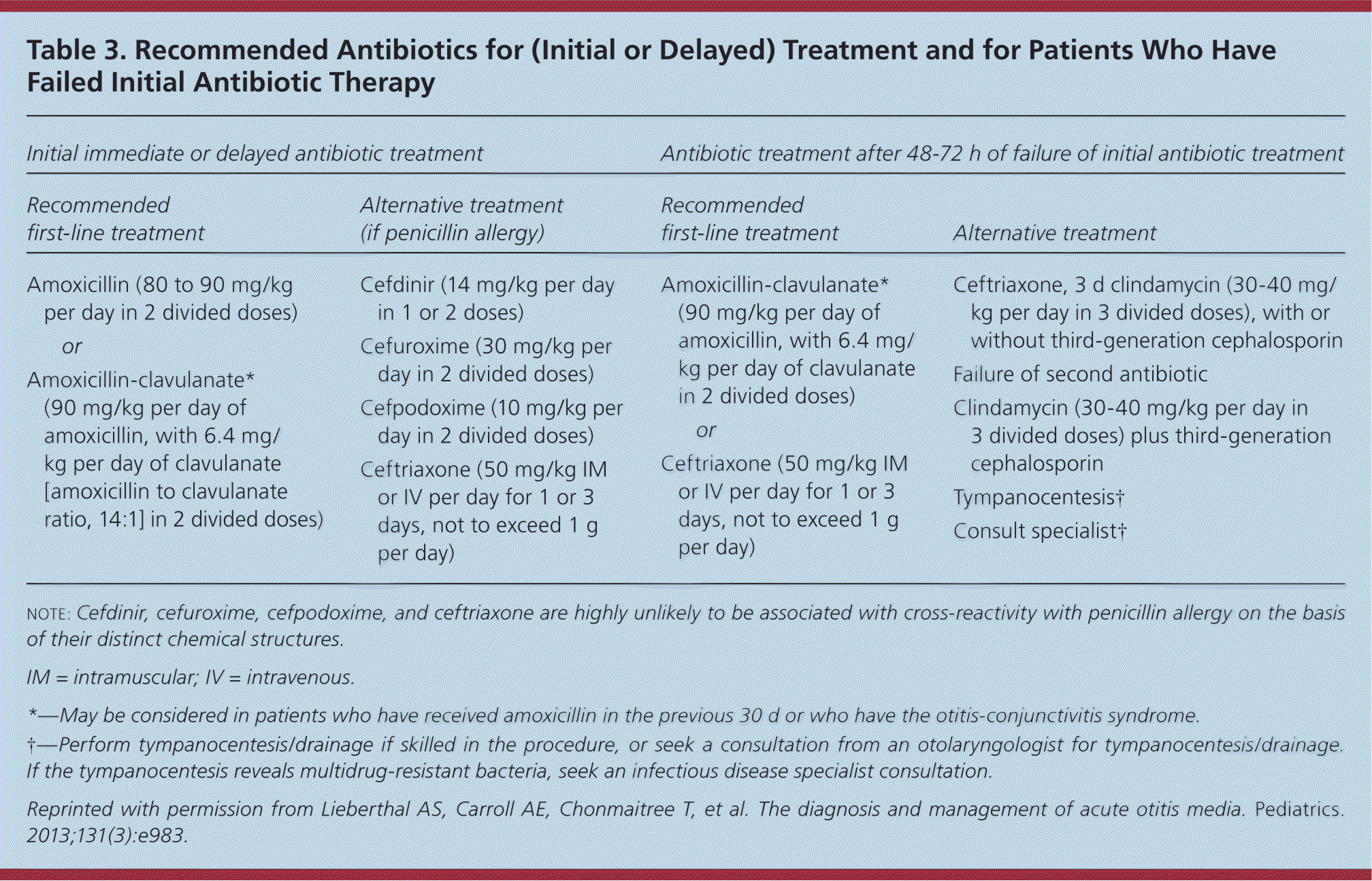
For those dealing with otitis media, amoxicillin serves as a reliable antibiotic choice. This medication effectively targets the bacterial pathogens commonly responsible for middle ear infections, leading to a prompt resolution of symptoms in many cases.
