When your healthcare provider prescribes amoxicillin, it’s important to understand how to take it correctly for the best results. This antibiotic is commonly used to treat various bacterial infections, including pneumonia, bronchitis, and certain ear, nose, and throat infections. Following the prescribed dosage and duration is crucial to effectively eliminate the infection and prevent antibiotic resistance.
Taking amoxicillin with or without food is acceptable; however, consistency can help avoid stomach upset. It’s typically recommended to space doses evenly throughout the day. Make sure to complete the full course, even if you start feeling better before finishing the medication. Discontinuing early can lead to a resurgence of the infection.
Monitor for side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, or allergic reactions. If you experience severe symptoms like rash, itching, or breathing difficulties, seek medical attention immediately. Communication with your healthcare provider is vital regarding any existing conditions or medications you might be taking that could interact with amoxicillin.
Though generally safe for most individuals, it’s advisable for pregnant or breastfeeding women to discuss potential risks with their doctor. Understanding these details ensures you benefit from amoxicillin while minimizing any unnecessary complications.
- Prescription Amoxicillin: A Comprehensive Overview
- Understanding Amoxicillin: What You Need to Know
- How Amoxicillin Works
- Possible Side Effects
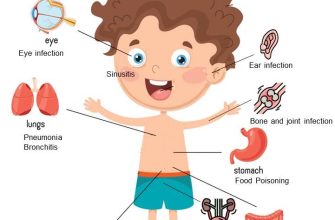
- Common Conditions Treated with Amoxicillin
- Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
- Ear and Throat Infections
- Recommended Dosages and Administration Guidelines
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of Using Amoxicillin
- Interactions with Other Medications: What to Watch For
- Anticoagulants
- Oral Contraceptives
- How to Properly Store Amoxicillin for Optimal Effectiveness
- Check Expiration Dates
- Safeguard from Children
- Important Considerations Before Starting Amoxicillin Therapy
- Medication Interactions
- Symptoms Monitoring
Prescription Amoxicillin: A Comprehensive Overview
Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for various bacterial infections. This antibiotic belongs to the penicillin group and works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. Healthcare providers often recommend it for conditions like streptococcal pharyngitis, acute otitis media, and pneumonia.
Dosage typically depends on the type and severity of the infection. Adults may receive a dose of 500 mg every eight hours or 875 mg every twelve hours. Pediatric dosages are calculated based on the child’s weight, usually around 20-40 mg/kg/day divided into doses.
Administer amoxicillin with or without food. Taking it with food may help reduce stomach upset. Complete the prescribed course to ensure the infection is fully treated, even if symptoms improve early. Failure to do so may lead to antibiotic resistance.
Side effects may include nausea, diarrhea, and rash. Serious allergic reactions, while rare, are possible. Signs of an allergic response include hives, difficulty breathing, and swelling of the face or throat. If these occur, seek immediate medical attention.
Before starting amoxicillin, inform your healthcare provider about any allergies or current medications. Certain drugs, such as allopurinol, may increase the risk of rashes. Monitoring may be necessary for individuals with kidney disorders or conditions affecting liver function.
Consult your doctor if you notice any unusual symptoms or if the condition doesn’t improve within a few days. Regular follow-ups can ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
In summary, amoxicillin serves as a reliable option for treating bacterial infections. Understanding proper use and potential risks will help maximize its benefits. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions closely.
Understanding Amoxicillin: What You Need to Know
Amoxicillin serves as a commonly prescribed antibiotic, actively targeting bacterial infections. Patients typically receive this medication for conditions such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and urinary tract infections. Following the prescribed dosage is key to achieving the best outcomes and minimizing resistance.
How Amoxicillin Works
This antibiotic functions by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. It interferes with cell wall synthesis, which ultimately leads to the death of the bacterial cells. As a result, infections can diminish and symptoms lessen over time. Always complete the full course of amoxicillin, even if symptoms improve, to ensure all bacteria are eliminated.
Possible Side Effects
While amoxicillin is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience side effects. Common reactions include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and skin rashes. Severe allergic reactions, although rare, can occur. Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience swelling, difficulty breathing, or any unusual symptoms.
| Condition Treated | Typical Dosage |
|---|---|
| Pneumonia | 500 mg every 8 hours |
| Urinary Tract Infection | 500 mg every 12 hours |
| Bronchitis | 875 mg every 12 hours |
Ensure you inform your healthcare provider about any other medications you’re taking, as interactions can affect efficacy or increase side effects. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should discuss the implications with their healthcare provider before starting amoxicillin. Regularly reviewing your medical history can help facilitate safe and effective treatment.
Common Conditions Treated with Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for several bacterial infections. One prevalent use is in treating sinusitis. This condition often results from a bacterial infection in the nasal passages and can be effectively managed with Amoxicillin, typically prescribed for 10 to 14 days to alleviate symptoms.
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Amoxicillin is also effective against pneumonia, especially in cases caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Patients may experience symptoms such as coughing, fever, and shortness of breath. A complete course can enhance recovery and prevent complications.
