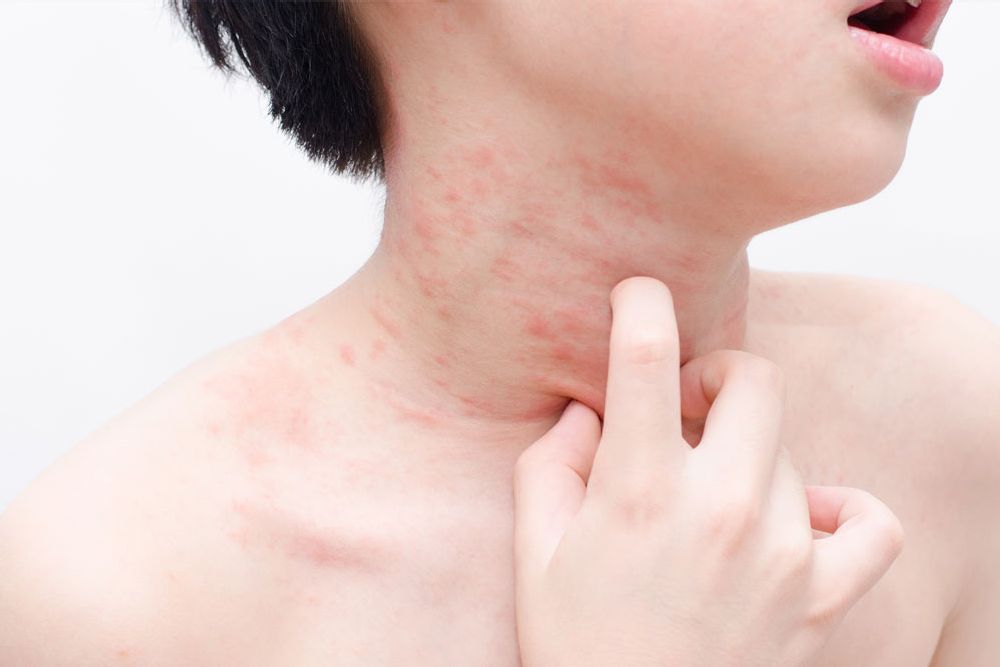
Yes, amoxicillin can cause hives, a common allergic reaction. This reaction manifests as itchy, raised welts on the skin. It’s crucial to understand that the severity varies greatly; some people experience mild hives, while others face more severe reactions requiring immediate medical attention.
Hives from amoxicillin typically appear within hours of taking the medication, but they can sometimes develop later. Symptoms often include swelling, besides the hives themselves. If you notice any skin rash, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, or difficulty breathing after taking amoxicillin, seek immediate medical help. This is a sign of a potentially life-threatening allergic reaction called anaphylaxis.
If you experience milder hives without other symptoms, contact your doctor. They may advise discontinuing amoxicillin and exploring alternative antibiotics. Prevention involves carefully reviewing your medical history with your doctor before starting any antibiotic treatment. Open communication is key to minimizing risks.
Remember: This information isn’t a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a doctor or pharmacist before making any changes to your medication regimen. They can assess your specific situation and provide the best course of action.
- Can Amoxicillin Cause Hives?
- Understanding Amoxicillin and Allergic Reactions
- Recognizing Allergic Symptoms
- Understanding the Allergy Mechanism
- Managing Amoxicillin Allergies
- Alternative Antibiotics
- Symptoms of Amoxicillin-Induced Hives
- What to Do if You Develop Hives After Taking Amoxicillin
- Immediate Actions
- If Symptoms Worsen
- Follow-Up
- Preventing Amoxicillin-Related Hives
- Knowing Your Risk Factors
Can Amoxicillin Cause Hives?
Yes, amoxicillin can cause hives. This allergic reaction manifests as raised, itchy welts on the skin. Hives are a common side effect, occurring in a small percentage of people taking amoxicillin.
Hives can range from mild to severe. Mild reactions usually involve a small number of hives and minimal discomfort. Severe reactions can cause widespread hives, swelling, and difficulty breathing. This requires immediate medical attention.
If you develop hives after taking amoxicillin, stop taking the medication immediately and contact your doctor or seek medical care. Do not assume the hives will resolve on their own; prompt action is important.
Other symptoms that may accompany amoxicillin-induced hives include swelling of the face, lips, or tongue (angioedema), itching, and difficulty swallowing or breathing. These warrant emergency medical care.
Your doctor can determine if your hives are caused by amoxicillin and recommend appropriate treatment, which may include antihistamines or, in severe cases, epinephrine.
Prior exposure to penicillin antibiotics, including amoxicillin, increases your risk of experiencing an allergic reaction, including hives.
