Yes, amoxicillin can sometimes reduce appetite. This side effect isn’t experienced by everyone, but it’s a documented possibility. The severity varies; some individuals may only notice a slight decrease in their usual food intake, while others might experience significant appetite suppression.
Several factors influence the likelihood and intensity of this side effect. Your individual sensitivity to amoxicillin plays a crucial role. Dosage also matters; higher doses might increase the chances of appetite changes. Underlying health conditions can further impact your body’s response to the medication. If you’re concerned, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Managing appetite changes while on amoxicillin involves simple strategies. Focus on smaller, more frequent meals instead of three large ones. Opt for nutrient-rich foods that are easy to digest. Staying hydrated is also very important. If the loss of appetite is severe or persistent, seeking medical advice is recommended. Your doctor can assess the situation and adjust your treatment plan accordingly, perhaps suggesting alternative antibiotics or managing any related symptoms.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge and doesn’t substitute professional medical guidance. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice related to your medication and health status.
- Does Amoxicillin Cause Loss of Appetite?
- Amoxicillin’s Side Effects and Their Frequency
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Allergic Reactions
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Understanding the Mechanism: Why Amoxicillin Might Affect Appetite
- Direct Gastrointestinal Irritation
- Indirect Effects
- Factors Influencing Appetite Suppression
- Addressing Appetite Loss
- Further Research
- When to Consult a Doctor: Distinguishing Normal Side Effects from Serious Concerns
- Recognizing Allergic Reactions
- Monitoring for Less Common, but Serious, Side Effects
- When to Schedule a Follow-Up
Does Amoxicillin Cause Loss of Appetite?
Yes, amoxicillin can sometimes cause a loss of appetite as a side effect. This isn’t experienced by everyone, but it’s a relatively common complaint.
The mechanism isn’t fully understood, but it’s thought to be related to the drug’s effects on the gastrointestinal tract. Some people report nausea or stomach upset alongside the appetite loss.
If you experience a significant decrease in appetite while taking amoxicillin, it’s important to monitor your symptoms. Mild appetite changes usually resolve on their own. However, if the loss of appetite is severe or accompanied by other symptoms like vomiting, diarrhea, or significant weight loss, contact your doctor immediately. They can assess the situation and determine if adjustments to your medication or further treatment are necessary.
Remember, this information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your physician or pharmacist before making any changes to your medication regimen.
Amoxicillin’s Side Effects and Their Frequency
Amoxicillin, while generally safe and effective, can cause side effects. Knowing their likelihood helps you manage expectations and discuss any concerns with your doctor.
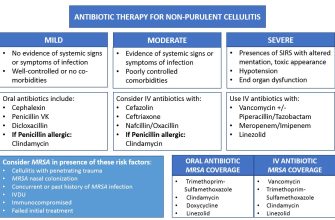
Gastrointestinal Issues
- Diarrhea: This is a common side effect, affecting around 10% of users. It usually resolves without treatment.
- Nausea: Similar frequency to diarrhea. Consider taking amoxicillin with food to mitigate this.
- Vomiting: Less common than diarrhea or nausea, but still a possibility. Again, food intake may help.
- Abdominal pain: Relatively infrequent, but possible. Contact your doctor if it’s severe.
Allergic Reactions
While rare, allergic reactions are serious. Watch for:
- Skin rash: A common sign of allergy, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Hives: Raised, itchy welts on the skin – seek medical help immediately.
- Swelling: Facial swelling, especially of the lips, tongue, or throat, is a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment.
- Difficulty breathing: A serious allergic reaction needing immediate emergency care.
Other Potential Side Effects
- Vaginal yeast infection: Amoxicillin can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina, leading to yeast overgrowth. This occurs in a small percentage of users.
- Headache: A relatively common side effect, often mild.
- Dizziness: Less frequent than headache, but potential side effect to be aware of.
Remember, this information isn’t exhaustive, and individual experiences vary. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist regarding any concerns about side effects.
Understanding the Mechanism: Why Amoxicillin Might Affect Appetite
Amoxicillin’s impact on appetite isn’t fully understood, but several factors likely contribute. Gastrointestinal upset, a common side effect, directly reduces appetite. Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, often associated with amoxicillin use, make eating unappealing or even impossible.
Direct Gastrointestinal Irritation
Amoxicillin, like many antibiotics, can irritate the lining of the stomach and intestines. This irritation triggers the body’s natural defense mechanisms, leading to discomfort and reduced desire to eat. The severity varies between individuals, with some experiencing mild discomfort and others more significant issues.
Indirect Effects
Amoxicillin’s effect on gut bacteria also plays a role. Disrupting the normal gut microbiome can indirectly influence appetite regulation. This disruption can lead to imbalances that affect hormone production and signaling, further impacting hunger cues.
Factors Influencing Appetite Suppression
| Factor | Mechanism |
|---|---|
| Dosage | Higher doses may increase the likelihood of gastrointestinal side effects. |
| Individual Sensitivity | Some individuals are more susceptible to gastrointestinal side effects than others. |
| Concurrent Medications | Interaction with other medications might exacerbate gastrointestinal issues. |
Addressing Appetite Loss
If amoxicillin causes significant appetite loss, discuss it with your doctor. They may suggest adjustments to your medication or recommend strategies to manage side effects, such as eating smaller, more frequent meals or focusing on easily digestible foods. Remember, reporting side effects allows your healthcare provider to help you manage your treatment effectively.
Further Research
While the exact mechanisms behind amoxicillin’s influence on appetite require further study, current understanding points to direct gastrointestinal irritation and alterations in the gut microbiome as key contributing factors.
When to Consult a Doctor: Distinguishing Normal Side Effects from Serious Concerns
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe diarrhea, which can be a sign of Clostridium difficile infection, a potentially serious complication. This is particularly important if the diarrhea is watery or bloody.
Recognizing Allergic Reactions
Seek immediate medical attention for allergic reactions. These can manifest as hives, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue (angioedema), difficulty breathing, or a rapid heartbeat. These symptoms require prompt treatment.
Monitoring for Less Common, but Serious, Side Effects
While loss of appetite is a common side effect, persistent or significant weight loss warrants a doctor’s visit. Also, report any signs of liver problems, such as yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), dark urine, or unusual fatigue. These symptoms need evaluation.
When to Schedule a Follow-Up
Mild side effects like nausea or mild diarrhea usually subside within a few days. If these persist beyond a week, or worsen, contact your physician. Regularly scheduled follow-up appointments are important to monitor your overall health while taking amoxicillin and confirm the medication’s effectiveness.