For bacterial infections, amoxicillin is a commonly prescribed antibiotic. It addresses various conditions such as respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, and skin infections. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine if amoxicillin is the right choice for your specific situation. They can provide guidance on the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment.
When prescribed amoxicillin, adhere strictly to the recommended dosage instructions. Taking the full course, even if symptoms improve, helps prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Side effects may occur and can include nausea, diarrhea, or rash. Report any severe reactions to your doctor promptly.
Inform your healthcare provider about any existing medical conditions or medications you are taking. This information is crucial to avoid potential interactions and ensure amoxicillin’s effectiveness. If you experience an adverse reaction or have concerns about the prescription, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare team for advice and support.
- Amoxicillin Prescription
- Dosage Guidelines
- Consulting a Healthcare Provider
- What Is Amoxicillin and How It Works
- Mechanism of Action
- Common Uses and Dosage
- Indications for Amoxicillin Prescription
- Dosage Guidelines for Amoxicillin
- Potential Side Effects of Amoxicillin
- Common Side Effects
- Serious Reactions
- Drug Interactions to Consider with Amoxicillin
- Anticoagulants
- Other Antibiotics
- Guidelines for Amoxicillin Use in Special Populations
- Children
- Pregnant Women
- What to Do in Case of Amoxicillin Overdose
- Signs of Overdose
- First Steps at Home
- Importance of Completing the Amoxicillin Course
- Preventing Antibiotic Resistance
- Consulting Your Healthcare Provider
Amoxicillin Prescription
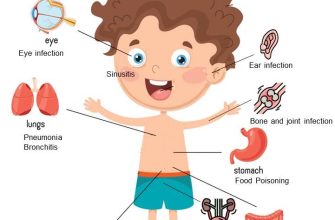
Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for various bacterial infections, including ear infections, pneumonia, and urinary tract infections. When receiving a prescription for amoxicillin, it’s crucial to follow the dosage instructions from your healthcare provider accurately. Typically, the dosage varies based on the type and severity of the infection, as well as the patient’s age and weight.
Dosage Guidelines
Adult patients usually receive 500 mg every 12 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours, depending on the infection. For pediatric patients, the dosage is generally based on the child’s weight, commonly set at 20-40 mg/kg/day divided into two or three doses. Always complete the entire course of medication, even if symptoms improve, to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance.
Consulting a Healthcare Provider
Consult your healthcare provider before starting amoxicillin if you have a history of allergies to penicillin or other antibiotics. Inform them about any other medications you are currently taking to avoid potential interactions. Regular follow-ups may be necessary to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and make any needed adjustments to the prescription.
What Is Amoxicillin and How It Works
Amoxicillin is a penicillin-type antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections. It acts by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls, leading to the destruction of the bacteria. This antibiotic is effective against a range of infections, including those of the ear, nose, throat, and urinary tract, as well as certain skin infections.
Mechanism of Action
Amoxicillin targets the enzymes responsible for building the bacterial cell wall. By blocking these enzymes, it prevents the bacteria from maintaining their structural integrity. As a result, the bacteria become unable to survive and replicate, which helps the body to eliminate the infection efficiently.
Common Uses and Dosage
Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for conditions such as strep throat, pneumonia, and bronchitis. The dosage varies depending on the specific infection and the patient’s age and weight. Generally, adults may take 250 mg to 500 mg every 8 hours. For children, the dosage is based on body weight. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for the best results.
Indications for Amoxicillin Prescription
Amoxicillin is widely prescribed for treating various bacterial infections. It is particularly effective against infections of the respiratory tract, skin, and urinary system. Here’s a detailed look at specific conditions where amoxicillin is typically recommended:
| Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Sinusitis | Amoxicillin helps alleviate symptoms of acute sinusitis caused by susceptible bacteria, relieving congestion and facial pain. |
| Otitis Media | This antibiotic is effective for middle ear infections, especially in children, targeting bacterial pathogens like Streptococcus pneumoniae. |
| Pneumonia | Amoxicillin treats mild to moderate pneumonia caused by susceptible strains, accelerating recovery time. |
| Streptococcal Pharyngitis | It is recommended for treating strep throat, which can prevent complications like rheumatic fever. |
| Skin Infections | Amoxicillin is effective in treating certain skin infections, particularly those caused by Staphylococcus aureus. |
| Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) | It is indicated for uncomplicated UTIs caused by susceptible bacteria, providing swift relief from symptoms. |
| Helicobacter pylori Eradication | In combination therapy, amoxicillin aids in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infections, which contribute to peptic ulcers. |
Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential before starting amoxicillin to ensure it is appropriate for your specific condition. Always follow prescribed dosages to maximize the benefits of this antibiotic.
Dosage Guidelines for Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin dosing hinges on the condition being treated, age, and weight of the patient. Follow these specific dosage recommendations:
- Adults:
- For most infections: 250 mg to 500 mg every 8 hours or 500 mg to 875 mg every 12 hours.
- For severe infections: Up to 1,000 mg every 8 hours may be prescribed.
