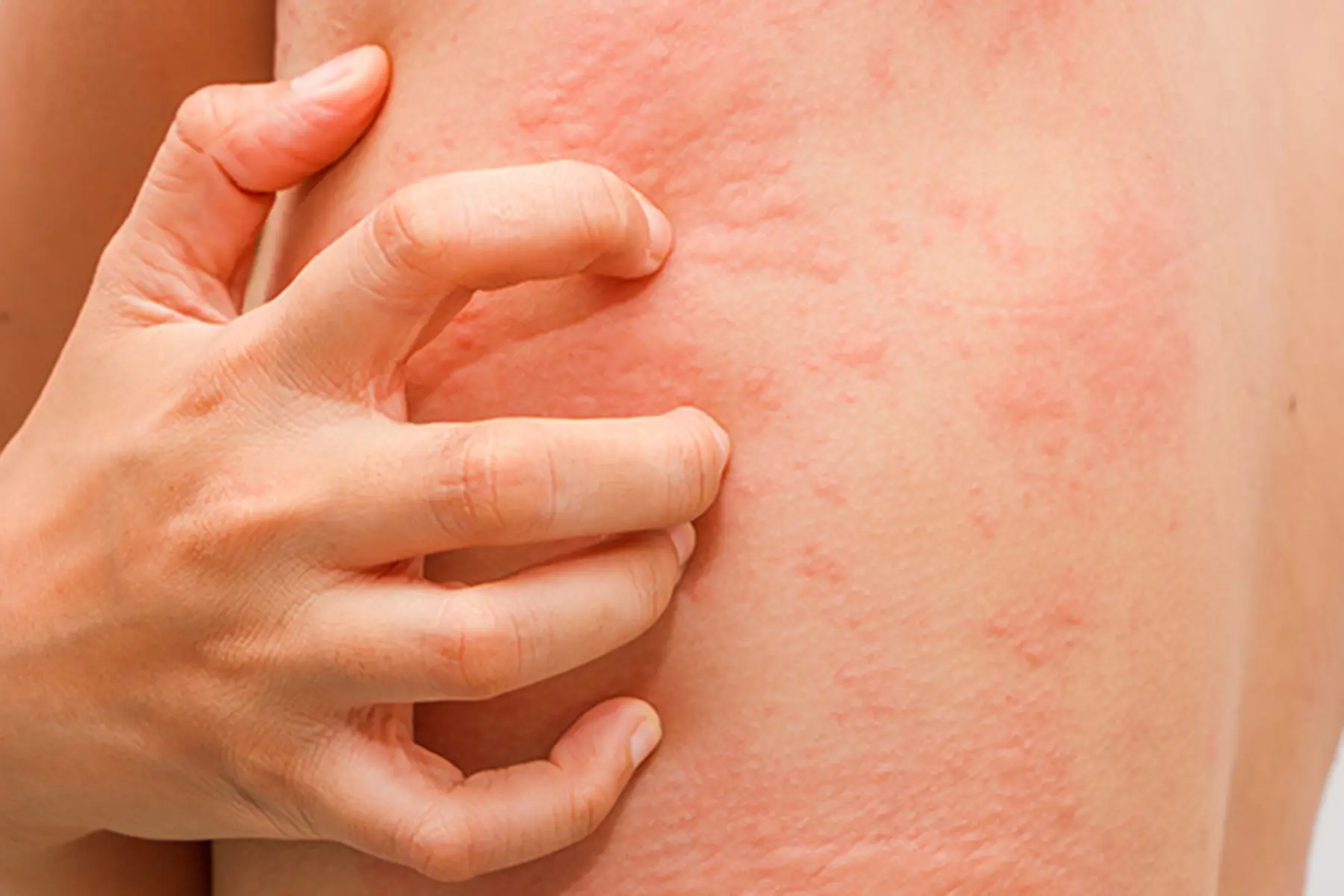
If you suspect an allergy rash from amoxicillin, seek medical advice immediately. This reaction can manifest as hives, redness, or swelling, often appearing within hours of taking the medication. Identifying the symptoms early allows for timely intervention and relief.