Typically prescribed for children, amoxicillin has shown a strong track record in treating otitis media. Dosage can vary based on age and weight, so consulting with a healthcare professional ensures the right amount tailored to individual needs. The most common course lasts around 5 to 10 days, but the specific duration depends on the severity of the infection.
While amoxicillin is generally well-tolerated, some side effects may occur, including gastrointestinal disturbances. Parents should monitor their children for any adverse reactions and communicate with their healthcare provider for guidance. Maintaining open dialogue allows for adjustments in treatment if necessary.
In cases where symptoms persist despite antibiotic therapy, a follow-up appointment may be needed to reassess the condition. Additional interventions, such as further diagnostic tests or a different antibiotic, can be considered to ensure effective management of the infection.
- Understanding Otitis Media and the Role of Amoxicillin
- How Amoxicillin Works
- Dosage and Administration
- Definition and Types of Otitis Media
- Types of Otitis Media
- Symptoms and Diagnosis of Otitis Media
- Amoxicillin: Mechanism of Action Against Otitis Media
- Spectrum of Activity
- Dosing Considerations
- Dosage Guidelines for Amoxicillin in Otitis Media Treatment
- Duration of Therapy
- Adjustments for Specific Populations
- Possible Side Effects and Precautions of Amoxicillin
- Alternative Treatments for Otitis Media in Case of Amoxicillin Resistance
- Home Remedies
- Alternative Medications
Understanding Otitis Media and the Role of Amoxicillin
Otitis media, an infection or inflammation of the middle ear, often requires prompt medical attention. Symptoms include ear pain, irritability in children, fever, and sometimes drainage from the ear. For many cases, especially those caused by bacteria, amoxicillin serves as the first-line antibiotic treatment. It effectively targets the bacteria responsible for the infection, promoting faster recovery and alleviating symptoms.
How Amoxicillin Works
Amoxicillin belongs to the penicillin class of antibiotics. It works by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis, ultimately leading to the death of the bacteria. When prescribed for otitis media, it significantly reduces pain and inflammation within a short period. It’s commonly used for children due to its safety profile and palatable formulations, making it easier for parents to administer.
Dosage and Administration
Dosage of amoxicillin for treating otitis media is typically based on the child’s age and weight. It’s critical to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms resolve early, to prevent recurrence and antibiotic resistance. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider ensures the infection is adequately managed. Always consult with a healthcare professional for the best course of action regarding symptoms and treatment options.
Definition and Types of Otitis Media
Otitis media refers to inflammation or infection of the middle ear. This condition is common in children, often linked to upper respiratory infections. Understanding the types can aid in effective management and treatment.
Types of Otitis Media
- Acute Otitis Media (AOM): This type occurs suddenly and is characterized by rapid onset of ear pain and fever. It usually follows a cold and can resolve quickly with or without antibiotics.
- Chronic Otitis Media (COM): Defined by persistent fluid in the middle ear lasting more than three months. This type can lead to hearing loss and may require surgical intervention.
- Otitis Media with Effusion (OME): In this case, fluid accumulates in the middle ear without infection. It often follows AOM and can impact hearing temporarily.
Promptly addressing symptoms can lead to better outcomes, especially in children who are at higher risk for complications. Consult a healthcare provider for tailored advice and treatment options.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Otitis Media
Common symptoms of otitis media include ear pain, fluid drainage from the ear, and hearing loss. Children may exhibit irritability, difficulty sleeping, or a reduced appetite. Keep an eye out for fever, which can occur alongside these signs.
For diagnosis, a healthcare provider will conduct a physical examination, often using an otoscope to visualize the eardrum. Look for signs of redness, swelling, or fluid buildup. Additional tests like tympanometry may assess the mobility of the eardrum, confirming fluid presence in the middle ear.
When symptoms persist or worsen, follow up promptly. Persistent symptoms may indicate complications or a need for further treatment options. It’s beneficial to have clear communication with your healthcare provider regarding symptoms and any changes observed.
Amoxicillin: Mechanism of Action Against Otitis Media
Amoxicillin targets bacterial infections in the middle ear effectively, making it a primary choice for treating otitis media. It inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis, which is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of bacteria. By disrupting the formation of peptidoglycan, the essential component of the bacterial cell wall, amoxicillin causes the bacteria to undergo lysis and die, alleviating infection and associated inflammation.