- Children:
- Typically, 20 mg to 40 mg per kg of body weight per day, divided into two or three doses.
- For severe infections: 40 mg to 90 mg per kg of body weight per day, divided into two or three doses.
- Specific Conditions:
- Strep throat: 500 mg every 12 hours or 250 mg every 8 hours for 10 days.
- Pneumonia: 500 mg every 12 hours for 7 to 10 days, depending on severity.
Adjustments may be necessary for those with kidney dysfunction. Consult a healthcare professional for tailored guidance based on individual circumstances.
Complete the prescribed course, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. Skipping doses can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Potential Side Effects of Amoxicillin
Patients taking Amoxicillin may experience certain side effects. Being aware of these can help manage any reactions effectively.
Common Side Effects
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Rash
- Headache
If these side effects occur, they are usually mild and may resolve on their own. Staying hydrated can mitigate nausea and diarrhea. Consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist.
Serious Reactions
- Allergic reactions (hives, swelling, difficulty breathing)
- Severe skin reactions
- Liver problems (yellowing of skin or eyes)
- Kidney issues (changes in urine output)
Seek immediate medical attention if any serious symptoms occur. Early intervention can prevent complications. Regular check-ups can help monitor any unusual changes during treatment.
Always discuss any concerns or pre-existing conditions with your healthcare provider before starting Amoxicillin. Being proactive ensures safer use and better management of potential side effects.
Drug Interactions to Consider with Amoxicillin
Before prescribing amoxicillin, evaluate potential drug interactions that may impact treatment efficacy or increase the risk of adverse effects. Some key interactions to monitor include:
Anticoagulants
Amoxicillin can enhance the effects of anticoagulants like warfarin. Regular monitoring of INR levels is essential, as adjustments to anticoagulant dosing may be necessary during amoxicillin treatment.
Other Antibiotics
Combining amoxicillin with other antibiotics, especially bacteriostatic agents such as tetracyclines, may reduce the effectiveness of one or both medications. Assess the need for concomitant therapy carefully, and choose antibiotics with complementary mechanisms of action when necessary.
Additionally, inform patients about potential interactions with antacids containing magnesium or aluminum, as these can interfere with amoxicillin absorption. Advise taking amoxicillin at least 2 hours apart from these antacids.
Remain vigilant regarding patient medication lists and adjust treatment plans to avoid complications associated with these interactions. Prioritize patient education to empower individuals in managing their therapy effectively.
Guidelines for Amoxicillin Use in Special Populations
Prescribing amoxicillin requires careful consideration in special populations such as children, pregnant women, and individuals with renal impairment.
Children
For pediatric patients, weight-based dosing is critical. The typical dose is 20 to 40 mg/kg/day divided into two or three doses, depending on the severity of the infection. Ensure accurate weight measurement for precise dosing. For those under 3 months, any signs of infection should prompt immediate medical evaluation.
Pregnant Women
Amoxicillin is generally considered safe during pregnancy. The recommended dosage remains the same as for non-pregnant adults. Monitor for any allergic reactions or gastrointestinal disturbances more closely in this population. Review the risks and benefits of treatment with the patient, ensuring they understand any potential impacts on their pregnancy.
In individuals with renal impairment, adjust dosing based on the degree of renal dysfunction. Mild to moderate impairment may require a dose adjustment, while severe impairment calls for significant alterations and careful monitoring of drug levels in the body to avoid toxicity.
What to Do in Case of Amoxicillin Overdose
If an overdose of amoxicillin is suspected, seek immediate medical attention. Do not wait for symptoms to appear. Call your local emergency number or head to the nearest hospital.
Signs of Overdose
Watch for symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, or skin rash. In severe cases, confusion or seizures may occur. Document any symptoms and share them with medical professionals.
First Steps at Home
If you have accessible information, provide details about the dosage and time of ingestion. Do not induce vomiting unless instructed by a healthcare provider. Keep the medication label handy, as it may assist with treatment decisions.
Importance of Completing the Amoxicillin Course
Always complete the full course of Amoxicillin prescribed by your doctor, even if you start feeling better before finishing the medication. Stopping treatment prematurely can allow bacteria to survive and develop resistance to the antibiotic. This makes future infections harder to treat.
One of the main reasons for completing the course is to ensure that the infection is fully eradicated. Incomplete treatment might lead to a resurgence of symptoms and prolong recovery. Studies show that patients who adhere to their prescribed antibiotic regimens experience faster healing and a lower risk of complications.
Preventing Antibiotic Resistance
Finishing the Amoxicillin course helps combat antibiotic resistance, a growing global health threat. Resistant bacteria can lead to infections that are difficult to manage, making it critical to use antibiotics properly. By adhering to the prescribed dosage and duration, you help preserve the effectiveness of Amoxicillin for yourself and others.
Consulting Your Healthcare Provider
If you encounter side effects or have concerns about the medication, discuss these with your healthcare provider rather than discontinuing use. They may adjust your treatment while still ensuring the infection is managed effectively. Collaboration with your healthcare professional leads to better health outcomes and reduces the likelihood of recurrence.