Discontinue the use of amoxicillin if you experience these signs. Your healthcare provider may recommend alternative antibiotics that are safer for you. Document any specific reactions and share this information during follow-up consultations to help refine your treatment plan.
In severe cases, an allergic reaction may lead to anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition. Familiarize yourself with other common symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or swelling in the face and throat, which require immediate emergency care. Carry an epinephrine auto-injector if you have a history of severe allergies.
Maintaining open communication with your healthcare team ensures you receive the best care tailored to your individual allergies. Regularly review any medications you’re taking and inform your doctor about past reactions, as this knowledge is critical for your safety and well-being.
- Allergy Rash to Amoxicillin
- Understanding Amoxicillin and Its Uses
- Common Uses of Amoxicillin
- Considerations and Advice
- Signs and Symptoms of Allergy Rash
- Types of Rash
- Associated Symptoms
- Causes of Amoxicillin Allergy Reactions
- Diagnosis of Amoxicillin Allergy Rash
- Treatment Options for Allergy Rash
- Preventing Reactions to Amoxicillin
- Safe Alternatives to Amoxicillin
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- Watch for Serious Symptoms
- Follow Up on Persistent Symptoms
- Long-term Management of Antibiotic Allergies
Allergy Rash to Amoxicillin
If you suspect an allergy rash from amoxicillin, stop taking the medication immediately and seek medical assistance. Do not resume use without consulting a healthcare professional.
Here are key points to consider regarding an allergy rash from amoxicillin:
- Symptoms: Look for red, itchy rashes, hives, or any swelling, particularly around the face or throat.
- Immediate Actions: Use antihistamines like cetirizine or diphenhydramine for mild reactions. Severe cases may require epinephrine, so ensure you have access to an EpiPen if you have a history of severe allergies.
- Consultation: Schedule an appointment with an allergist or your primary care physician to discuss your symptoms and consider allergy testing.
- Alternative Antibiotics: Inform your doctor about your allergy so they can prescribe a suitable alternative, such as azithromycin or clindamycin.
Keep a record of any medication allergies and communicate them clearly to all healthcare providers. This ensures a safer treatment plan in the future.
Stay aware of potential cross-reactivity with other antibiotics, particularly penicillin-related drugs. If you have had a rash or any adverse reaction before, inform your healthcare provider.
Monitoring your response to new medications is crucial. If symptoms persist or worsen, revisit your healthcare provider without delay.
Understanding Amoxicillin and Its Uses
Amoxicillin serves as a broad-spectrum antibiotic, primarily targeting bacterial infections. Healthcare providers often prescribe it for conditions like pneumonia, bronchitis, and infections of the ears, nose, throat, skin, and urinary tract. This medication works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, which helps your immune system eliminate the infection more effectively.
Patients typically find amoxicillin in tablet or liquid form. Dosage often depends on the type and severity of the infection. Following your provider’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment is critical for achieving the best outcomes and minimizing the risk of resistance. Complete the full course, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
Common Uses of Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin frequently treats various infections caused by susceptible bacteria. Commonly addressed conditions include:
- Streptococcal infections
- H. pylori eradication in peptic ulcer disease
- Sinusitis caused by bacterial infections
- Skin and soft tissue infections
Considerations and Advice
Patients with allergies to penicillin or cephalosporins should avoid amoxicillin. Report any history of allergic reactions to your healthcare provider before starting the medication. If a rash or other symptoms arise during treatment, seek medical attention promptly. Always discuss your complete medical history and any other medications you are taking to avoid potential interactions.
Signs and Symptoms of Allergy Rash
Recognize the signs of an allergy rash to amoxicillin quickly for effective management. Common symptoms include redness, swelling, and itching on the skin. These rashes may appear within hours after taking the medication.
