For adults and children diagnosed with an ear infection, the typical dosage of Amoxicillin ranges from 250 mg to 500 mg every 8 hours, or 500 mg to 875 mg every 12 hours, depending on the severity of the infection. For children, the dosage is usually calculated based on weight, often at 20 to 40 mg per kg of body weight per day, divided into two or three doses.
Timing is crucial in administering Amoxicillin. It’s essential to complete the full course, usually lasting about 7 to 10 days, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. This approach helps to ensure that the infection is fully cleared and reduces the risk of antibiotic resistance.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it’s almost time for your next dose, skip the missed one and continue with your regular schedule. Never double up on doses to make up for a missed one.
Consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations tailored to your specific situation, especially if there are underlying health conditions or the patient is on other medications. Regular follow-ups may be necessary to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Amoxicillin Ear Infection Dosage
- Understanding Amoxicillin for Ear Infections
- Recommended Dosage Based on Age Groups
- Children Aged 6 to 12 Years
- Adults
- Dosage Adjustments for Patients with Kidney Problems
- Recommended Dosage Adjustments
- Monitoring and Recommendations
- How to Measure Amoxicillin for Accurate Dosing
- Side Effects and Precautions to Consider
- Precautions
- When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Amoxicillin Ear Infection Dosage
The typical dosage of amoxicillin for treating ear infections in children is 80 to 90 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three doses. For most adults, the usual dose ranges from 500 mg to 875 mg every 12 hours. Always adhere to the prescribing physician’s guidance, as individual circumstances may vary.
Children with a severe infection may require higher doses, potentially reaching 90 mg/kg/day. For those with recurrent ear infections, a higher daily dosage may be prescribed. It’s essential to complete the full course of amoxicillin, usually lasting 7 to 10 days, even if symptoms improve early.
For individuals with allergies to penicillin, alternatives exist. Choose the appropriate antibiotic based on medical history and sensitivity to medications. Always consult your healthcare provider when in doubt about dosage or effectiveness.
Monitor for side effects, including gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, diarrhea, or rash. If any severe reactions occur, contact a healthcare professional immediately. Adjusting dosage or switching medications might be necessary based on tolerance.
Staying hydrated and giving children fluids can help them recover faster. Combining supportive care with the right dosage enhances treatment outcomes. Ensure regular follow-ups to assess progress and further adjust treatment as needed.
Understanding Amoxicillin for Ear Infections
For treating ear infections, the typical dosage of Amoxicillin varies based on the age and weight of the patient. Generally, children receive around 20 to 40 mg/kg per day, divided into two or three doses. Adults usually take 500 mg every 12 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours, depending on the severity of the infection.
Amoxicillin targets the bacteria responsible for the infection, effectively reducing inflammation and pain. It’s crucial to complete the full course prescribed, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication, to prevent the return of the infection and resistances.
Monitor for potential side effects, including gastrointestinal issues, skin rashes, or allergic reactions. If you notice severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing or swelling, seek medical assistance immediately. Regular follow-ups after treatment can verify recovery and address any lingering concerns.
For those with a history of allergies to penicillin or other related antibiotics, informing your healthcare provider is vital before starting Amoxicillin. Alternative antibiotics may be necessary to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Stay hydrated and rest during the treatment to aid recovery. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage discomfort associated with ear infections while on Amoxicillin.
Recommended Dosage Based on Age Groups
For children aged 6 months to 2 years, the typical dosage of amoxicillin for ear infections is 20-40 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three doses. For children aged 2 to 6 years, the recommended dosage usually increases to 125 mg to 250 mg two or three times daily, depending on the severity of the infection.
Children Aged 6 to 12 Years
In this age group, the dosage can range from 250 mg to 500 mg taken two to three times a day. A healthcare provider may consider the child’s weight and the seriousness of the infection when determining the exact dose.
Adults
For adults, the standard dosage for ear infections typically is 500 mg three times daily or 875 mg twice daily. The duration of treatment generally spans from 5 to 10 days, but this may vary based on specific circumstances.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any medication. Individual needs may vary based on health conditions and other factors.
