For most adult infections, a standard amoxicillin dose is 500mg every 8 hours or 250mg every 12 hours. This dosage is generally effective for treating common bacterial infections like strep throat or ear infections. However, remember to always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage and duration.
Your physician will tailor the amoxicillin dosage to your specific condition and health. Factors influencing the prescription may include the severity of your infection, your weight, and any pre-existing medical conditions. Never adjust the dosage yourself; always consult with your doctor or pharmacist before making any changes.
Severe infections might require a higher dose or a different administration schedule. For example, some serious bacterial infections may necessitate higher doses, administered more frequently, possibly intravenously. Always discuss your treatment plan with your healthcare provider to ensure you receive the most appropriate care.
Important Note: Amoxicillin can cause side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and rash. If you experience any unusual symptoms, contact your doctor immediately. Also, inform your doctor of any allergies or current medications before starting amoxicillin treatment.
Dosage Amoxicillin Adults
Standard adult amoxicillin dosage for common infections is 500mg every 8 hours or 250mg every 12 hours. This is a general guideline; your doctor will adjust the dosage based on your specific condition and medical history.
For more severe infections, higher doses may be prescribed, potentially reaching up to 1000mg every 8 hours. This is always determined by a physician.
The duration of treatment varies depending on the infection. Typical treatment spans 5 to 14 days. Complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better before the medication runs out. This prevents the infection from returning.
Amoxicillin comes in various forms: capsules, tablets, and suspensions (liquid). Follow your prescription instructions carefully regarding the form and frequency of administration.
Side effects, though infrequent, can include nausea, diarrhea, and skin rashes. Report any concerning side effects to your healthcare provider immediately.
Always consult your doctor before taking amoxicillin, especially if you have allergies, kidney problems, or are pregnant or breastfeeding. This information is for general knowledge and does not substitute medical advice.
Standard Amoxicillin Dosage for Adults
The typical adult dosage for amoxicillin is 250-500 milligrams (mg) every 8 hours, or 500-875 mg every 12 hours. Your doctor will determine the best dosage based on your specific infection and overall health.
However, dosages can vary. For instance, severe infections might require higher doses, potentially up to 1 gram every 8 hours. Conversely, less severe infections may necessitate lower doses.
Amoxicillin is available in various forms: capsules, tablets, and suspensions (liquid). Your doctor will prescribe the most suitable form for you. Always follow the prescription instructions carefully.
The duration of treatment also varies depending on the infection. It typically ranges from 5 to 14 days. Completing the full course of antibiotics is critical to ensure complete eradication of the bacteria, even if you begin to feel better sooner. Never stop taking amoxicillin without consulting your doctor.
| Dosage Form | Typical Dosage | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Capsules/Tablets | 250-500 mg | Every 8 hours |
| Capsules/Tablets | 500-875 mg | Every 12 hours |
| Suspension (Liquid) | Dosage varies; follow prescription instructions | As directed |
Remember, this information is for general guidance only. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking amoxicillin or any medication. They can provide personalized advice and address any concerns you may have about potential side effects or drug interactions.
Factors Affecting Amoxicillin Dosage in Adults
Your doctor determines your amoxicillin dosage based on several key factors. The severity of your infection significantly impacts the prescribed amount. More serious infections usually require higher doses.
Your weight plays a crucial role. Higher weight generally means a higher dose, as it relates to drug distribution within the body. Your doctor will calculate the appropriate dose based on your individual weight.
Kidney function significantly affects how your body processes amoxicillin. Reduced kidney function necessitates dosage adjustments to prevent drug accumulation and potential side effects. Your doctor will consider creatinine clearance or eGFR (estimated glomerular filtration rate) values when making these adjustments.
Liver function also influences amoxicillin dosage. Impaired liver function can affect drug metabolism, requiring a lower dose or more frequent monitoring. Your doctor will assess your liver function tests before prescribing the medication.
The type of infection you have directly influences the dosage. Different infections respond differently to amoxicillin and require varying doses for optimal treatment. For example, a respiratory infection might necessitate a different dose than a urinary tract infection.
Your doctor may also consider your age, alongside other health conditions and medications you are currently taking. Pre-existing conditions could lead to adjustments. Always inform your doctor about all other medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs, to avoid potential interactions.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding your amoxicillin dosage and treatment plan.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Amoxicillin, while generally safe, can cause side effects. Most are mild and temporary, but some require medical attention.
- Common side effects: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain. These usually resolve without treatment. Drink plenty of fluids to manage diarrhea.
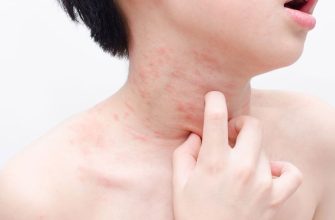
- Less common side effects: Skin rash, itching, dizziness. Contact your doctor if these develop.
- Rare but serious side effects: Difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat (angioedema), severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis). Seek immediate medical help if these occur. Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency.
Before starting amoxicillin, inform your doctor about:
- Any allergies, particularly penicillin allergies.
- Current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal remedies. Interactions can occur.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding status. Amoxicillin is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but discuss this with your doctor.
- Existing liver or kidney problems. Dosage adjustments may be necessary.
During treatment:
- Take amoxicillin exactly as prescribed. Don’t stop early, even if you feel better.
- Complete the entire course of antibiotics. This prevents antibiotic resistance.
- Monitor for side effects and contact your doctor if concerns arise.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking amoxicillin or any medication.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience a severe allergic reaction, including hives, swelling of your face, lips, or tongue, or difficulty breathing. These are signs of a serious allergic reaction requiring immediate medical attention.
Severe Symptoms Requiring Immediate Attention
Seek immediate medical help if you develop severe diarrhea, persistent vomiting, or significant abdominal pain. These could indicate a serious complication. Also, contact your doctor if your symptoms worsen or don’t improve after completing the full course of amoxicillin.
When to Monitor and Follow Up
Monitor yourself for signs of infection improvement. If your fever persists for more than a few days, or if other symptoms like cough or sore throat don’t show improvement within a reasonable timeframe (consult your doctor for specific expectations), schedule a follow-up appointment. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding the duration of treatment and follow-up care.
Remember, this information is for guidance only. Always consult your physician or other qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment. Self-treating can be dangerous.