Ear and Throat Infections
For children and adults alike, acute otitis media (ear infections) and pharyngitis (sore throat) are frequently treated with Amoxicillin. The typical duration for such treatments ranges from 5 to 10 days. Early intervention can clear the infection and reduce the risk of further issues.
Many healthcare providers choose Amoxicillin due to its broad-spectrum activity and favorable side effect profile. Always consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations tailored to individual needs.
Recommended Dosages and Administration Guidelines
For adults and children over 40 kg, the standard dosage of amoxicillin is 500 mg administered every 12 hours or 250 mg every 8 hours. This regimen is effective for treating a variety of infections, including respiratory tract infections and urinary tract infections.
In pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg, the dosage is typically based on body weight, calculating 20 to 40 mg/kg/day divided into two or three doses. For specific conditions like otitis media, a higher dose of 80 to 90 mg/kg/day may be necessary.
Amoxicillin can be taken with or without food, although taking it with food may help reduce potential gastrointestinal upset. For optimal absorption, maintain consistent intervals between doses. Ensure to complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
In cases of renal impairment, dosage adjustments may be required. It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations based on kidney function. Also, never use amoxicillin in patients with a known allergy to penicillin or cephalosporins.
When prescribing amoxicillin, consider any concomitant medications that might interact. Regular monitoring for side effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances or allergic reactions, is recommended throughout the treatment course.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Using Amoxicillin
Consult your healthcare provider about potential side effects when using amoxicillin. While it is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience adverse reactions.
- Allergic Reactions: Skin rash, itching, or hives can occur. Severe reactions like anaphylaxis, though rare, require immediate medical attention.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain may arise. Staying hydrated can help alleviate these symptoms.
- Yeast Infections: Disruption of normal flora can lead to overgrowth of Candida, resulting in oral or vaginal yeast infections.
- Blood Disorders: Rarely, amoxicillin can cause changes in blood cell counts, leading to conditions such as thrombocytopenia or neutropenia. Regular blood tests may be advised for those on long-term treatment.
- Liver Effects: Monitor liver function, especially if you have a pre-existing condition. Signs of liver damage include jaundice and dark urine.
Risk factors include pre-existing allergies to penicillin or cephalosporins, liver or kidney problems, and certain medical conditions. Disclose your full medical history to your healthcare provider before starting treatment.
If you notice any unusual symptoms, contact your healthcare provider promptly. Regular follow-up appointments can help manage any potential side effects effectively.
Interactions with Other Medications: What to Watch For
Be cautious when combining amoxicillin with certain medications. Notably, it interacts with probenecid, which can increase amoxicillin levels in the bloodstream, enhancing the risk of side effects. Adjust dosages appropriately and monitor for unusual reactions.
Anticoagulants
When taking amoxicillin alongside anticoagulants, such as warfarin, monitor for prolonged bleeding or unusual bruising. Amoxicillin may intensify the effects of these medications, necessitating dose adjustments. Regularly check INR levels for safety.
Oral Contraceptives
Amoxicillin may reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives. Consider using additional non-hormonal methods during treatment. Discuss alternative options with your healthcare provider to ensure effective contraception.
Always inform your healthcare practitioner about all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This enables a comprehensive evaluation of potential interactions and ensures a safe treatment plan.
How to Properly Store Amoxicillin for Optimal Effectiveness
Store amoxicillin at room temperature, typically between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Ensure the medication remains in a tightly closed container to prevent exposure to moisture and light.
Avoid placing amoxicillin in bathrooms or kitchens where humidity levels fluctuate frequently. Instead, choose a dry, cool location such as a cabinet or drawer. If prescribed liquid amoxicillin, refrigerate it to maintain potency, but do not freeze it.
Check Expiration Dates
Always check the expiration date on the label before use. Discard any expired medications appropriately, as they may not work effectively and could pose health risks.
Safeguard from Children
Store all medications, including amoxicillin, out of reach of children. Use childproof caps and consider a locked cabinet to enhance safety. Regularly review your medications to ensure proper storage and to discard items that are no longer needed.
Important Considerations Before Starting Amoxicillin Therapy
Consult your healthcare provider about any allergies, especially to penicillin or other antibiotics. Disclose your full medical history, including liver and kidney conditions, as these may impact dosage and effectiveness.
Medication Interactions
Review all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements. Certain medications, like anticoagulants, may interact negatively with amoxicillin.
Symptoms Monitoring
- Watch for signs of allergic reactions such as rashes, itching, or difficulty breathing.
- Inform your doctor if symptoms worsen or do not improve after a few days of treatment.
- Stay alert for side effects like diarrhea or gastrointestinal discomfort and report them promptly.
Ensure that you complete the entire course of amoxicillin as prescribed, even if you start feeling better sooner. This helps prevent antibiotic resistance and ensures a full recovery. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider can aid in assessing treatment effectiveness.