Need reliable information on Amoxicillin 500mg? This article provides clear, concise details. We’ll cover dosage, potential side effects, and important precautions. Remember, this information is for general knowledge and doesn’t replace professional medical advice.
Amoxicillin, the active ingredient in Generic Amoxil, is a penicillin antibiotic widely used to treat bacterial infections. A 30-tablet pack of 500mg tablets offers a sufficient course of treatment for many common ailments. Always follow your doctor’s prescription instructions precisely; deviating from the recommended dosage can affect treatment efficacy.
Common side effects may include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. More serious, though rare, reactions warrant immediate medical attention. These include allergic reactions (like hives or difficulty breathing) and severe stomach pain. Before starting this medication, inform your doctor about any allergies, current medications, or underlying health conditions, especially kidney or liver problems. This ensures safe and effective medication use.
Specific dosage instructions are crucial and vary based on individual needs. Never self-medicate or alter your prescribed dose. This guide provides general information; consult a healthcare professional for personalized treatment plans and to discuss potential drug interactions.
- Generic Amoxil 30x500mg: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Generic Amoxil
- Proper Usage and Storage
- Potential Side Effects
- Alternative Treatment Options
- What is Amoxicillin (Generic Amoxil)?
- Common Bacterial Infections Treated with Amoxicillin
- Respiratory Infections
- Ear Infections
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Other Infections
- Important Note:
- Dosage and Administration of Amoxil 500mg
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- Medication Interactions
- Specific Precautions
- Monitoring Your Health
- Drug Interactions with Amoxicillin
- Allopurinol and Probenecid
- Oral Contraceptives
- Anticoagulants (like Warfarin)
- Methotrexate
- Other Medications
- When to Consult a Doctor
- Storing Amoxicillin Safely and Effectively
- Protecting Amoxicillin from Degradation
- Proper Disposal of Amoxicillin
- Monitoring Expiry Date
- Safe Handling Practices
- Understanding Liquid Amoxicillin Storage
- Alternatives to Amoxicillin and When They Might Be Necessary
Generic Amoxil 30x500mg: A Detailed Guide
Always consult your doctor before starting any medication, including generic Amoxil. This guide provides information, not medical advice.
Understanding Generic Amoxil
Generic Amoxil, containing amoxicillin, is a penicillin antibiotic. Each 500mg tablet combats bacterial infections. A 30-tablet pack provides a common course of treatment. Dosage depends on the infection’s severity and your doctor’s prescription. Common uses include ear infections, pneumonia, and urinary tract infections.
Proper Usage and Storage
Take Amoxil exactly as prescribed. Complete the entire course, even if you feel better sooner. Stopping early can lead to resistant bacteria. Store tablets at room temperature, away from moisture and direct sunlight. Keep out of reach of children.
Potential Side Effects
Amoxicillin can cause side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and rash. Severe allergic reactions are rare but require immediate medical attention. Inform your doctor about any existing allergies or health conditions before taking Amoxil. This medication can interact with other drugs, so list all medications you’re currently taking.
Alternative Treatment Options
If you have an allergy to penicillin, your doctor will prescribe an alternative antibiotic. Discuss treatment options if you experience severe or persistent side effects. Accurate diagnosis is key; Amoxil treats bacterial, not viral, infections.
What is Amoxicillin (Generic Amoxil)?
Amoxicillin is a penicillin-based antibiotic. It combats bacterial infections by preventing bacteria from building cell walls, effectively killing them.
Doctors prescribe it for various bacterial infections, including ear infections, strep throat, bronchitis, and pneumonia. Amoxicillin is also effective against some urinary tract infections and skin infections.
Amoxil is a brand name; generic amoxicillin offers the same active ingredient at a lower cost. Both are equally effective.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Complete the entire course, even if you feel better, to prevent the bacteria from becoming resistant.
Potential side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and rash. Inform your doctor immediately if you experience severe allergic reactions such as difficulty breathing or swelling.
Amoxicillin is generally safe, but you should inform your doctor about any existing allergies or medical conditions before taking it, especially if you’re pregnant, breastfeeding, or have kidney problems.
