Taking 1000 mg of amoxicillin is a common prescription for treating various bacterial infections. This dosage helps ensure effective penetration into the body, maximizing the antibiotic’s ability to combat pathogens. If prescribed this amount, follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully, as they tailored the dosage based on your specific condition.
Amoxicillin works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, causing the bacteria to die. It is commonly used for infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and urinary tract infections. Always complete the full course, even if symptoms improve, to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance.
Be mindful of potential side effects, which may include gastrointestinal disturbances, skin rashes, or allergic reactions. If you experience severe reactions like difficulty breathing or swelling, seek medical attention immediately. Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet can help mitigate some discomfort during treatment.
Before starting amoxicillin, inform your doctor about any other medications you are taking, as interactions can occur. If you have a history of allergies to penicillin or other related antibiotics, it’s crucial to mention this as well. Your healthcare provider may recommend alternatives to ensure your safety while effectively treating your infection.
- Understanding 1000 mg of Amoxicillin
- Dosage Instructions
- Side Effects and Precautions
- What Is Amoxicillin and Its Common Uses?
- Dosing Guidelines for 1000 mg of Amoxicillin
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of 1000 mg Amoxicillin
- Tips for Maximizing the Effectiveness of Amoxicillin
- Timing and Dosage
- Hydration and Nutrition
Understanding 1000 mg of Amoxicillin
Taking 1000 mg of amoxicillin is typically recommended for treating specific bacterial infections. This dosage is usually prescribed when healthcare professionals determine that the infection requires a stronger intervention, often for conditions like pneumonia, ear infections, or skin infections.
Dosage Instructions
Always follow the prescribed dosage from your healthcare provider. The standard course lasts about 7 to 10 days, taken every 8 to 12 hours. Consistency is key; take your doses at evenly spaced intervals to maintain effective drug levels in your system. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, skip it if the next scheduled dose is near. Avoid doubling doses.
Side Effects and Precautions
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and rash. If you experience severe reactions like difficulty breathing or swelling, seek medical attention immediately. Inform your doctor about any allergies or current medications to avoid adverse interactions. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should discuss risks and benefits with their healthcare provider before starting amoxicillin.
What Is Amoxicillin and Its Common Uses?
Amoxicillin is a penicillin antibiotic that fights bacteria in the body. It works by inhibiting the growth of bacterial cell walls, leading to their destruction. This medication treats a variety of infections, making it a common choice among healthcare providers.
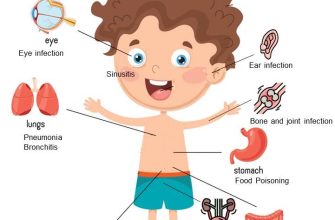
Common uses of amoxicillin include treating:
- Ear infections: Particularly effective against otitis media in children.
- Sinus infections: Helps alleviate symptoms of sinusitis caused by bacteria.
- Throat infections: Frequently prescribed for strep throat.
- Respiratory infections: Used for pneumonia and bronchitis, addressing various bacterial strains.
- Urinary tract infections: Effective in treating UTIs and preventing complications.
- Skin infections: Works well against certain bacterial skin infections.
Healthcare providers may also prescribe amoxicillin for dental infections or as part of a combination therapy for more complicated infections. Always follow your healthcare professional’s instructions regarding dosage and duration to ensure optimal results and minimize resistance development.
While generally well-tolerated, users should be aware of potential side effects, including nausea, diarrhea, or allergic reactions. Consult a healthcare provider if any unusual symptoms arise or if there’s a history of penicillin allergies.
Dosing Guidelines for 1000 mg of Amoxicillin
The standard adult dosage for amoxicillin is typically 1000 mg taken every 12 hours or 500 mg every 8 hours, depending on the infection being treated. For patients with more severe infections, a healthcare provider might prescribe a higher frequency of 1000 mg every 8 hours.
For pediatric patients, dosing is generally based on weight. The typical recommendation is 20 to 40 mg per kg of body weight per day, divided into two or three doses. For more severe infections, dosages may increase to 45 mg per kg, rounded to the nearest available formulation.
Patients with renal impairment need adjusted doses. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for specific modifications based on individual kidney function. Monitoring for potential side effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances and allergic reactions, remains crucial during treatment.
When considering duration, mild infections usually require 5 to 7 days of treatment, while more severe or complicated infections may necessitate a course of 10 to 14 days. Always follow the prescribed course even if symptoms improve before completion.
To ensure optimal absorption, amoxicillin can be taken with or without food. Drinking a full glass of water with each dose helps maintain hydration and aids in medication effectiveness.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of 1000 mg Amoxicillin
Taking 1000 mg of amoxicillin may lead to specific side effects. Recognizing these can help manage any potential risks effectively.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Commonly reported effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Staying hydrated can alleviate some discomfort.
- Allergic Reactions: Skin rashes, itching, and swelling can occur. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing or swelling of the face or throat.
- Superinfection: Prolonged use may lead to overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms, such as fungus or bacteria. Monitor for new symptoms if treatment exceeds recommended duration.
Healthcare providers usually weigh the benefits against potential risks before prescribing. Always follow dosage instructions closely to minimize side effects.
- Drug Interactions: Inform your physician of all medications and supplements being taken. This can help prevent adverse interactions.
- Kidney Health: Amoxicillin is excreted through the kidneys. Patients with renal impairment should be monitored closely during treatment.
Reporting unusual symptoms to a healthcare provider ensures timely intervention. Regular check-ins can optimize treatment outcomes while minimizing risks. Prioritize understanding your body’s responses and stay informed about any changes during your course of treatment.
Tips for Maximizing the Effectiveness of Amoxicillin
Take amoxicillin exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Stick to the recommended dosage and duration to achieve the best outcome. Missing doses can reduce the drug’s efficacy and may lead to antibiotic resistance.
Timing and Dosage
Maintain regular intervals between doses. If you need to take amoxicillin every 8 hours, set reminders to ensure that you do not forget a dose. Consistent blood levels of the medication enhance its effectiveness against bacterial infections.
Hydration and Nutrition
Stay well-hydrated while on amoxicillin. Water assists in metabolizing the medication and flushing toxins from your body. Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports your immune system during treatment.
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Adhere to Prescriptions | Follow your healthcare provider’s directions closely. |
| Regular Schedule | Keep a consistent dosing schedule to maintain effective levels. |
| Stay Hydrated | Drink plenty of water to help with the medication’s absorption. |
| Healthy Diet | Consume a balanced diet to support your body. |
Avoid combining amoxicillin with alcohol unless your doctor advises otherwise, as alcohol can interfere with the medication’s action and increase the risk of side effects.
Report any side effects to your healthcare provider immediately. Prompt communication can lead to adjustments in therapy if needed, ensuring your treatment stays on track.
Storing amoxicillin correctly is also important. Keep it at room temperature, away from moisture and heat, to preserve its effectiveness throughout the treatment period.