Types of Rash
Identify different forms of allergy rashes. Urticaria, commonly known as hives, presents as raised, itchy welts. Meanwhile, a maculopapular rash features flat, red spots with small bumps, often covering larger areas. Some individuals may experience more severe reactions, leading to conditions like erythema multiforme.
Associated Symptoms
Pay attention to accompanying symptoms. Fever, fatigue, or gastrointestinal issues may indicate a more systemic allergic reaction. In severe cases, watch for difficulty breathing or swelling of the face and throat, which may signal anaphylaxis, requiring immediate medical attention.
Consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment if you notice any of these symptoms after taking amoxicillin. Timely intervention can prevent complications and promote recovery.
Causes of Amoxicillin Allergy Reactions
Amoxicillin allergy reactions are primarily caused by an immune system response to the antibiotic. The body mistakenly identifies amoxicillin as a harmful substance, triggering the release of chemicals like histamine. This reaction can lead to various symptoms, including rashes.
Several factors contribute to the likelihood of an allergic reaction:
- Genetic predisposition: A family history of drug allergies increases the risk of developing an allergy to amoxicillin.
- Previous exposure: Individuals who have had prior allergic reactions to penicillin or related antibiotics are more likely to react to amoxicillin.
- Cross-reactivity: People allergic to penicillin may also experience reactions to amoxicillin due to structural similarities in these drugs.
- Underlying health conditions: Certain conditions, like asthma or eczema, can heighten the risk of allergic responses to medications.
Symptoms may vary in severity. Common reactions include:
- Skin rash or hives
- Itching or swelling
- Respiratory issues
Immediate medical attention is crucial for severe symptoms like anaphylaxis, which can include difficulty breathing or swelling of the face and throat.
If you suspect an allergy to amoxicillin, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and alternative treatment options.
Diagnosis of Amoxicillin Allergy Rash
To diagnose an amoxicillin allergy rash, a thorough patient history is crucial. Start by documenting all medications taken, including amoxicillin and any previous allergic reactions. Note the timeline of rash appearance after amoxicillin administration to establish a correlation.
Conduct a physical examination focusing on the rash’s characteristics, such as location, itching, and appearance. Commonly, the rash may present as urticaria or maculopapular eruptions. Classifying the rash helps inform the next steps in diagnosis.
Consider skin testing for immediate hypersensitivity reactions if the patient has a history of anaphylaxis or other severe reactions. Skin prick tests or intradermal tests can confirm immediate hypersensitivity, though they may not detect delayed-type reactions.
If skin testing is inconclusive, refer to an allergist for further evaluation. They may recommend a graded oral challenge under controlled conditions. This approach ensures safety while assessing for a true allergy.
Finally, keep in mind that cross-reactivity with other beta-lactam antibiotics may occur. Assessing the patient’s reactions to other medications can guide future treatment options.
Treatment Options for Allergy Rash
For an allergy rash linked to amoxicillin, discontinue the medication immediately. Inform a healthcare provider about the reaction to seek alternative treatments. Over-the-counter antihistamines like diphenhydramine or cetirizine can ease itching and reduce inflammation.
If the rash worsens or persists, consult a doctor. They may prescribe topical corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone cream to alleviate symptoms. In severe cases, oral corticosteroids might be necessary to manage inflammation effectively.
Hydration plays a key role in recovery. Drink plenty of fluids to help flush allergens from your system. Gentle skin care is essential; use mild soap and moisturizers to protect and soothe the affected areas.
| Treatment | Form | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Antihistamines | Oral | As needed for itching |
| Corticosteroid Cream | Topical | Apply to rash 1-2 times daily |
| Corticosteroids | Oral | Short course for severe cases |
| Moisturizers | Topical | Apply regularly to soothe skin |
Monitor any changes in your condition. If symptoms worsen, seek immediate medical attention. Keeping a record of all medications and any allergic reactions can help healthcare providers select safe alternatives in the future.