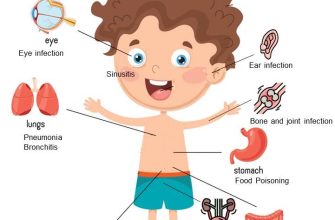
Common Bacterial Infections Treated with Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin effectively combats various bacterial infections. It’s crucial to remember that this information isn’t a substitute for professional medical advice; always consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Respiratory Infections
- Sinusitis: Amoxicillin treats bacterial sinusitis, characterized by facial pain and nasal congestion. A doctor will determine the cause.
- Bronchitis: Acute bronchitis, a lung infection causing cough and inflammation, often responds well to amoxicillin if bacterial.
- Pneumonia: In some cases, amoxicillin can be used to treat bacterial pneumonia, a serious lung infection, but other antibiotics are often preferred.
Ear Infections
Amoxicillin is frequently prescribed for otitis media, or middle ear infections, particularly in children. Symptoms include earache and fluid buildup.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
- Cellulitis: This skin infection, marked by redness, swelling, and pain, can be treated with amoxicillin in milder cases.
- Impetigo: A highly contagious skin infection with blister-like sores, often responds to amoxicillin treatment.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Amoxicillin can be effective against some UTIs, characterized by painful urination and frequent urges. However, resistance is increasing, and other antibiotics may be necessary.
Other Infections
- Lyme disease: In its early stages, amoxicillin may be used to treat Lyme disease, a bacterial infection transmitted by ticks.
- Dental infections: Amoxicillin can effectively treat infections arising from dental procedures or oral health issues.
Important Note:
Amoxicillin’s effectiveness depends on the specific bacteria causing the infection and the antibiotic’s susceptibility. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and treatment duration. Ignoring this advice may lead to treatment failure or the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Dosage and Administration of Amoxil 500mg
Amoxil 500mg tablets are typically swallowed whole with a glass of water. Dosage depends entirely on your specific infection and your doctor’s prescription. Do not adjust your dose without consulting your physician.
Typical adult dosage for common infections ranges from 250mg to 500mg, taken every 8 hours or as directed. Some infections may require a higher dose or a different dosing schedule.
Children’s dosages vary significantly with weight and age. Your doctor will calculate the appropriate dose based on your child’s individual needs. Never administer adult-strength Amoxil to children.
Complete the full course of antibiotics, even if you feel better before the medication runs out. Stopping early can lead to treatment failure and the development of antibiotic resistance.
Store Amoxil in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Keep it out of children’s reach.
Inform your doctor about any allergies, underlying medical conditions, or medications you are currently taking before starting Amoxil. This is crucial for safe and effective treatment.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe allergic reactions such as hives, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, or difficulty breathing.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Amoxicillin, the active ingredient in Amoxil, generally causes mild side effects. However, some individuals experience digestive upset, including diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. These usually resolve without treatment. Less common, but still possible, are allergic reactions ranging from skin rashes to severe, life-threatening anaphylaxis. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, or hives.
Medication Interactions
Amoxicillin can interact with certain medications, particularly anticoagulants like warfarin. This interaction may increase bleeding risk. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking before starting Amoxil. This includes over-the-counter drugs.
Specific Precautions
Before taking Amoxicillin, discuss your medical history with your doctor. This is especially important if you have a history of kidney or liver disease, allergies to penicillin or cephalosporin antibiotics, or mononucleosis (glandular fever). Pregnancy and breastfeeding should also be disclosed, as Amoxicillin may be transferred to the baby. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Complete the entire course of medication, even if you feel better before finishing. Failure to complete the course can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Monitoring Your Health
While taking Amoxicillin, pay close attention to any unusual symptoms. Report any persistent or worsening side effects to your doctor or pharmacist promptly. Regular monitoring is especially important for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions.
Drug Interactions with Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin, a common antibiotic, can interact negatively with certain medications. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs. This ensures safe and effective treatment.
Allopurinol and Probenecid
Taking amoxicillin with allopurinol (for gout) may increase the risk of skin reactions. Similarly, concurrent use with probenecid (also for gout) can raise amoxicillin levels in your blood, potentially leading to side effects. Your doctor might adjust dosages or choose alternative medications.
