Obtaining amoxicillin without a prescription can be tempting, especially for those seeking quick relief from bacterial infections. However, understanding the implications and risks involved is essential. Over-the-counter access to this antibiotic is limited in many regions, and using it without proper medical guidance can lead to misuse or adverse reactions.
Before considering purchasing amoxicillin without a prescription, consult with a healthcare provider. They can assess symptoms and determine if this antibiotic is appropriate for your specific condition. A thorough medical evaluation ensures that the treatment is safe and effective, reducing the risk of complications.
For those in urgent need, some online pharmacies claim to offer amoxicillin without a prescription. Exercise caution when navigating these options. Verify the legality and credibility of the pharmacy. Counterfeit medications can pose serious health risks, so always prioritize obtaining medications from reputable sources.
Ultimately, knowing when and how to use amoxicillin is crucial. Self-treating infections without professional advice can lead to antibiotic resistance and other health issues. Always prioritize your health by seeking professional medical recommendations before proceeding.
- Amoxicillin Without a Prescription
- Understanding Amoxicillin: Uses and Benefits
- Uses of Amoxicillin
- Benefits of Amoxicillin
- Risks and Consequences of Using Amoxicillin Without a Prescription
- Legal Status of Amoxicillin in Different Countries
- United States
- European Union
- Table of Global Legal Status
- Symptoms That May Require Amoxicillin Treatment
- Sinus Infection Symptoms
- Ear Infections
- Alternatives to Amoxicillin for Common Infections
- Safe Practices When Acquiring Medication Without a Prescription
Amoxicillin Without a Prescription
Amoxicillin is often sought after for treating bacterial infections. It’s crucial to use this antibiotic responsibly. Purchasing it without a prescription can pose risks, including incorrect dosage, inappropriate use, and the chance of developing antibiotic resistance.
Consult a healthcare professional before taking amoxicillin. They evaluate symptoms and decide if it’s the right choice. Self-diagnosis can lead to using antibiotics for viral infections, for which amoxicillin is ineffective.
If you do have a prescription, follow the dosage instructions carefully. Taking the full course is important, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. Stopping early can allow bacteria to survive and become resistant.
For those considering online pharmacies, ensure they are reputable and require prescriptions. Verify their legitimacy through regulatory bodies. This step protects against counterfeit medications that could be harmful.
Stay informed about side effects, which can include gastrointestinal issues, rash, or allergic reactions. If any severe reactions occur, seek immediate medical attention.
Informed decisions lead to safer outcomes when considering amoxicillin or any antibiotic. Prioritize your health by consulting qualified professionals.
Understanding Amoxicillin: Uses and Benefits
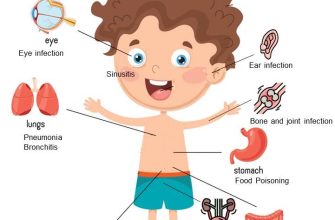
Amoxicillin is widely prescribed to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, ear infections, and urinary tract infections. It belongs to the penicillin group of antibiotics and works by stopping the growth of bacteria. This medication is particularly effective against specific strains of bacteria that are responsible for these common infections.
Uses of Amoxicillin
Physicians commonly recommend amoxicillin for:
1. Pneumonia: It helps combat bacterial pneumonia effectively.
2. Bronchitis: It is useful in treating acute bronchitis caused by bacterial infections.
3. Sinusitis: Amoxicillin provides relief from symptoms of bacterial sinus infections.
4. Ear Infections: It is often the first choice for managing otitis media in children.
5. Skin Infections: Amoxicillin addresses certain skin and soft tissue infections caused by susceptible bacteria.
Benefits of Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin offers several benefits that contribute to its popularity:
1. Broad Spectrum Activity: It is effective against a wide range of bacteria, making it a versatile choice.
2. Oral Administration: Available in various forms, including tablets and liquid, it is easy to take, especially for children.
3. Minimal Side Effects: Most individuals experience few side effects, which are typically mild and manageable.
4. Cost-Effective: Generally, amoxicillin is affordable compared to other antibiotics, increasing accessibility for patients.
5. Rapid Action: Patients often notice improvement in symptoms within a few days of starting treatment.
Consult a healthcare provider before using amoxicillin without a prescription to ensure it is the appropriate treatment for your condition.
Risks and Consequences of Using Amoxicillin Without a Prescription
Using amoxicillin without a prescription can lead to significant health risks. Self-diagnosing a bacterial infection might result in treating a viral illness, where antibiotics like amoxicillin are ineffective. This misuse can delay appropriate treatment, worsening your condition.
Without medical guidance, dosage might be incorrect. Taking too high a dose can cause harmful side effects, including gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Conversely, a low dose may not adequately address the infection, leading to resistance. Antibiotic resistance complicates future treatments, making common infections harder to treat.
