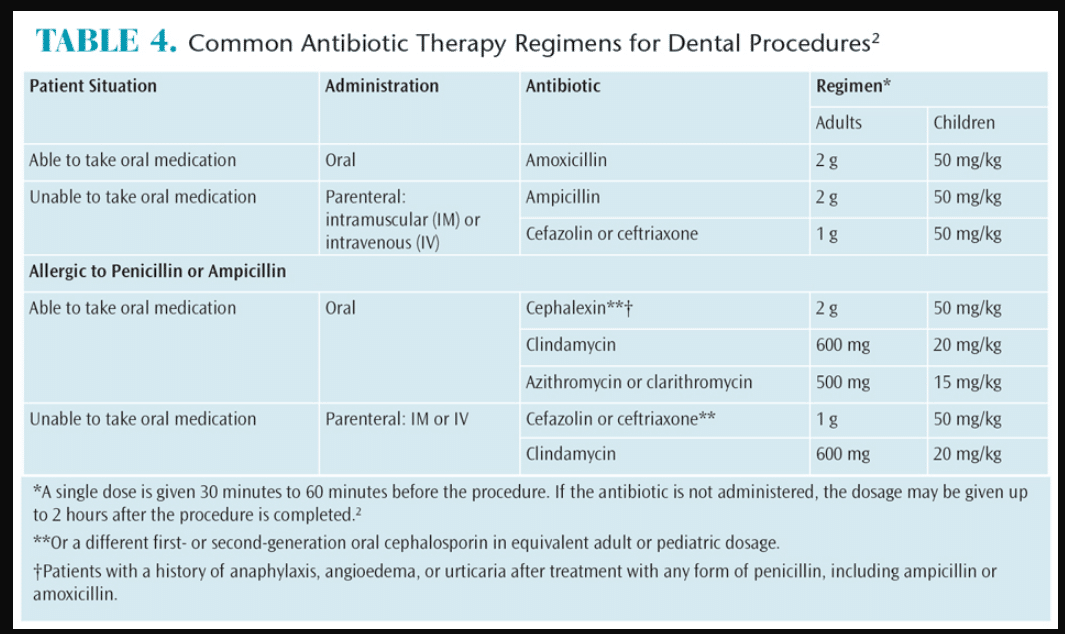
The recommended dosage of amoxicillin for dental prophylaxis is typically 2 grams, taken orally, one hour before the dental procedure. This dosage applies to adults and children over 40 kg (approximately 88 lbs). For children under 40 kg, the recommended dose is 50 mg/kg, also taken one hour prior to the dental appointment.
For patients with a history of penicillin allergies, alternative antibiotics such as clindamycin or azithromycin are preferred. It’s crucial for healthcare providers to assess the patient’s allergy history to ensure safety. If allergic, clindamycin should be administered at a dosage of 600 mg for adults or 20 mg/kg for children, while azithromycin dosage is 500 mg for adults and 15 mg/kg for children.
After administering the prophylactic dose, patients should be advised to hydrate and inform their dentist of any adverse reactions or concerns. Proper communication between patients and dental professionals ensures optimal care and minimizes the risk of infection during procedures. Always consult your dentist for personalized recommendations based on your specific health needs.
- Dental Prophylaxis Amoxicillin Dosage
- Dosage for Children
- Considerations and Special Cases
- Recommended Amoxicillin Dosage for Dental Prophylaxis in Adults
- Administration Guidelines
- Considerations for Dosage Adjustments
- Dosage Guidelines for Pediatric Patients Undergoing Dental Procedures
- Administration Considerations
- Follow-Up Care
- Considerations for Amoxicillin Dosage in Patients with Allergies or Medical Conditions
Dental Prophylaxis Amoxicillin Dosage
For dental prophylaxis, the recommended dosage of Amoxicillin varies based on patient factors. The common standard dosage for adults is 2 grams (2000 mg) administered orally, typically taken one hour before the dental procedure.
