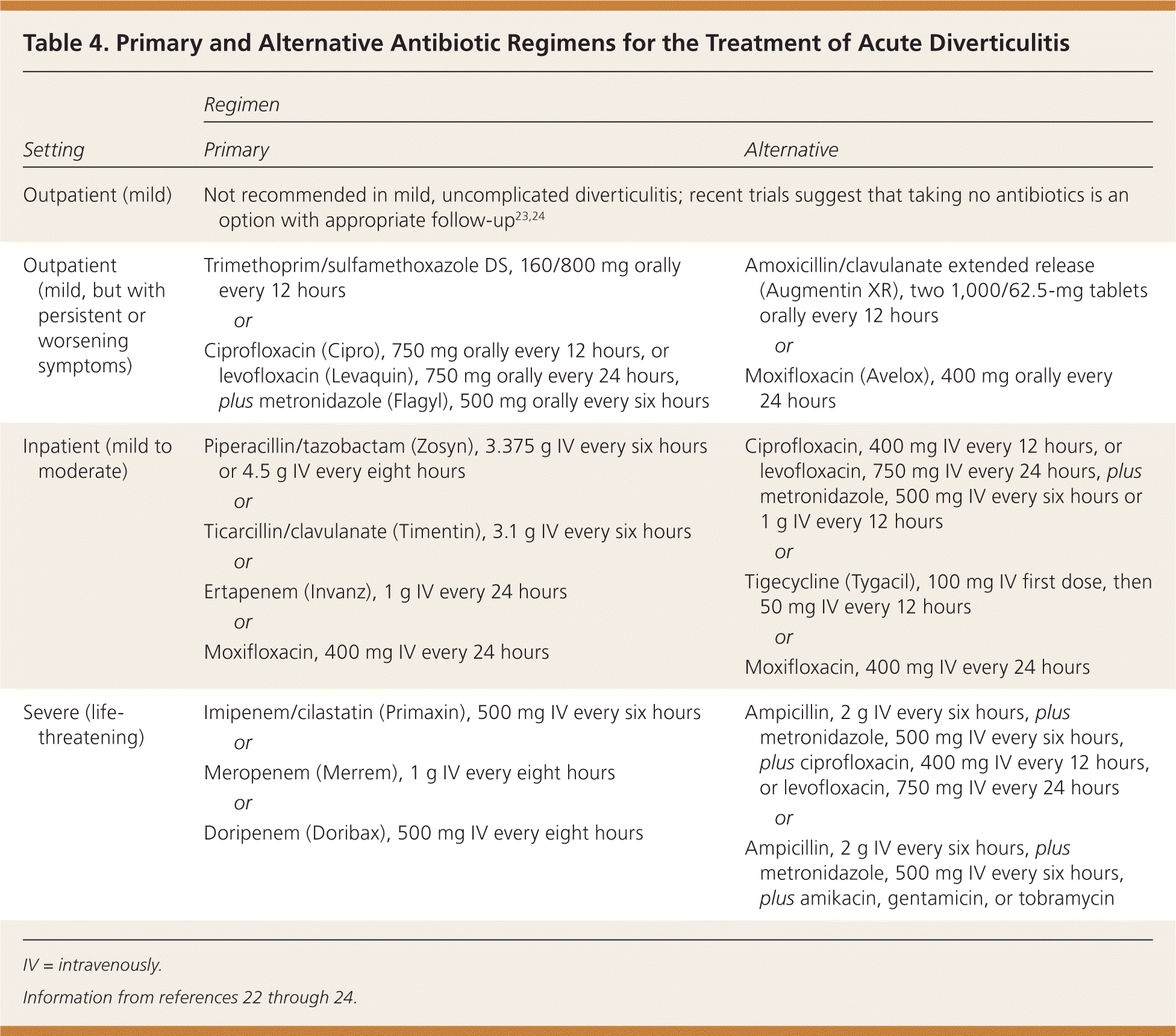
The recommended Ciprofloxacin dosage for diverticulitis typically ranges from 500mg to 750mg twice daily. This is a general guideline, and your doctor will determine the precise dosage based on your individual needs, the severity of your infection, and other health factors.
Treatment duration usually lasts 7-14 days. Never adjust your medication schedule or dosage without consulting your physician. Early and complete treatment is vital to prevent complications.
Important Considerations: Ciprofloxacin is a powerful antibiotic, and side effects are possible. Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Severe allergic reactions, while rare, require immediate medical attention. Discuss any concerns or pre-existing conditions with your doctor before starting treatment.
Remember, this information is for general knowledge and doesn’t substitute professional medical advice. Always seek guidance from a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment of diverticulitis. They can perform a proper assessment and tailor a treatment plan suitable for your specific circumstances.
