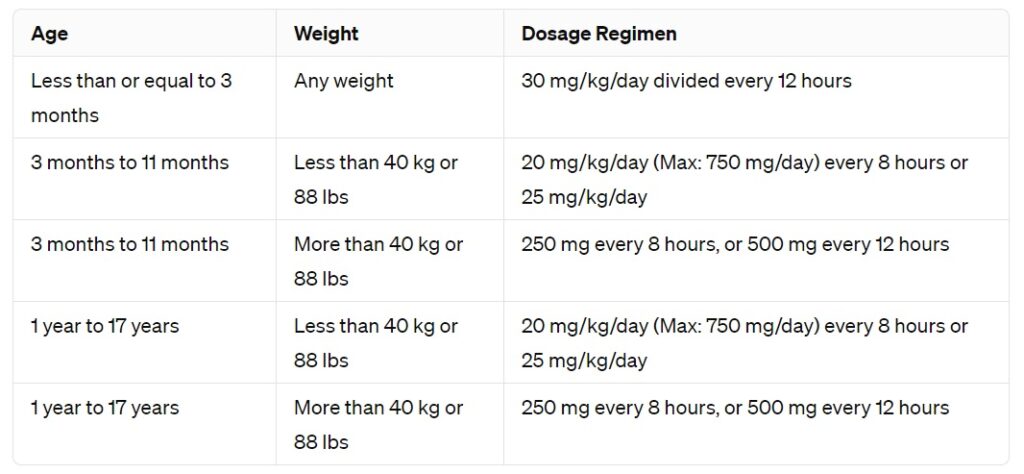
For optimal results with amoxicillin, specific dosages based on body weight enhance its effectiveness. Generally, the typical dosage for adults ranges from 250 mg to 500 mg every eight hours, while children usually receive 20 to 40 mg per kilogram of weight daily, adjusted for the severity of the infection.
Using a weight-based formula helps ensure that individuals receive an adequate amount of the medication to combat bacterial infections without risking toxicity. An example of calculation for children is amoxicillin 25 mg/kg divided into two or three doses throughout the day, depending on the doctor’s prescription.
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for precise dosage tailored to specific needs and conditions. Following recommendations closely aids in achieving the best therapeutic outcomes while minimizing side effects and risks of resistance.
- Is Amoxicillin Dosage Weight-Based?
- Recommended Dosage Guidelines
- Factors Influencing Dosage
- Understanding Amoxicillin: Uses and Mechanism
- Factors Influencing Amoxicillin Dosage
- Weight-Based Dosing for Children: Guidelines and Calculations
- Calculating Total Daily Dose
- Adjustments for Specific Conditions
- Dosage Adjustments for Adults: Considerations and Recommendations
- Common Side Effects of Amoxicillin: Dosage Implications
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Allergic Reactions
- When to Consult a Healthcare Professional about Dosage
Is Amoxicillin Dosage Weight-Based?
Yes, the dosage of amoxicillin is often based on a patient’s weight. This practice ensures that individuals receive the appropriate amount of the medication for effective treatment while minimizing the risk of side effects.
Recommended Dosage Guidelines
For children, the typical dosage of amoxicillin is calculated based on body weight:
- Standard dosing is usually 20 to 40 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three doses.
- In some cases, such as severe infections, the dosage may increase to 80 mg/kg/day.
For adults, a standard dose usually ranges from 250 mg to 500 mg every 8 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours, depending on the condition being treated.
Factors Influencing Dosage
Several factors can affect amoxicillin dosage:
- Type of infection: Different infections may require different doses.
- Patient’s health status: Existing conditions may necessitate adjustments.
- Age: Children require careful weight-based calculations.
Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage tailored to individual needs. Always adhere to prescribed guidelines for safety and efficacy.
Understanding Amoxicillin: Uses and Mechanism
Amoxicillin targets bacterial infections effectively. It functions as a penicillin-type antibiotic, disrupting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. This disruption leads to cell lysis and ultimately kills the bacteria.
Commonly, healthcare providers prescribe amoxicillin for respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, and skin infections. It also treats conditions like pneumonia and ear infections. Awareness of proper dosage is crucial for effectiveness and minimizing resistance development.
Amoxicillin works best in combination with other antibiotics or treatments for certain complicated infections, like those caused by multidrug-resistant organisms. Taking it with food can improve absorption, but strict adherence to the prescribed schedule is necessary for optimal results.
Side effects are often mild and can include nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. Monitoring for any adverse effects is important, especially in patients with a history of allergies to penicillin or related medications. In such cases, alternative treatments may be required.
Awareness of the local resistance patterns is key. If the infection does not improve within the expected timeframe, consulting a healthcare professional for reassessment and possible alternative therapy is wise. This proactive approach enhances treatment outcomes.
Factors Influencing Amoxicillin Dosage
Dosage of amoxicillin largely depends on patient weight, typically calculated at 20-40 mg/kg per day for children. Adjustments might be necessary to achieve optimal therapeutic effects while minimizing side effects.
Age plays a significant role. Pediatric patients often require lower dosages compared to adults due to variations in metabolism. It’s crucial to assess their weight accurately for precise dosing.
Infection severity directly influences required dosage. Mild infections may respond well to lower doses, while more severe infections typically necessitate higher amounts to ensure effective treatment.
