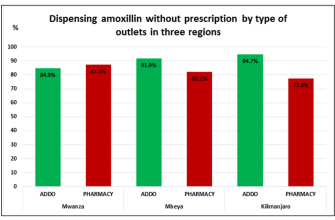
Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for chest infections, especially those caused by bacterial agents. It works by targeting the bacterial cell wall, leading to the destruction of the bacteria and alleviating infection symptoms. When dealing with conditions like pneumonia or bronchitis caused by susceptible bacteria, amoxicillin can be a strong contender for treatment.
It’s important to confirm that the infection you are experiencing is bacterial rather than viral, as antibiotics like amoxicillin have no effect on viral infections. If you suspect a chest infection, seek medical advice to receive a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment recommendations.
For effective treatment, adherence to the prescribed dosage is crucial. Patients typically take amoxicillin for 5 to 14 days, depending on the severity of the infection and the individual’s response to the medication. Always complete the full course to ensure that the bacteria are fully eliminated and to reduce the risk of developing antibiotic-resistant strains.
Consulting a healthcare professional is essential for appropriate use of amoxicillin. If symptoms persist or worsen during treatment, contact your doctor for further evaluation and management.
- Is Amoxicillin for Chest Infections?
- Understanding Chest Infections
- Role of Antibiotics in Treating Chest Infections
- What is Amoxicillin and How Does it Work?
- Mechanism of Action
- Uses in Chest Infections
- Specific Conditions Treated by Amoxicillin
- Indications for Use
- Important Considerations
- Possible Side Effects of Amoxicillin
- Guidelines for Using Amoxicillin for Chest Infections
- Identify Symptoms
- Consider Allergies and Interactions
- When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Is Amoxicillin for Chest Infections?
Amoxicillin is often prescribed for certain types of chest infections, particularly those caused by bacteria. It works effectively against pathogens such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae, common culprits in respiratory infections.
For accurate use, consider the following:
- Indications: Amoxicillin is suitable for bacterial pneumonia and bronchitis. It is less effective against viral infections.
- Dosage: A typical dosage is 500 mg every eight hours or 875 mg every twelve hours. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding the prescription.
- Duration: Treatment usually lasts 5 to 10 days, depending on the severity of the infection and individual response.
Consult a doctor for proper diagnosis before starting amoxicillin. They may perform tests to determine if a bacterial infection is present, as misuse can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Monitor for side effects, which may include:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Allergic reactions
If you experience severe symptoms or allergic reactions, seek medical attention immediately. Always complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
Amoxicillin can be a reliable option for bacterial chest infections when used appropriately. Be proactive in discussing treatment options with your healthcare provider to ensure the best approach for your situation.
Understanding Chest Infections
Chest infections, including pneumonia and bronchitis, occur when bacteria or viruses invade the lungs or airways. Symptoms often involve a persistent cough, difficulty breathing, fever, and chest pain. Timely diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent complications.
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and sometimes imaging like X-rays or CT scans to visualize lung involvement. Laboratory tests, such as sputum cultures, help identify the specific pathogen causing the infection.
Antibiotics, including amoxicillin, are prescribed for bacterial infections, whereas viral infections may require supportive care. Staying hydrated and resting significantly aid recovery. Watch for worsening symptoms or signs such as high fever, increased difficulty breathing, or chest pain, as they may indicate a need for immediate medical attention.
Prevention strategies include regular handwashing, avoiding tobacco smoke, and receiving vaccinations for influenza and pneumonia. Incorporating these practices helps reduce the risk of chest infections and supports overall respiratory health.
Role of Antibiotics in Treating Chest Infections
Antibiotics play a significant role in clearing bacterial chest infections such as pneumonia and bronchitis. When prescribed for bacterial causes, they effectively target the infection, reducing symptoms and shortening recovery time. Amoxicillin is often a first-line treatment due to its efficacy against several common pathogens.
Medical professionals recommend identifying the specific bacteria responsible for the infection when possible. This helps in selecting the most appropriate antibiotic. For many patients, a broad-spectrum antibiotic like amoxicillin can be an adequate choice, particularly if the exact pathogen isn’t determined immediately.
Patients should adhere to the prescribed dosage and duration of treatment to prevent antibiotic resistance. Stopping treatment early, even if symptoms improve, can lead to a resurgence of the infection. Regular check-ups ensure that the antibiotic is working as intended.
In cases where the infection is viral rather than bacterial, antibiotics will not help. Understanding whether the infection is caused by a virus is crucial in preventing unnecessary antibiotic use. This distinction supports overall public health by reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
In summary, the right antibiotic treatment can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with bacterial chest infections. Always consult a healthcare provider for appropriate diagnosis and treatment options tailored to individual health needs.
What is Amoxicillin and How Does it Work?
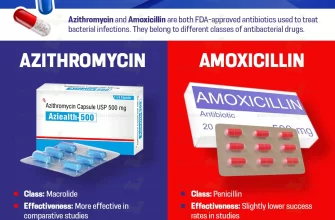
Amoxicillin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic widely used to treat bacterial infections, including those affecting the chest, such as pneumonia and bronchitis. It belongs to the penicillin class of antibiotics and operates by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls, ultimately leading to the destruction of the bacteria.