- Cipro Dose for Diverticulitis: A Detailed Guide
- Factors Affecting Cipro Dosage
- Alternative Antibiotics and Treatment Considerations
- Important Note: Consult Your Doctor
- Possible Side Effects
- Understanding Diverticulitis and its Treatment
- Ciprofloxacin: Mechanism of Action in Diverticulitis
- Standard Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Diverticulitis
- Factors Influencing Dosage
- Alternative Antibiotics
- Duration of Ciprofloxacin Treatment for Diverticulitis
- Potential Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin
- Ciprofloxacin and Interactions with Other Medications
- When to Seek Alternative Treatments for Diverticulitis
- Alternative Treatment Options
Cipro Dose for Diverticulitis: A Detailed Guide
Typically, doctors prescribe 500 mg of Ciprofloxacin twice daily for 7-10 days to treat uncomplicated diverticulitis. This dosage targets the common bacteria causing the infection.
Factors Affecting Cipro Dosage
Your doctor will consider several factors when determining your specific Cipro dose. These include the severity of your infection, your overall health, and any potential drug interactions. Kidney function plays a significant role; individuals with impaired kidney function may require a lower dose or less frequent administration. Age can also influence dosage, with adjustments often made for older adults.
Alternative Antibiotics and Treatment Considerations
Ciprofloxacin isn’t always the first-line treatment for diverticulitis. Metronidazole, either alone or in combination with other antibiotics, is another common option. Severe cases might require intravenous antibiotics in a hospital setting. Treatment always depends on the individual’s needs and the doctor’s assessment.
Important Note: Consult Your Doctor
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your physician or another qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. They can accurately assess your condition, determine the appropriate antibiotic, and adjust the dose based on your unique circumstances. Ignoring a doctor’s recommendations or self-treating can have serious consequences.
Possible Side Effects
Common side effects of Ciprofloxacin include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Less common but more serious effects are possible; inform your doctor immediately if you experience unusual symptoms.
Understanding Diverticulitis and its Treatment
Diverticulitis is inflammation or infection of small pouches (diverticula) that can form in the colon. These pouches usually cause no problems, but if they become inflamed or infected, you may experience symptoms like abdominal pain, fever, nausea, and changes in bowel habits. The pain often localizes in the lower left abdomen.
Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam and imaging tests, like a CT scan, to visualize the affected area. Treatment depends on the severity of the disease. Mild cases often respond well to antibiotics, such as Ciprofloxacin, often combined with metronidazole, and a high-fiber diet to promote regular bowel movements and prevent future episodes. Doctors may prescribe Cipro alone, depending on individual circumstances and antibiotic sensitivities. Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions regarding dosage and duration of antibiotic treatment.
For moderate to severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for intravenous antibiotics and possibly bowel rest. In severe instances, surgery might be required to repair or remove the affected section of the colon. A high-fiber diet, increased fluid intake, and regular exercise are key to managing diverticulitis long-term and reducing the risk of recurrence. These lifestyle changes help to prevent constipation, a major risk factor for diverticulitis.
Your doctor will determine the best course of treatment based on your individual health and the severity of your diverticulitis. Regular checkups and open communication with your physician are vital for managing this condition.
Ciprofloxacin: Mechanism of Action in Diverticulitis
Ciprofloxacin combats diverticulitis by targeting the bacteria commonly responsible for infection. It achieves this through inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, enzymes crucial for DNA replication and cell division. This disruption halts bacterial growth and ultimately leads to bacterial death.
Specifically, ciprofloxacin binds to these enzymes, preventing them from functioning correctly. This action is particularly effective against gram-negative bacteria, a frequent culprit in diverticulitis. However, its effectiveness against gram-positive bacteria is less consistent. Therefore, physicians often consider the patient’s specific bacterial profile when prescribing Ciprofloxacin.
| Enzyme | Function | Ciprofloxacin’s Effect |
|---|---|---|
| DNA Gyrase | Unwinds and supercoils DNA during replication | Inhibits unwinding, halting replication |
| Topoisomerase IV | Separates replicated DNA during cell division | Prevents separation, blocking cell division |
The concentration of ciprofloxacin reaching the infected site is a key determinant of its success. Factors such as the severity of infection and the individual’s metabolism influence this concentration. This is why appropriate dosage and duration are critical for treatment.
Remember, ciprofloxacin is a powerful antibiotic and should only be used as prescribed by a healthcare professional. They will consider individual patient factors to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for diverticulitis.
Standard Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Diverticulitis
Ciprofloxacin is often prescribed for uncomplicated diverticulitis, usually in combination with metronidazole. A typical dosage involves 500mg of Ciprofloxacin taken twice daily for 7-14 days. The specific duration depends on your individual response to treatment and your doctor’s assessment.
Factors Influencing Dosage
Your doctor will consider several factors when determining the appropriate Ciprofloxacin dosage. These include the severity of your diverticulitis, your age, kidney function, and other health conditions. They may adjust the dosage or treatment duration based on your specific needs. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully, and report any side effects immediately. Do not alter the dosage without consulting your physician.