Renal function also affects dosage recommendations. Patients with impaired kidney function may need dosage adjustments to prevent toxicity. Regular monitoring of renal parameters helps guide this process.
Allergic reactions to penicillins warrant careful monitoring. If a patient has a history of allergies, alternative antibiotics should be considered rather than simply adjusting the amoxicillin dose.
Concurrent medications can impact amoxicillin’s efficacy. Drug interactions may either enhance or reduce its effectiveness; thus, it’s important to review the patient’s complete medication list before prescribing.
Finally, adherence to the prescribed regimen influences outcomes. Educating patients about the importance of completing the course can prevent the development of resistant bacteria, ensuring amoxicillin remains effective for future use.
Weight-Based Dosing for Children: Guidelines and Calculations
For pediatric patients, dosing medications like amoxicillin requires careful calculation based on weight. Generally, the recommended dosage of amoxicillin for children is between 20 to 40 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three doses. This ensures the medication is both safe and effective.
Calculating Total Daily Dose
To determine the total daily dose, first weigh the child in kilograms. Multiply the child’s weight by the appropriate mg/kg dose. For instance, for a child weighing 15 kg, if the healthcare provider recommends 25 mg/kg/day, the calculation would be:
15 kg x 25 mg/kg/day = 375 mg/day
This total can be divided as needed, for example, into two doses of 187.5 mg each or three doses of 125 mg each, depending on the frequency prescribed by the doctor.
Adjustments for Specific Conditions
Certain medical conditions may necessitate adjustments to the standard dosage. For instance, in cases of severe infections, the higher end of the dosing range may apply. Always consult with a healthcare provider regarding any modifications. Additionally, be mindful of a child’s renal function, as kidney impairment can alter dosing requirements.
Regularly monitoring the child for any adverse reactions or changes in condition is essential during treatment. Keeping an accurate weight record helps in promptly adjusting dosages as needed. By adhering to these guidelines, caregivers can ensure safe and effective use of amoxicillin in pediatric patients.
Dosage Adjustments for Adults: Considerations and Recommendations
Amoxicillin dosage for adults typically ranges from 250 mg to 500 mg every 8 hours or 500 mg to 875 mg every 12 hours. Adjustments may be necessary based on specific conditions.
In patients with renal impairment, dosage should be reduced. For moderate impairment, recommend 250 mg every 12 hours or 500 mg every 24 hours. In severe cases, further decrease the dosage to 250 mg every 24 hours.
Age and body weight also influence amoxicillin dosing. For individuals weighing less than 40 kg, calculate the dosage based on body weight, typically around 20 mg/kg per day divided into two or three doses.
Monitor patients with a history of allergies to penicillin or cephalosporins closely. Adjust or avoid amoxicillin if any allergic reactions occur, regardless of the dosage.
For patients with hepatic dysfunction, consider a cautious approach. While no specific dose adjustment is recommended, continual assessment is vital to ensure patient safety.
Regularly reviewing renal function and conducting routine blood tests can guide necessary dosage adjustments. Encourage patients to report any unusual symptoms or side effects during treatment.
Consult guidelines or a pharmacist for special populations such as pregnant or breastfeeding women. Safety profiles vary, and individualized plans may enhance therapeutic outcomes.
Stay vigilant about potential drug interactions. Inform patients about the importance of disclosing all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter products.
Common Side Effects of Amoxicillin: Dosage Implications
Amoxicillin can induce several side effects, which vary in frequency and severity. Understanding the relationship between dosage and these effects is vital for safety. Common side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances, skin reactions, and potential allergic responses.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are frequently reported when taking amoxicillin. Higher doses increase the likelihood of these gastrointestinal disturbances. To mitigate these effects, take amoxicillin with food. Adjusting the dosage may also help if disturbances occur.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions may present as rashes, itching, or even more severe symptoms like difficulty breathing. Individuals with a known allergy to penicillin should avoid amoxicillin altogether. If a rash appears, consult a healthcare provider to discuss potential dosage adjustments or alternative antibiotics.
| Side Effect | Frequency | Dosage Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Nausea | Common | Consider lower doses with food |
| Diarrhea | Common | Hydration and possible dosage adjustment |
| Skin Rash | Less common | Monitor closely; reduce dose if needed |
| Allergic Reactions | Rare | Avoid use; consult if symptoms arise |
Monitoring side effects directly linked to dosage ensures a safer treatment experience. Regular consultations with healthcare providers help in managing any adverse reactions effectively.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional about Dosage
If you experience side effects such as rash, difficulty breathing, or severe stomach pain after taking amoxicillin, seek medical advice immediately. These symptoms may indicate an allergic reaction or other serious issues.
If you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning to become pregnant, discuss your amoxicillin dosage with a healthcare professional. Adjustments may be necessary to ensure safety for both you and your baby.
Consult with a doctor if you notice no improvement in your condition after a few days of treatment. They can reassess your situation and, if needed, modify your dosage or prescribe an alternative medication.
Patients with kidney problems should communicate their condition to their healthcare provider. Dosage changes may be required to prevent toxicity and ensure the medication is safe.
If you are taking other medications or have underlying health issues, discussing potential interactions is crucial. A professional can help you navigate your treatment safely.
Regular follow-up appointments during your treatment can help monitor your condition and make necessary dosage adjustments based on your progress.