Dosage for Children
For pediatric patients, the dosage is determined by the child’s weight. The usual recommendation is 50 mg/kg of body weight, with a maximum dose of 2 grams. This also should be taken one hour prior to dental intervention.
Considerations and Special Cases
- Patients allergic to penicillin should not use Amoxicillin for prophylaxis.
- Those with a history of infective endocarditis may require different guidelines based on their healthcare provider’s advice.
- Consultation with a dentist or physician is essential for determining specific needs based on medical history and conditions.
Ensure accurate timing for administration to maximize prophylactic benefits and consult a healthcare professional if there are any uncertainties regarding dosage or suitability.
Recommended Amoxicillin Dosage for Dental Prophylaxis in Adults
The standard dosage of amoxicillin for dental prophylaxis in adults is 2 grams (2000 mg) taken 30 to 60 minutes before the dental procedure. This dosage effectively helps prevent bacterial endocarditis and other infections associated with invasive dental work.
Administration Guidelines
Amoxicillin should be taken orally with a full glass of water. If an adult is unable to take oral medication, an alternative parenteral antibiotic may be necessary under a healthcare professional’s guidance. It’s advisable to consult with a dentist or physician if an allergic reaction to penicillin or any other concern exists.
Considerations for Dosage Adjustments
For adults with renal impairment, dosage adjustments may be required based on the severity of the condition. Review of the patient’s medical history and current medications is essential to ensure safety and efficacy. Always follow the prescribing physician’s directives regarding dosage changes or alternative therapies.
Dosage Guidelines for Pediatric Patients Undergoing Dental Procedures
For pediatric patients undergoing dental procedures who require prophylaxis with amoxicillin, the recommended dosage is 50 mg/kg, up to a maximum of 2 grams. Administer this dosage orally at least one hour before the procedure. This guideline applies to patients who are at risk for infective endocarditis or have certain heart conditions.
Administration Considerations
When administering amoxicillin, calculate the total dose based on the child’s weight. For example, if a child weighs 30 kg, the proper dose is 1500 mg (30 kg x 50 mg/kg). If the calculated dosage exceeds 2000 mg, limit the dose to 2000 mg. Ensure the patient is able to swallow capsules or tablets; if not, a liquid formulation may be used, providing the concentration aligns with the dosing guidelines.
Follow-Up Care
Observe for any signs of allergic reactions or side effects after administration. Schedule a follow-up with the pediatric patients and their caregivers to assess oral health post-procedure. Encourage parents to report any unusual symptoms that may arise following treatment.
Considerations for Amoxicillin Dosage in Patients with Allergies or Medical Conditions
Adjust dosages carefully for patients with known allergies to penicillin or related antibiotics. For individuals with such allergies, alternative antibiotic therapy should be considered. Always inquire about the severity of the allergic reaction, as this influences the choice of medication. A history of anaphylaxis necessitates the avoidance of amoxicillin altogether.
When treating patients with renal conditions, consider kidney function when prescribing amoxicillin. Dosage adjustments are necessary for those with impaired renal function to avoid accumulation of the drug and potential toxicity. Utilize creatinine clearance metrics to determine the appropriate dosage.
Patients with liver disease may require caution as well, although amoxicillin is predominantly eliminated by the kidneys. Monitor liver function closely in patients with severe hepatic impairment, as reduced liver function can affect overall drug metabolism.
For those with gastrointestinal disorders, assess the potential impact on absorption. Amoxicillin’s bioavailability may be altered in patients with conditions affecting the GI tract. Adjust dosages accordingly and consider alternative formulations to ensure adequate therapeutic levels.
Monitor for interactions if patients take medications such as anticoagulants or allopurinol. Amoxicillin can potentiate the effects of warfarin, leading to increased bleeding risk. Evaluate patient medication lists carefully to prevent adverse reactions.
Lastly, consider age and body weight when determining dosage for pediatric or elderly patients. Dosing in these groups often requires careful calculations based on the patient’s specific circumstances to ensure safety and efficacy.