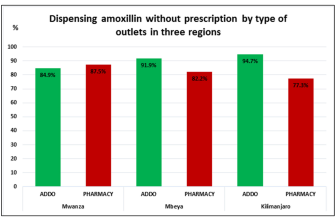
For treating dental infections, amoxicillin serves as a reliable antibiotic choice. It effectively combats bacteria responsible for various dental issues, including abscesses and periodontal diseases. Taking amoxicillin as prescribed can significantly reduce pain and swelling associated with these conditions.
Typically prescribed at a dosage of 250 to 500 mg every 8 hours, it’s crucial to adhere to your dentist’s recommendations. Always complete the full course to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance. If you experience side effects such as rashes or gastrointestinal upset, contact your healthcare provider promptly.
In specific cases, dental professionals might recommend amoxicillin before procedures for patients with certain heart conditions or a history of endocarditis. This preventive measure helps reduce the risk of infections that could arise from invasive treatments.
While amoxicillin can provide substantial benefits, it’s vital to combine its use with good dental hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing. Regular dental check-ups will ensure any emerging issues are addressed early, minimizing the need for extensive treatments.
Amoxicillin for Dental Problems
Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for dental infections and can effectively treat conditions like abscesses or periodontal disease. For adults with severe pain or swelling, a typical dosage is 500 mg every 8 hours for 7 to 10 days, depending on the severity of the infection.
Patients should take the medication as directed, completing the full course even if symptoms improve earlier. This approach helps to prevent antibiotic resistance and ensures that the infection is thoroughly addressed.
Allergies to penicillin are significant; individuals with such allergies should inform their dentist before taking amoxicillin. Alternative antibiotics may be considered in those cases. Side effects can include gastrointestinal discomfort, so consider taking the medication with food to minimize this issue.
Consulting a dentist is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. While amoxicillin alleviates infection, it does not substitute for necessary dental procedures. Regular oral hygiene and follow-up appointments will promote long-term dental health after the infection is treated.
Understanding Amoxicillin: Its Role in Dental Infections
Amoxicillin is frequently prescribed to manage dental infections due to its broad-spectrum antibacterial properties. It is particularly effective against bacteria responsible for common oral health issues, such as abscesses and periodontal disease.
Patients experiencing symptoms like swelling, pain, or pus discharge from the gums should consider consulting a dentist. If an infection is confirmed, amoxicillin may be recommended as part of the treatment plan. This antibiotic targets bacteria by inhibiting cell wall synthesis, helping to clear the infection quickly.
Here are some key points regarding amoxicillin’s use in dental infections:
- Dosing: Dosage typically depends on the severity of the infection. Standard adult dosages range from 500 mg to 875 mg taken every 12 hours. Always follow your dentist’s specific instructions.
- Duration: Treatment usually lasts 7 to 10 days. Completing the full course, even if symptoms improve, is crucial to prevent antibiotic resistance.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like nausea or diarrhea. If severe allergic reactions occur, such as rash or difficulty breathing, seek medical attention immediately.
- Interactions: Inform your dentist about any other medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid potential interactions.
It is important to acknowledge that not all dental infections require antibiotics. Your dentist will give advice based on the infection type and severity. In some cases, procedures such as drainage or tooth extraction might be necessary alongside antibiotic therapy.
Regular dental check-ups can help prevent infections and identify issues early. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash, supports overall dental health and can minimize the need for medications like amoxicillin.
Dosage Guidelines and Administration for Dental Care
The typical dosage of amoxicillin for dental issues is 500 mg every 8 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours. For children, the recommended dose is 20-40 mg/kg per day divided into two or three doses, depending on the severity of the infection. Ensure that the total daily dosage does not exceed 1,000 mg for adults and 2,000 mg for pediatric patients.
Duration of Treatment
For most dental infections, a treatment duration of 7-10 days is standard. Always consult with a dentist to confirm the proper treatment length based on the specific situation and severity of the infection. Signs of improvement often appear within a few days, but completing the entire course is essential to prevent resistance.
Administration Tips
Take amoxicillin with or without food. Swallow capsules or tablets whole with a full glass of water. If using a liquid form, shake well before measuring the dose. Adhere to the prescribed schedule, even if symptoms improve, to ensure the effectiveness of the antibiotic. If a dose is missed, take it as soon as you remember unless it is close to the next scheduled dose. Avoid doubling up on doses.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations in Dental Use
Amoxicillin, commonly prescribed for dental infections, can lead to side effects. Gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea, diarrhea, and upset stomach, are among the most reported. If you experience severe abdominal pain or persistent diarrhea, consult your dentist or healthcare provider immediately.
Allergic Reactions
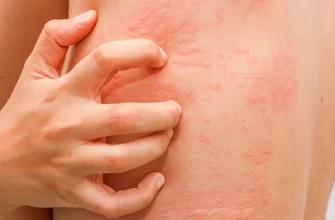
Some individuals may have allergic reactions to amoxicillin. Symptoms can range from mild rashes to more severe reactions like difficulty breathing or swelling of the face and throat. If you notice any signs of an allergic reaction, seek medical attention without delay.
Drug Interactions
Amoxicillin may interact with other medications, including anticoagulants and certain antivirals. Discuss your current medications with your dentist before starting amoxicillin to avoid potential interactions. Always inform your healthcare provider about your medical history and any ongoing treatments to ensure safe use.