Oral Contraceptives
Amoxicillin may decrease the effectiveness of certain oral contraceptives. Consider using additional birth control methods during treatment and for a short period afterward. Discuss this with your doctor or pharmacist.
Anticoagulants (like Warfarin)
Amoxicillin can interact with anticoagulants, potentially increasing the risk of bleeding. Regular blood tests are usually recommended to monitor your blood clotting time while taking both medications. Close monitoring is critical to avoid complications.
Methotrexate
Combining amoxicillin and methotrexate (used for certain cancers and autoimmune diseases) can elevate methotrexate levels in your blood, possibly causing serious side effects. Careful monitoring and dose adjustments are necessary.
Other Medications
Amoxicillin can also interact with other medications, including some antibiotics and certain types of diuretics. Always provide a complete medication list to your healthcare provider to prevent potential drug interactions. Your doctor can assess your individual situation and recommend the safest course of action.
When to Consult a Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience a severe allergic reaction, including difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, or tongue, or hives.
Contact your doctor if your symptoms don’t improve after 7 days of taking Amoxil, or if they worsen. This includes persistent or worsening diarrhea, which could indicate Clostridium difficile infection.
Schedule a doctor’s appointment if you notice any new or unusual symptoms while taking Amoxil. This could include unusual fatigue, dark urine, or jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting Amoxil to avoid potential drug interactions. This includes anticoagulants and oral contraceptives.
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Severe allergic reaction | Go to the emergency room immediately. |
| Symptoms not improving or worsening after 7 days | Contact your doctor. |
| New or unusual symptoms | Schedule a doctor’s appointment. |
| Persistent or worsening diarrhea | Contact your doctor immediately. |
Remember, this information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for guidance regarding your specific health condition and medication.
Storing Amoxicillin Safely and Effectively
Keep Amoxicillin in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat. Ideal storage temperature is below 77°F (25°C).
Protecting Amoxicillin from Degradation
- Avoid storing Amoxicillin in the bathroom, where humidity is higher.
- Don’t freeze Amoxicillin. Freezing can alter its structure and reduce its effectiveness.
- Store the medication in its original container. This container protects the tablets from moisture and light.
Proper Disposal of Amoxicillin
Once your prescription is finished, discard any leftover Amoxicillin safely. Never flush medications down the toilet. Follow your local guidelines for proper medication disposal. Many pharmacies offer safe medication disposal programs.
Monitoring Expiry Date
- Check the expiration date printed on the packaging.
- Discard Amoxicillin once it expires. Using expired medication can be ineffective and potentially harmful.
- Pay close attention to the expiration date, especially with liquid Amoxicillin, which may degrade more quickly.
Safe Handling Practices
- Wash your hands before and after handling Amoxicillin.
- Keep Amoxicillin out of reach of children and pets.
- If you suspect accidental ingestion, contact a poison control center immediately.
Understanding Liquid Amoxicillin Storage
Refrigerate reconstituted liquid Amoxicillin. After reconstitution, check the label for specific storage instructions and the shelf-life of the prepared liquid. Use the entire bottle within the recommended timeframe.
Alternatives to Amoxicillin and When They Might Be Necessary
Consider alternatives if you’re allergic to penicillin, experience side effects like diarrhea or rash, or the infection doesn’t respond to Amoxicillin.
Cefuroxime offers a similar antibacterial effect and is a good choice for respiratory or urinary tract infections. It’s often prescribed for patients with penicillin allergies, though cross-reactivity is possible.
Azithromycin, a macrolide antibiotic, effectively treats various bacterial infections, including those Amoxicillin targets. It’s particularly useful for community-acquired pneumonia and some sexually transmitted infections.
Clindamycin is another alternative, often used for skin infections, dental abscesses, and pelvic inflammatory disease. It’s crucial to note that resistance is a growing concern, so appropriate testing is necessary.
Doxycycline, a tetracycline, works well against various bacterial infections, including those affecting the respiratory and urinary tracts. It’s also a frequent choice for treating certain sexually transmitted diseases.
Always consult a physician before changing medication. They will assess your specific situation, consider your medical history, and choose the most suitable antibiotic based on the infection type and your individual needs. Incorrect antibiotic selection can lead to treatment failure and increased resistance.