Amoxicillin is not an effective treatment for trichomoniasis. This sexually transmitted infection is primarily caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, which requires specific antimicrobial medications for successful eradication.
The recommended treatments for trichomoniasis typically include metronidazole or tinidazole. These medications target the parasite directly and have demonstrated high success rates in clearing the infection. In cases of trichomoniasis, using amoxicillin may lead to unnecessary side effects without addressing the underlying cause.
If you suspect you have trichomoniasis or have been diagnosed, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate evaluation and treatment options. They can prescribe the correct medication to effectively eliminate the infection and address any associated symptoms. Taking the right approach ensures a faster recovery and reduces the risk of transmission to partners.
Does Amoxicillin Treat Trichomoniasis?
Amoxicillin does not treat trichomoniasis. This infection, caused by the protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, requires specific antibiotics for effective treatment. Metronidazole and tinidazole are the first-line medications recommended by healthcare professionals. They specifically target the organism responsible for the infection.
Using amoxicillin for trichomoniasis is not appropriate, as it targets bacterial infections, not parasites. Misusing antibiotics can lead to resistance, which complicates treatment for other bacterial infections. For those diagnosed with trichomoniasis, it is crucial to follow the advice of a healthcare provider and complete the prescribed course of metronidazole or tinidazole.
Additionally, it is advisable to inform sexual partners about the infection so they can also seek treatment. Regular testing for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) plays a part in ensuring sexual health and minimizing the risk of transmission.
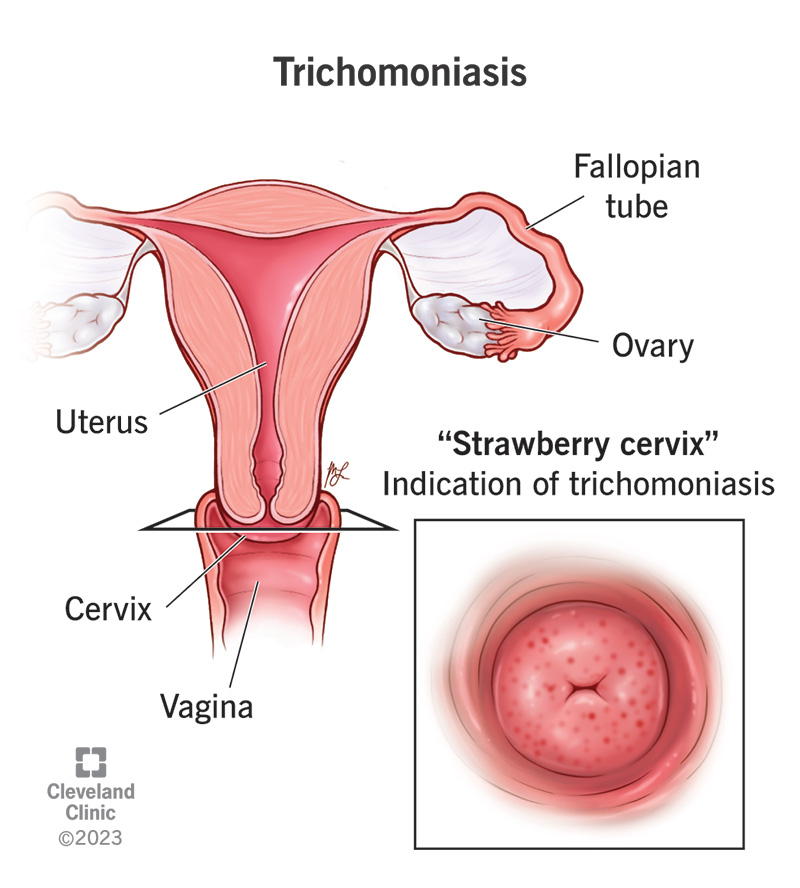
Understanding Trichomoniasis: Causes and Symptoms
Trichomoniasis is primarily caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. This single-celled organism is commonly transmitted through sexual contact. It can infect both men and women but is more prevalent in women. Maintaining open communication with sexual partners and practicing safe sex can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Common symptoms of trichomoniasis in women include a frothy, greenish-yellow discharge, itching, burning sensations during urination, and discomfort during intercourse. Some women may experience lower abdominal pain. Symptoms can sometimes be mild or absent, making regular screenings essential for sexually active individuals.
In men, symptoms are often less noticeable but can involve irritation inside the penis, discharge, or discomfort during urination. While many men may not show symptoms, they can still spread the infection.
If you suspect an infection, seek medical advice for diagnosis and treatment options. Antiparasitic medications, such as metronidazole or tinidazole, are commonly prescribed. Timely treatment helps alleviate symptoms and prevents transmission to partners.
Regular health check-ups and being aware of personal health status contribute to better sexual health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper hygiene and safe sexual practices, further aids in prevention.
The Role of Antibiotics in Treating Trichomoniasis
Antibiotics specifically designed to combat Trichomoniasis include metronidazole and tinidazole. These medications effectively target the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, leading to successful treatment outcomes. Amoxicillin, a common antibiotic, does not treat this infection as it is not effective against the specific pathogen responsible for Trichomoniasis.
Prescribing metronidazole is the standard approach, with a single dose often sufficient for cure. Tinidazole is another alternative, offering a similar efficacy profile. Both drugs work by disrupting the DNA of the protozoan, ultimately eliminating the infection. Medical professionals often recommend that sexual partners receive treatment simultaneously to prevent reinfection.
Patients typically experience symptom relief within a few days after starting the appropriate antibiotic regimen. However, completing the full course is necessary to ensure the infection is fully eradicated. Testing for reinfection is advisable, especially in cases of persistent or recurring symptoms.
Maintaining open communication with healthcare providers is crucial for managing Trichomoniasis effectively. Regular screenings and discussing any concerns about symptoms can help ensure proper treatment and prevent complications. Awareness of other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) is also important, as co-infections can occur. Taking proactive steps toward sexual health can significantly contribute to overall well-being.
Amoxicillin vs. Recommended Treatments for Trichomoniasis
Amoxicillin is not a recommended treatment for trichomoniasis. The primary medication used to treat this sexually transmitted infection is metronidazole or tinidazole. Amoxicillin does not target the parasite responsible for trichomoniasis effectively.
For effective treatment, follow these guidelines:
- Metronidazole: Typically prescribed as a single dose of 2 grams or taken over seven days (500 mg twice daily). This is the most common and effective treatment.
- Tinidazole: Administered as a single dose of 2 grams or 1 gram daily for five days. It is another effective alternative.
Consult a healthcare provider for appropriate diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan. Both partners should be treated simultaneously to prevent reinfection. Abstaining from sexual activity until treatment has been completed and follow-up testing is advisable.
Side effects of metronidazole may include nausea, vomiting, and a metallic taste. Tinidazole can cause similar effects but is generally better tolerated. Always discuss potential side effects with a healthcare provider.
In summary, rely on metronidazole or tinidazole for trichomoniasis. Amoxicillin should not be used for this specific infection. Always seek professional medical advice for proper treatment and management.