The maximum recommended dose of amoxicillin for children is typically 50 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three doses. This means a child weighing 20 kg would receive a maximum daily dose of 1000 mg (20kg x 50mg/kg).
However, always consult your pediatrician before administering any medication to your child. They will consider your child’s specific weight, age, and overall health to determine the appropriate dosage. Factors like kidney function can influence the safe and effective amoxicillin dose. Never exceed the prescribed dosage.
Important Note: This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Severe infections may require higher doses under strict medical supervision. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Observe your child closely for any adverse reactions and contact your doctor immediately if you notice anything unusual.
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. More serious, though rare, reactions require immediate medical attention. Keeping a detailed record of your child’s medication and any observed side effects is beneficial for your doctor.
- Amoxicillin Max Dose for Pediatrics: A Detailed Guide
- Factors Influencing Amoxicillin Dosage
- Common Amoxicillin Dosages for Children (Consult your doctor for accurate dosage):
- Important Considerations:
- Calculating the Safe Amoxicillin Dose for Your Child
- Understanding Amoxicillin’s Role in Pediatric Infections
- Factors Affecting Amoxicillin Dosage in Children
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions with Amoxicillin
- Allergic Reactions
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Precautions
- Monitoring Your Child
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Amoxicillin Dosage
- Signs Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
- Dosage Adjustments and Specific Conditions
Amoxicillin Max Dose for Pediatrics: A Detailed Guide
The maximum daily dose of amoxicillin for children is generally 50 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three doses. This is a guideline, and a doctor will determine the appropriate dose based on your child’s weight, age, and the specific infection.
Factors Influencing Amoxicillin Dosage
- Weight: Dosage is calculated based on the child’s weight in kilograms.
- Age: Infants and very young children may require adjusted dosages.
- Infection Severity: More severe infections might necessitate a higher dose, under strict medical supervision.
- Kidney Function: Children with kidney problems need adjusted dosages to prevent drug accumulation.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never exceed the recommended dosage.
Common Amoxicillin Dosages for Children (Consult your doctor for accurate dosage):
- Infants (under 3 months): Dosages are carefully determined by a pediatrician based on individual needs.
- Children (3 months to 12 years): The typical dose is 25-50 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three administrations.
- Adolescents (12 years and older): The dosage usually aligns with adult recommendations (check with a doctor).
Administer amoxicillin with food to minimize stomach upset. Observe your child for any side effects, such as diarrhea, rash, or vomiting. Report any concerns to your physician immediately.
Important Considerations:
- This information serves as a general guide; it is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
- Always consult a pediatrician before administering amoxicillin to your child.
- Accurate weight measurement is crucial for precise dosage calculations.
- Keep amoxicillin out of reach of children.
This guide aims to provide helpful information. Always prioritize professional medical advice for your child’s health.
Calculating the Safe Amoxicillin Dose for Your Child
Always follow your doctor’s prescription precisely. Never adjust the dosage yourself.
The typical pediatric amoxicillin dose is 20-50 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three doses. For instance, a 20 kg child might receive 400 mg twice daily (40 mg/kg/day), or a higher dose as directed by a physician.
Accurate weight is crucial. Use a reliable scale to get your child’s weight in kilograms. Many online converters can help if you have their weight in pounds.
Your doctor will consider factors like your child’s age, weight, and the specific infection being treated when determining the appropriate dose. Severe infections may require a higher dose.
Always administer amoxicillin with food to minimize stomach upset. Follow the instructions on the prescription label carefully regarding how to administer the medication (e.g., with a spoonful of food or liquid).
If you notice any unusual side effects, such as rash, diarrhea, or vomiting, contact your doctor immediately.
Keep amoxicillin out of your child’s reach. Proper storage is also important to maintain its effectiveness. Discard any unused medication after the expiry date.
This information is for guidance only and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult your pediatrician for personalized recommendations and any concerns regarding amoxicillin dosage for your child.
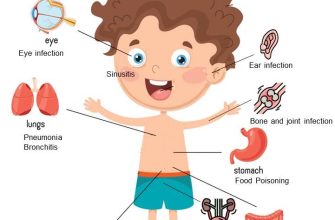
Understanding Amoxicillin’s Role in Pediatric Infections
Amoxicillin treats many common bacterial infections in children, including ear infections (otitis media), strep throat, pneumonia, and urinary tract infections. It’s a versatile antibiotic, effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria.