Allergies to amoxicillin can occur, sometimes resulting in severe reactions like hives or anaphylaxis. If patients are unaware of their allergy status, they risk serious health complications. Consulting a healthcare provider ensures safety and appropriate use of antibiotics.
Using amoxicillin without proper indication might also disrupt your gut microbiome. This disruption can lead to conditions such as yeast infections or Clostridium difficile infections, which can be severe and difficult to treat.
Additionally, acquiring amoxicillin without a prescription raises legal concerns. Purchasing medication in this manner is typically against regulations in many countries. This practice not only endangers personal health but can also have broader public health implications by contributing to antibiotic resistance.
Consult healthcare professionals for diagnostic clarity and appropriate treatment options. Taking responsible steps ensures both personal health and community well-being.
Legal Status of Amoxicillin in Different Countries
Amoxicillin’s availability without a prescription varies significantly across countries. Understanding the legal status is crucial for safe use and access to this antibiotic.
United States
In the U.S., amoxicillin is classified as a prescription medication. Patients must obtain a prescription from a licensed healthcare provider. This regulation helps ensure appropriate use and minimizes the risk of antibiotic resistance.
European Union
In most EU countries, amoxicillin also requires a prescription. However, some countries have provisions for over-the-counter availability in specific pharmacies. Consult local regulations for guidance.
Table of Global Legal Status
| Country | Prescription Requirement |
|---|---|
| United States | Prescription required |
| United Kingdom | Prescription required |
| Germany | Prescription required |
| Mexico | Available over-the-counter |
| India | Available over-the-counter |
Research local regulations before attempting to purchase amoxicillin, as unauthorized use can lead to health complications and contribute to resistance issues.
Symptoms That May Require Amoxicillin Treatment
Seek amoxicillin treatment if you experience persistent fever alongside a sore throat, which may indicate bacterial pharyngitis. This combination often warrants antibiotic intervention.
Sinus Infection Symptoms
Watch for symptoms like facial pain, nasal congestion, and thick yellow or green mucus. If these last more than 10 days, consult a healthcare provider about possibly using amoxicillin to treat a bacterial sinus infection.
Ear Infections
If you notice ear pain, fever, or irritability in children, this may signal an ear infection. Promptly get a medical evaluation to determine if amoxicillin is needed to clear the infection.
For any unusual symptoms, including skin rashes or lingering coughs, consider consulting a healthcare professional to assess the necessity of antibiotics. Your health is best managed through proper evaluation and guidance.
Alternatives to Amoxicillin for Common Infections
Consider these alternatives for treating common infections without using amoxicillin:
- Azithromycin: Effective for respiratory infections and certain skin infections, this antibiotic works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis.
- Ciprofloxacin: A fluoroquinolone antibiotic suitable for urinary tract infections and gastrointestinal infections, it acts by blocking bacterial DNA replication.
- Doxycycline: Often prescribed for respiratory tract infections, acne, and Lyme disease, doxycycline interferes with bacterial protein synthesis.
- Clindamycin: Useful for skin and soft tissue infections, this antibiotic targets anaerobic bacteria and certain streptococcal infections.
- Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole: This combination works well for urinary tract infections and some respiratory infections by inhibiting bacterial folate synthesis.
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any medication. They will guide you on the appropriate choice based on your specific infection and medical history.
In addition to antibiotics, consider non-antibiotic options:
- Rest: Adequate sleep and relaxation support the body’s healing processes.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids helps flush out toxins and maintains bodily functions.
- Warm compresses: Applying heat can relieve localized pain or swelling in certain infections.
- Over-the-counter medications: Pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can alleviate symptoms while your body fights the infection.
Adopting a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can further aid recovery, bolstering the immune system against infections.
Safe Practices When Acquiring Medication Without a Prescription
Always consult with a healthcare professional before acquiring any medication without a prescription. They can provide guidance tailored to your specific health needs.
Consider these practices to ensure safety:
- Research the Medication: Understand the purpose, dosage, and potential side effects of the drug you are considering. Reliable sources include medical websites and health organizations.
- Check the Source: Only purchase from reputable pharmacies or online providers. Look for pharmacies that require a consultation with a pharmacist before dispensing medication.
- Verify Licensing: Ensure that the pharmacy is licensed and regulated. Check for appropriate certifications and read reviews from other customers.
- Avoid Unsolicited Offers: Be cautious of advertisements or messages promoting medications without prescriptions. Legitimate health providers do not solicit customers in this manner.
- Monitor Your Health: After taking the medication, keep track of any changes in your health. Report any adverse effects to a healthcare professional immediately.
- Stay Informed about Alternatives: Some conditions may have over-the-counter options or natural remedies that are safer and effective alternatives.
- Understand the Risks: Recognize that using medication without professional oversight can lead to complications or interactions with other medications.
Prioritize your health and well-being by approaching medication acquisition with caution and awareness. Always seek professional advice when in doubt.