Mechanism of Action
Amoxicillin targets specific proteins, known as penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), located in the bacterial cell wall. By binding to these proteins, it prevents bacteria from forming a protective cell wall, which is crucial for their survival. This action results in cell lysis and death, effectively eliminating the infection.
Uses in Chest Infections
For chest infections, amoxicillin is often prescribed when the infection is caused by susceptible strains of bacteria. It helps reduce symptoms, improves breathing, and aids in the recovery process. When considering amoxicillin for chest infections, a healthcare provider evaluates symptoms and medical history to determine if this antibiotic is suitable.
Adhering to the prescribed dosage and duration is essential for achieving optimal results and minimizing the risk of antibiotic resistance. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable for further evaluation and potential alternative treatments.
Specific Conditions Treated by Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin serves as an effective treatment for various infections. Common conditions it targets include:
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infections: Amoxicillin effectively addresses bacterial sinusitis and otitis media, reducing symptoms and promoting recovery.
- Pneumonia: This antibiotic is often prescribed for specific bacterial pneumonia cases, aiding in clearing the infection.
- Gastrointestinal Infections: Amoxicillin plays a role in treating infections such as Helicobacter pylori, contributing to ulcer management.
- Skin Infections: For cellulitis and other bacterial skin infections, it offers a reliable treatment option.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Amoxicillin can help manage uncomplicated UTIs, alleviating discomfort and infection.
Indications for Use
Physicians commonly prescribe amoxicillin based on the identified bacterial infections. It’s vital to confirm that the infection is bacterial, as antibiotics like amoxicillin don’t treat viral infections such as the common cold or flu.
Important Considerations
- Allergies: Check for penicillin allergies before starting treatment.
- Dosage: Follow prescribed dosages for effective treatment outcomes.
- Side Effects: Be aware of potential side effects, including diarrhea and allergic reactions, and inform your doctor if they occur.
Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and effective management of specific conditions. Amoxicillin offers reliable support in combating identified bacterial infections when indicated.
Possible Side Effects of Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin may trigger some side effects. Watch for gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. These can occur in a minority of users but may affect overall comfort.
Allergic reactions are another concern. Symptoms like rash, itching, or swelling indicate a need for immediate medical attention. Severe reactions, although rare, include difficulty breathing and anaphylaxis.
Monitor for changes in liver function as indicated by yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine, or abdominal discomfort. These symptoms warrant a prompt consultation with a healthcare professional.
Some individuals might experience dizziness or headache. Generally mild, these symptoms typically resolve without intervention. Staying hydrated can help alleviate discomfort.
Establishing communication with your healthcare provider about any side effects ensures appropriate management. Regular check-ins can help you stay informed about your treatment progress and any necessary adjustments.
Guidelines for Using Amoxicillin for Chest Infections
Start treatment with amoxicillin if a bacterial chest infection is confirmed or highly suspected. The typical dosage for adults is 500 mg three times a day for 7 to 10 days. For children, the dosage is adjusted according to their weight and age, often ranging from 20 to 40 mg per kg per day, divided into two or three doses.
Identify Symptoms
Recognize common symptoms indicating a chest infection, such as persistent cough, fever, and yellow or green sputum. Consult a healthcare provider to determine whether amoxicillin is the appropriate choice based on these symptoms and overall health.
Consider Allergies and Interactions
Assess any history of allergic reactions to penicillin or other beta-lactam antibiotics before starting treatment. Inform your healthcare provider about all medications you’re currently taking to avoid potential interactions. Adjustments may be necessary depending on concurrent medications.
Monitor for side effects such as digestive issues or skin rashes. Report any severe reactions immediately. Completing the entire course of amoxicillin is crucial to ensure the infection is fully resolved, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
Review progress with your healthcare provider, especially if symptoms do not improve within a few days. They may need to reassess the diagnosis or prescribe alternative treatments. Prioritize follow-up appointments to ensure recovery and adjust treatment if necessary.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you experience persistent cough, chest pain, or difficulty breathing lasting more than a few days, seek medical advice. Early consultation can prevent complications and assist in effective treatment.
Fever above 101°F (38.3°C) that lasts more than 48 hours warrants attention. High fever may indicate a more serious infection requiring different treatment than amoxicillin.
Implement caution if you notice blood in your sputum or if your symptoms worsen after starting an antibiotic. These may signal a need for a different therapeutic approach.
Individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), should get evaluated sooner. Managing underlying health problems is crucial during any respiratory infection.
| Symptoms to Monitor | Action to Take |
|---|---|
| Persistent cough | Consult a healthcare professional |
| High fever above 101°F | Seek medical attention |
| Shortness of breath | Visit a healthcare provider |
| Blood in sputum | Contact your doctor immediately |
| Worsening symptoms | Reevaluate treatment plan with a doctor |
Always prioritize your health. Consult a healthcare professional if you’re unsure about your symptoms or treatment options. Taking action early can lead to better outcomes.