Doctors prescribe amoxicillin based on the suspected infection and the child’s age and weight. Accurate diagnosis is crucial; amoxicillin is ineffective against viral infections, and using it unnecessarily contributes to antibiotic resistance.
The medication is typically administered orally, in liquid or capsule form, making it easy for most children to take. Parents should always follow the dosage instructions precisely. Never adjust the dose without consulting a physician.
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and rash. Serious allergic reactions, though rare, require immediate medical attention. Parents should monitor their child closely for any unusual symptoms after starting amoxicillin.
Amoxicillin’s effectiveness can be impacted by factors such as the specific bacteria causing the infection and the child’s overall health. Sometimes, a different antibiotic might be necessary. Always discuss treatment options with your pediatrician.
Remember, responsible antibiotic use protects against resistance. Complete the full course of amoxicillin even if your child feels better before finishing the prescription. This prevents recurrence and reduces the risk of developing resistant strains.
Factors Affecting Amoxicillin Dosage in Children
A child’s weight is the primary determinant of amoxicillin dosage. Doctors typically use milligrams per kilogram (mg/kg) of body weight to calculate the appropriate dose. Accurate weight measurement is crucial for precise dosing.
The severity of the infection significantly influences the dosage. More severe infections may require higher doses administered more frequently than milder infections.
A child’s age plays a secondary role. While weight is paramount, age might inform dosage adjustments, especially in infants, who may have different metabolic rates than older children.
Renal function impacts amoxicillin clearance. Children with kidney problems may require dose adjustments to prevent drug accumulation and potential side effects. Doctors should always review kidney function tests before prescribing amoxicillin to such children.
Hepatic function, or liver function, also influences how the body processes amoxicillin. Children with liver disease might require lower doses or altered dosing schedules. Liver function tests should be reviewed before initiating amoxicillin treatment in such cases.
Any known allergies or hypersensitivities to penicillin-type antibiotics mandate careful consideration. Amoxicillin belongs to the penicillin family, and prior allergic reactions call for alternative treatments.
Concurrent medications can interact with amoxicillin, potentially affecting its efficacy or causing adverse reactions. A complete medication history must be obtained to identify potential drug interactions. This is paramount for ensuring patient safety.
Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions regarding amoxicillin dosage. Never adjust the dosage without consulting a healthcare professional.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions with Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin, while generally safe, can cause side effects. The most common are diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. These usually are mild and resolve without treatment. However, severe diarrhea could indicate Clostridium difficile infection, requiring immediate medical attention. Report persistent or severe diarrhea to your doctor.
Allergic Reactions
Amoxicillin is a penicillin antibiotic, and allergic reactions are possible. These can range from mild skin rashes to severe, life-threatening anaphylaxis. Symptoms of a serious allergic reaction include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, and hives. Seek immediate medical care if you experience any of these symptoms.
Other Potential Side Effects
Less common side effects include:
| Side Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Yeast infections (thrush) | Oral or vaginal yeast infections can occur, especially in women. |
| Headache | Mild headaches may develop. |
| Dizziness | Feeling lightheaded is a possibility. |
| Increased liver enzyme levels | Your doctor may monitor liver function tests. |
Precautions
Before starting Amoxicillin, inform your doctor about any existing medical conditions, particularly liver or kidney problems, and any allergies you have, especially penicillin allergies. Always give Amoxicillin exactly as prescribed. Do not stop the medication early, even if symptoms improve. Finish the entire course to ensure the infection is fully treated. Proper hydration is important while taking Amoxicillin. Finally, discuss any concerns with your pediatrician before administering Amoxicillin to your child.
Monitoring Your Child
Closely monitor your child for any side effects. If you have concerns, contact your pediatrician immediately. They can assess the situation and advise you on the best course of action.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Amoxicillin Dosage
Always contact your pediatrician if you have any questions or concerns about amoxicillin dosage for your child. This includes situations where your child experiences any side effects, such as rash, diarrhea, or vomiting. Don’t hesitate to call if the infection doesn’t improve within a few days of starting the medication, or if it worsens.
Signs Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention if your child exhibits any signs of allergic reaction, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or hives. Also, contact your doctor immediately if your child develops severe diarrhea, as this could indicate Clostridium difficile infection. Remember, accurate diagnosis and treatment are crucial for your child’s health.
Dosage Adjustments and Specific Conditions
Never adjust the amoxicillin dosage without consulting your doctor. Dosage depends on factors such as your child’s weight, age, and the specific infection being treated. Your doctor will consider these factors and provide tailored recommendations. They may also need to adjust the dose based on kidney or liver function.