Spectrum of Activity
Amoxicillin is particularly effective against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae, two common pathogens associated with otitis media. The drug’s broad spectrum allows it to combat various bacterial strains, increasing its utility in diverse cases of ear infections. In cases of beta-lactamase producing bacteria, a combination with clavulanic acid may enhance its efficacy, countering potential resistance.
Dosing Considerations
The dosing of amoxicillin in otitis media typically follows weight-based recommendations, ensuring optimal therapeutic levels. Administering the medication at regular intervals maintains effective concentrations in the bloodstream, maximizing bacterial eradication. Monitoring for adverse effects like gastrointestinal disturbances is advisable, as they can occur in some patients, but overall, amoxicillin remains a well-tolerated option.
Dosage Guidelines for Amoxicillin in Otitis Media Treatment
For the treatment of otitis media in children, the recommended dosage of amoxicillin is typically 80-90 mg per kg of body weight per day, administered in divided doses. This dosage should be spread out over 24 hours, generally in two or three doses. For children weighing less than 40 kg, this translates to approximately 500 mg every 12 hours or 250 mg every 8 hours, depending on the severity of the infection.
Duration of Therapy
The usual treatment duration for uncomplicated otitis media is 7-10 days. Children under the age of 2 or those with severe infections may benefit from a full 10-day course to ensure complete recovery and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Adjustments for Specific Populations
In cases of renal impairment, amoxicillin dosage may require adjustment. Consult a healthcare provider for precise recommendations based on the patient’s kidney function. For adults with otitis media, standard dosing is usually 500 mg every 8 hours for 7 days, or as directed by a physician.
Monitor for any side effects, such as gastrointestinal issues or allergic reactions, and contact a healthcare professional if these occur. Regular follow-ups after the treatment can help ensure full resolution of the infection.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions of Amoxicillin
Patients taking amoxicillin should be aware of potential side effects and necessary precautions. Here are the common side effects you may encounter:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Rash or itching
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
If you experience severe allergic reactions, such as swelling of the face or throat, difficulty breathing, or hives, seek immediate medical attention. These symptoms may indicate anaphylaxis.
Inform your healthcare provider of any pre-existing conditions. Pay particular attention to:
- Kidney disease
- Liver disease
- Allergic reactions to antibiotics or medications
Notify your doctor about all medications you are taking. Certain interactions could enhance side effects or reduce effectiveness. Specifically, consider:
- Anticoagulants such as warfarin
- Other antibiotics
- Probenecid
Adhere strictly to the prescribed dosage to avoid complications. Avoid skipping doses. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, but skip the missed dose if it’s almost time for your next one. Do not double up to make up for a missed dose.
Avoid alcohol during treatment to minimize stomach irritation. Stay hydrated and proper rest also contribute to recovery.
Consult with your healthcare provider if side effects persist or worsen. Regular follow-up appointments can help monitor your health during treatment.
Alternative Treatments for Otitis Media in Case of Amoxicillin Resistance
Consider using a combination of supportive care and natural therapies if amoxicillin proves ineffective against otitis media. Start with pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to reduce discomfort and manage fever.
Home Remedies
Applying a warm compress to the affected ear can help alleviate pain. Heat promotes circulation and offers soothing relief. Additionally, you may explore the benefits of garlic oil or olive oil as ear drops. These natural remedies have antimicrobial properties that can provide some support in combating infection.
Alternative Medications
If antibiotic treatments are necessary, consult a healthcare professional about alternatives such as azithromycin or cephalosporins. These antibiotics can serve as effective substitutes when amoxicillin is not a viable option. Always ensure that any medication is appropriate for the specific case of otitis media, taking into account the patient’s medical history and allergies.
| Alternative Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Warm Compress | Applied to the ear to relieve pain and discomfort. |
| Garlic Oil | Possesses antimicrobial properties; can be used as ear drops. |
| Ibuprofen | Reduces pain and fever effectively. |
| Azithromycin | An alternative antibiotic for treating resistant infections. |
Consider consulting an ear, nose, and throat specialist for persistent cases. They may recommend further examination or treatments, such as tympanostomy tubes, especially in recurrent cases of otitis media. This approach provides additional possibilities for managing the condition effectively.