Alternative Antibiotics
While Ciprofloxacin is commonly used, other antibiotics may be more suitable depending on your situation. Your doctor will choose the most appropriate antibiotic based on your individual needs and any antibiotic resistance concerns. Always discuss your treatment plan with your doctor to ensure you receive the best possible care.
Duration of Ciprofloxacin Treatment for Diverticulitis
The typical duration of Ciprofloxacin treatment for uncomplicated diverticulitis is 7 to 10 days. This timeframe allows sufficient time for the infection to resolve.
However, treatment length can vary depending on several factors:
- Severity of infection: More severe cases may require a longer course of antibiotics.
- Patient response: Your doctor will monitor your progress and may adjust treatment based on your symptoms.
- Presence of complications: Abscesses or fistulas necessitate a longer treatment period and often require additional interventions beyond antibiotics.
- Underlying health conditions: Pre-existing conditions can influence antibiotic choice and treatment duration.
Your doctor will determine the appropriate course of treatment based on your individual needs. Always follow their instructions carefully. Do not stop taking Ciprofloxacin prematurely, even if your symptoms improve. Stopping early can lead to recurrence or antibiotic resistance.
Following your antibiotic course, you may experience lingering discomfort. This is normal, and usually resolves with time and dietary adjustments. If symptoms worsen or persist after completing the prescribed antibiotics, seek immediate medical attention.
- Consistent medication: Take your Ciprofloxacin as directed, at the same time each day.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to help flush out the infection.
- Diet: Eat a high-fiber diet to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation.
- Follow-up: Schedule a follow-up appointment with your doctor to monitor your progress and ensure the infection is fully cleared.
Potential Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin, while effective, can cause side effects. Common ones include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These are usually mild and resolve on their own.
Less common but more serious side effects include tendonitis or tendon rupture, particularly in older adults or those taking corticosteroids. You should report any new or worsening joint pain immediately.
Allergic reactions, ranging from mild skin rash to severe anaphylaxis, are possible. Stop taking Ciprofloxacin and seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing, swelling of your face or throat, or hives.
Ciprofloxacin can also affect your central nervous system. Symptoms like dizziness, confusion, or hallucinations are rare but possible. Avoid driving or operating machinery if you experience these.
Photosensitivity is another potential side effect; increased sun sensitivity can lead to sunburn. Protect your skin from the sun by wearing protective clothing and sunscreen.
This information is not exhaustive. Always discuss potential side effects with your doctor before starting Ciprofloxacin, and report any concerns promptly.
Ciprofloxacin and Interactions with Other Medications
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. Ciprofloxacin can interact negatively with several medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects.
Here are some key interactions to be aware of:
- Antacids: Taking antacids containing magnesium or aluminum within two hours of Ciprofloxacin significantly reduces its absorption. Separate your doses by at least two hours.
- Sucralfate: This medication for stomach ulcers also hinders Ciprofloxacin absorption. Maintain a similar two-hour gap between doses.
- Warfarin (Coumadin): Ciprofloxacin can increase the effect of warfarin, potentially leading to increased bleeding risk. Your doctor may need to monitor your INR levels more frequently.
- Theophylline: Combining Ciprofloxacin with theophylline (used for asthma and COPD) can raise theophylline levels, possibly causing side effects like heart palpitations or seizures. Careful monitoring is needed.
- Caffeine: Ciprofloxacin can slightly increase caffeine levels in the body. You might experience increased anxiety or insomnia.
- Probenecid: This drug can increase Ciprofloxacin levels in the blood, potentially increasing the risk of side effects. Your doctor should adjust your dosage accordingly.
This list isn’t exhaustive. Other potential interactions exist. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting Ciprofloxacin if you have pre-existing conditions or are taking other medications. Open communication with your doctor ensures your safety and treatment effectiveness.
- Discuss all medications and supplements with your doctor or pharmacist before starting Ciprofloxacin.
- Strictly adhere to the prescribed dosage and timing.
- Report any unexpected side effects immediately to your healthcare provider.
When to Seek Alternative Treatments for Diverticulitis
Consider alternative treatments if your diverticulitis doesn’t respond to Ciprofloxacin within 72 hours, or if you experience worsening symptoms like high fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C), severe abdominal pain, or signs of infection spreading, such as chills or increased heart rate. These indicate a more serious complication requiring immediate medical attention and possibly hospitalization.
Alternative Treatment Options
These may include intravenous antibiotics in a hospital setting to combat a severe infection. If recurring episodes occur despite antibiotic treatment, your doctor may suggest a colonoscopy to rule out other issues or explore surgical options like bowel resection in persistent cases. Dietary changes focusing on high-fiber foods to improve bowel regularity may also be recommended alongside, or instead of, antibiotics in less severe, recurring cases, after discussion with your physician.
Remember, always consult your doctor before starting any alternative treatment plan. Self-treating diverticulitis can lead to serious health problems. Your doctor will assess your individual situation and recommend the best course of action.