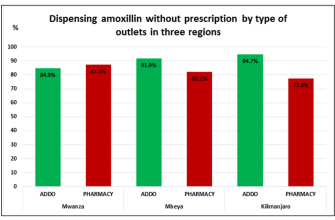
For individuals diagnosed with bacterial infections, amoxicillin often serves as a primary treatment option. As a widely prescribed antibiotic, it’s crucial to adhere to the dosage and duration outlined by your healthcare provider. Typically, the standard dosage for adults ranges from 250 mg to 500 mg every 8 hours, or 500 mg to 875 mg every 12 hours, depending on the severity and type of infection.
Do not skip doses or stop taking amoxicillin, even if symptoms improve. Completing the full course is essential to prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. If you experience side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, or an allergic reaction, contact your doctor promptly for guidance.
For pediatric patients, the dosage is usually determined by weight, generally calculated at 20 to 40 mg/kg per day, divided into two or three doses. Always use the measuring device provided to ensure accuracy. Keep an open channel of communication with your healthcare provider about any questions regarding treatment, as they can offer tailored advice based on individual health needs.
- Prescription for Amoxicillin
- Understanding Amoxicillin: Uses and Benefits
- Dosage Guidelines for Amoxicillin Prescription
- Dosage for Children
- Duration of Treatment
- Potential Side Effects of Amoxicillin
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Key Drug Interactions
- Monitoring and Advice
- Patient Considerations Before Taking Amoxicillin
- Current Medications
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Best Practices for Taking Amoxicillin
Prescription for Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for various bacterial infections, including pneumonia, bronchitis, and throat infections. The standard adult dosage typically ranges from 250 mg to 500 mg every eight hours, or 500 mg to 875 mg every twelve hours, depending on the severity of the infection.
For children, the dosage is calculated based on weight, generally around 20 to 40 mg per kg of body weight per day, divided into two or three doses. Always ensure to use a proper measuring device for liquid formulations to achieve accurate dosing.
Complete the entire course of amoxicillin, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. This practice helps prevent antibiotic resistance. It’s crucial to avoid self-medication and use amoxicillin only under a doctor’s supervision to ensure its suitability for your specific condition.
Side effects can occur, such as nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. Contact a healthcare provider if you experience severe side effects or signs of an allergic reaction, including rash, itching, or difficulty breathing.
Drink plenty of fluids during treatment to stay hydrated. Store amoxicillin in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight, and keep it out of reach of children. Regularly check expiration dates and dispose of expired medications responsibly.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting or stopping any medication, including amoxicillin, and inform them of any other medications or supplements you’re taking to prevent potential interactions.
Understanding Amoxicillin: Uses and Benefits
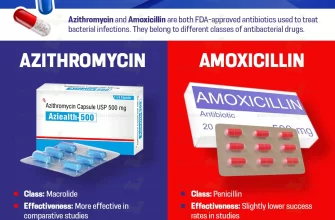
Amoxicillin treats a variety of bacterial infections effectively. It combats infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and infections in the ears, nose, and throat. Users often benefit from its broad spectrum, making it suitable for many common ailments.
This antibiotic targets specific bacteria, inhibiting their growth and replication. For those suffering from strep throat or urinary tract infections, amoxicillin offers a reliable solution. Doctors commonly prescribe it due to its well-established efficacy and relatively low risk of adverse effects.
Amoxicillin is popular in pediatric care, often utilized for infections in children because of its safety profile. It poses minimal gastrointestinal disturbances compared to some alternatives, making it easier for younger patients to tolerate.
In dental procedures, amoxicillin can prevent infections, serving as a precautionary measure, especially in patients with compromised immune systems. It plays a critical role in post-surgical care, reducing recovery time and complications.
For many, amoxicillin represents an accessible treatment option. It is typically available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and liquid suspensions, allowing for tailored dosing. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions to ensure optimal outcomes and reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Regular follow-ups and open communication with healthcare professionals help monitor the effectiveness of treatment and any potential side effects. By understanding how amoxicillin works and its applications, patients can better manage their health with this powerful antibiotic.
Dosage Guidelines for Amoxicillin Prescription
The typical adult dosage of amoxicillin for common infections, such as pneumonia or urinary tract infections, is 500 mg every 12 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours for more severe infections. For mild infections, 250 mg every 8 hours may be sufficient. Be sure to adjust dosages for patients with renal impairment, as dosage reduction might be necessary based on the degree of kidney function.
Dosage for Children
In pediatric cases, the recommended dosage is based on the child’s weight. A common guideline is 20-40 mg per kg of body weight per day, divided into two or three doses. For severe infections, dosing may increase up to 90 mg per kg per day. Always measure doses accurately and consult weight-based dosing charts for precision.