Dosage Adjustments for Patients with Kidney Problems
For patients with kidney issues, it is crucial to adjust the dosage of amoxicillin to prevent toxicity. The degree of renal impairment determines the extent of these modifications. Generally, creatinine clearance (CrCl) helps guide dosage adjustments.
Recommended Dosage Adjustments
Patients with varying degrees of kidney function should follow these guidelines:
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | Amoxicillin Dosage |
|---|---|
| ≥ 30 | Standard dosage: 500 mg every 8 hours |
| 10 – 29 | 250 mg every 12 hours |
| < 10 | Consult a healthcare provider; consider an alternative |
Monitoring and Recommendations
Regularly monitor renal function throughout treatment. Adjustments may be necessary based on ongoing assessments. Staying in close contact with a healthcare professional ensures that the treatment remains safe and effective for patients with compromised kidney function.
How to Measure Amoxicillin for Accurate Dosing
Use an oral syringe or a medicine spoon to ensure precise measurement of Amoxicillin. Avoid using household spoons, as they can vary greatly in size. Your pharmacist can provide an appropriate measuring tool if you don’t have one.
Check the prescribed dosage on the medication label. Dosages are often based on the patient’s weight and medical condition. Make sure to verify the concentration of the Amoxicillin solution, as this can vary between different formulations.
Before measuring, shake the bottle gently to mix the contents. Take the syringe or spoon and insert it into the liquid, drawing up the medication to the marked line indicating the correct dose. Ensure there are no air bubbles in the syringe; they can lead to an inaccurate measurement.
Administer the measured dose straight into the mouth, preferably towards the inside of the cheek for better swallowing. If the taste is unpalatable, follow with a small amount of water or juice to help wash it down.
Store Amoxicillin at room temperature, away from light and moisture, to maintain its effectiveness. Discard any unused medication after the prescribed duration, and keep track of doses to avoid missing any. Never double the dose if a dose is missed; simply continue with the next scheduled dose.
Side Effects and Precautions to Consider
Monitor for common side effects when taking amoxicillin for ear infections. These may include:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Skin rash
- Vomiting
If any severe reactions occur, seek medical attention immediately. Serious side effects may involve:
- Allergic reactions such as swelling, itching, or difficulty breathing
- Liver problems indicated by jaundice (yellowing of skin or eyes)
- Severe diarrhea due to Clostridium difficile infection
Precautions
Inform your healthcare provider about any allergies, particularly to penicillin or similar antibiotics. Discuss your complete medical history, especially regarding liver or kidney issues.
Avoid alcohol during treatment. It may increase side effects and hinder recovery. Ensure proper hydration and take the medication with or without food as prescribed.
Always complete the prescribed course, even if symptoms improve. This helps prevent antibiotic resistance.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
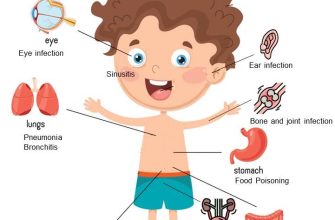
If you notice symptoms like persistent ear pain, fever, or drainage from the ear, seek medical advice. Additional signs include significant hearing loss or discomfort that lasts more than a couple of days. If symptoms worsen despite taking amoxicillin, it’s crucial to reach out to your healthcare provider.
Children experiencing difficulty sleeping or increased irritability due to ear discomfort should be evaluated. Monitor for any allergic reactions, such as rash or swelling, after starting amoxicillin, and contact a healthcare professional immediately if these occur.
Consult a provider if you have underlying health conditions or if the ear infection recurs frequently. Pregnant individuals should also discuss any treatment plans with their healthcare provider to ensure safety for both mother and child.
Don’t overlook signs of complications such as severe headache, neck stiffness, or balance issues, as these may indicate a more serious condition requiring urgent care. Prioritizing your health will lead to a more effective recovery.