Preventing Reactions to Amoxicillin
Consult your healthcare provider before starting amoxicillin, especially if you have a history of allergies to penicillin or other medications. Discuss alternative antibiotics if you are known to have such allergies.
Inform your doctor about any other medications, supplements, or herbal products you are taking. This helps prevent potential interactions that could increase the risk of allergic reactions.
Always follow the prescribed dosage and schedule. Taking excessive amounts can heighten the chance of side effects, including allergic reactions.
Keep an eye out for any unusual symptoms after starting amoxicillin. Symptoms like rash, itching, or swelling should be reported to your doctor immediately. Early detection aids in managing side effects effectively.
Consider requesting allergy testing if you suspect a sensitivity to amoxicillin or related antibiotics. Knowing your specific allergies can help guide your treatment plan and avoid future reactions.
Maintain an updated list of all your allergies and medications. Share this information with your healthcare providers to ensure safe prescribing practices.
If you experience an allergic reaction, seek medical attention without delay. Having a plan in place, such as carrying an epinephrine auto-injector if prescribed, can be lifesaving.
Safe Alternatives to Amoxicillin
If you have a documented allergy to amoxicillin, consider options such as azithromycin or clarithromycin. These macrolide antibiotics effectively treat various bacterial infections without the risk of cross-reactivity for those allergic to penicillin-based medications.
Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, serves as another alternative, particularly for urinary tract infections and respiratory issues. Ensure that it is appropriate for your specific condition, as its usage can depend on bacterial resistance patterns.
Doxycycline, a tetracycline antibiotic, is useful for infections like pneumonia and certain skin conditions. This option is generally well-tolerated in individuals allergic to penicillin.
For more localized infections, topical antibiotics such as bacitracin and mupirocin can treat skin infections without systemic effects.
Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable alternative based on your health history and specific infection type. They can help monitor closely for any adverse reactions and ensure the chosen antibiotic meets your needs.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience a rash after taking amoxicillin, contact a healthcare provider immediately. Rash severity can vary, and some reactions may develop into more serious conditions.
Watch for Serious Symptoms
Seek medical help if you notice swelling of the face, lips, or tongue. Difficulty breathing or swallowing requires urgent attention. Red, blistering, or peeling skin may indicate a severe reaction, demanding prompt evaluation.
Follow Up on Persistent Symptoms
If the rash does not improve within a few days or worsens, revisit your healthcare provider. Persistent symptoms can signal complications or indicate the need for alternative treatments.
Always prioritize your health and safety by recognizing warning signs and responding swiftly.
Long-term Management of Antibiotic Allergies
Identify and document any antibiotic allergies in medical records. Ensure that all healthcare providers are aware of these allergies to prevent prescriptions of unsafe medications.
Consider allergy testing if the reaction was unclear or if you need to take an antibiotic. Consult with an allergist about the possibility of skin testing or graded drug challenges, which can help clarify your allergic status.
Maintain an up-to-date list of all medications, noting specific reactions to each. Carry an allergy alert card and wear a medical alert bracelet. This information aids healthcare professionals in emergencies.
Explore alternatives whenever antibiotics are necessary. Discuss with your healthcare provider about non-allergic options that can effectively treat infections without risking an allergic reaction.
Educate yourself about the signs of allergic reactions. Recognizing symptoms early can facilitate prompt treatment. This knowledge also helps you to respond quickly in case of an accidental exposure.
Regularly review your allergy status with your healthcare provider. As time passes, your allergic reactions may change, and it’s vital to stay informed about your current health condition.
Advocate for your health by engaging in conversations with doctors about antibiotic use. Foster open communication to ensure you receive appropriate treatments that do not pose a risk of allergy.
Continuously research your antibiotic allergies, as new information and treatment options become available. Staying informed empowers you to make wise decisions regarding your health care.