Duration of Treatment
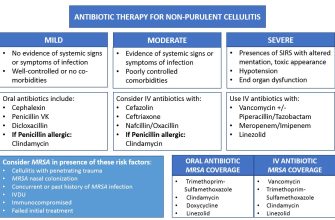
The treatment duration typically lasts from 5 to 14 days, depending on the type and severity of the infection. Strep throat may require about 10 days of therapy, while otitis media might be treated for 7 days. Monitor the patient’s response and adjust as needed.
Potential Side Effects of Amoxicillin
Take note of the potential side effects associated with amoxicillin. While many individuals tolerate this antibiotic well, some may experience adverse reactions. Understanding these effects ensures that you can respond appropriately if they occur.
- Gastrointestinal Issues:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
These are common and might be mild. Staying hydrated can help manage these symptoms.
- Allergic Reactions:
Some individuals may develop allergic responses, which can include:
- Rash or hives
- Itching
- Swelling, particularly of the face or throat
If you notice any of these signs, seek medical attention immediately.
- Skin Reactions:
In rare cases, some may develop severe skin reactions, such as:
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
Notify your healthcare provider if you experience any significant skin changes.
- Effects on Liver:
Though uncommon, elevated liver enzymes can occur. Symptoms may include:
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes
- Dark urine
Report these symptoms to a doctor promptly.
- Changes in Blood Cell Counts:
Rarely, amoxicillin can affect blood cell counts, leading to:
- Leukopenia (low white blood cells)
- Eosinophilia (high eosinophils)
A blood test may help monitor this.
Always consult your healthcare provider if you have concerns about side effects. They can provide guidance tailored to your situation and determine if amoxicillin is the right choice for you.
Interactions with Other Medications
Amoxicillin can interact with several medications, which may alter its effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects. It is crucial to consult a healthcare provider before starting amoxicillin, especially if you are currently taking other medications.
Key Drug Interactions
Here are some notable interactions to be aware of:
| Medication | Effect of Interaction |
|---|---|
| Probenecid | Increases amoxicillin levels in the blood, enhancing its effects. |
| Anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin) | May enhance the anticoagulant effects and increase bleeding risk. |
| Oral contraceptives | Potential reduction in effectiveness of birth control, leading to unintended pregnancy. |
| Other antibiotics (e.g., tetracyclines) | May interfere with amoxicillin’s activity; avoid concurrent use without guidance. |
Monitoring and Advice
When using amoxicillin alongside any medication, monitor for unusual symptoms. Report any changes to your healthcare provider. Adjustments may be necessary to ensure safety and efficacy. Always disclose all medications, herbal supplements, and over-the-counter products to your doctor to avoid interactions.
Patient Considerations Before Taking Amoxicillin
Inform your healthcare provider about any allergies, especially to penicillins or cephalosporins. If you have a history of allergic reactions, discuss these with your doctor, as an alternative antibiotic may be necessary.
Consider your medical history. Conditions like asthma, liver disease, or kidney problems can influence how your body processes this medication. Your doctor may need to adjust your dosage or monitor you closely.
Current Medications
Provide a complete list of all medications and supplements you are currently taking. Some drugs can interact with amoxicillin, affecting its effectiveness or leading to increased side effects. Pay close attention to blood thinners, other antibiotics, and certain antifungals.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Notify your healthcare provider if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding. Amoxicillin is generally considered safe during pregnancy, but your doctor will assess the benefits against any potential risks to ensure the best outcome for both you and your baby.
Best Practices for Taking Amoxicillin
Take amoxicillin exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Follow the dosage instructions carefully, including the frequency and duration of the treatment. Skipping doses can allow bacteria to continue to grow, which may lead to resistance.
Make sure to finish the entire course, even if you start feeling better. Stopping early can result in the infection returning or not fully clearing. Always check with your doctor if you’re unsure about the duration.
Space dosages evenly throughout the day. For example, if taking it three times a day, aim for every 8 hours. This helps maintain consistent levels of the medication in your system.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it’s almost time for the next dose, skip the missed one and continue with your regular schedule. Do not double up to make up for a missed dose.
Store amoxicillin at room temperature, away from light and moisture. Keep it out of reach of children. Dispose of any unused medication properly, following local guidelines.
Stay hydrated while using amoxicillin, as this can help your body flush out potential side effects. Monitor for any adverse reactions and report them to your healthcare provider.
Avoid alcohol while taking amoxicillin, as it could interfere with your recovery. Additionally, consult your doctor before combining it with other medications or supplements to prevent interactions.