Always inform your doctor about any prior allergic reactions you’ve had to medications before starting a new course of antibiotics. This aids in preventing future reactions.
Understanding Amoxicillin and Allergic Reactions
Amoxicillin, a common antibiotic, can trigger allergic reactions in some individuals. These reactions range from mild skin rashes to severe, life-threatening conditions. Knowing the signs and seeking prompt medical attention is crucial.
Recognizing Allergic Symptoms
Hives (urticaria) are a common sign, appearing as itchy, raised welts on the skin. Other symptoms include swelling (angioedema), particularly around the face, lips, or tongue; difficulty breathing; and a rapid heart rate. Less common reactions involve fever, joint pain, and gastrointestinal issues. Any new or worsening symptoms after taking amoxicillin warrant immediate medical evaluation.
Understanding the Allergy Mechanism
Amoxicillin allergy stems from your immune system misidentifying the antibiotic as a threat. This triggers an immune response, releasing histamine and other chemicals causing the allergic symptoms. The severity of the reaction varies greatly, depending on individual factors. Prior exposure to penicillin-type antibiotics increases the risk, but a first-time use can still cause a reaction.
Managing Amoxicillin Allergies
If you experience an allergic reaction, discontinue amoxicillin immediately. Contact your doctor or seek emergency medical care if symptoms are severe. Future prescriptions should avoid penicillin-type antibiotics. Your doctor may conduct allergy testing to confirm the diagnosis and help determine safer alternative medications.
Alternative Antibiotics
If amoxicillin isn’t suitable, numerous alternative antibiotics exist. Your doctor will choose one based on your specific infection and allergy history. Always discuss your medical history, including past allergic reactions, with your doctor before starting any new medication.
Symptoms of Amoxicillin-Induced Hives
Amoxicillin hives usually appear as raised, red, itchy welts on the skin. These welts can vary in size from small to large. Sometimes, they may merge together, forming larger areas of raised skin.
Besides the typical appearance, you might also experience intense itching. This itching can range from mild discomfort to severe irritation, making it difficult to get comfortable.
In some cases, swelling accompanies the hives. This swelling can affect different body parts, including the face, lips, tongue, and throat. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience swelling in your throat or difficulty breathing. This could indicate a severe allergic reaction.
Other symptoms sometimes associated with amoxicillin hives include:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Fever | Elevated body temperature |
| Fatigue | Unusual tiredness or weakness |
| Headache | Pain in the head |
| Nausea | Feeling sick to your stomach |
If you notice any of these symptoms after taking amoxicillin, discontinue use and contact your doctor or other healthcare professional immediately. Prompt action is key to managing potential allergic reactions.
What to Do if You Develop Hives After Taking Amoxicillin
Stop taking amoxicillin immediately. Hives are a common sign of an allergic reaction, and continuing the medication could worsen the reaction.
Immediate Actions
- Call your doctor or allergist right away. They will guide you on the next steps.
- Take an over-the-counter antihistamine like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) to help relieve the itching. Follow the dosage instructions on the package.
- Apply cool compresses or take a cool bath to soothe the hives. Avoid hot showers or baths as they can worsen the itching.
- Monitor your symptoms closely. Note the severity, location, and any other symptoms you experience, like swelling, shortness of breath, or dizziness.
If Symptoms Worsen
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Swelling of the face, lips, or tongue (angioedema)
- Widespread hives or hives that spread rapidly
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Rapid heartbeat
These symptoms could indicate a severe allergic reaction that requires emergency treatment.
Follow-Up
Your doctor may recommend alternative antibiotics or allergy testing to identify the cause of your reaction and prevent future occurrences. Follow their advice carefully.
Preventing Amoxicillin-Related Hives
First, always inform your doctor about any allergies, especially penicillin allergies, before taking amoxicillin. A thorough medical history is key. Discuss any previous reactions to antibiotics or other medications.
Knowing Your Risk Factors
Certain factors increase your susceptibility to amoxicillin-related hives. These include a personal or family history of allergies, particularly to penicillin-based antibiotics. Pre-existing conditions like eczema or asthma also raise your risk. Openly communicating these details with your doctor enables them to make informed decisions about your treatment.
If you’ve experienced hives before, even from a different medication, it’s crucial to share this information. This allows your doctor to assess your risk and potentially prescribe an alternative antibiotic or closely monitor you during treatment. If prescribed amoxicillin, carefully follow all instructions regarding dosage and duration. Never exceed the recommended dose.
Finally, in case of an allergic reaction, seek immediate medical attention. Symptoms like hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, or dizziness require prompt medical care. Early intervention can prevent serious complications.