amoxicillin
Individuals taking amoxicillin may experience side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. These reactions are generally mild and often resolve without medical intervention. Drinking plenty of fluids can help minimize some gastrointestinal issues.
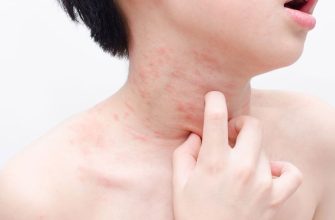
Allergic Reactions
Be alert for signs of an allergic reaction, which can include rash, itching, swelling, or trouble breathing. Seek immediate medical attention if these symptoms appear. Some patients may have a history of sensitivity to penicillin or related antibiotics, which can increase the risk of reactions.
Drug Interactions
Amoxicillin can interact with certain medications. Probenecid, a medication used to treat gout, may increase amoxicillin levels in the blood, enhancing its effects but also raising the risk of side effects. Anticoagulants, such as warfarin, may have their effects intensified, requiring careful monitoring of blood clotting levels. Inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements you take to ensure compatibility.
Women on oral contraceptives should be aware that antibiotics, including amoxicillin, may potentially reduce their effectiveness. Consider using additional contraceptive methods while on this medication to avoid unintended pregnancies.
Regular follow-up with your healthcare provider can help manage any side effects or interactions effectively. Always communicate any new symptoms or concerns during your treatment.