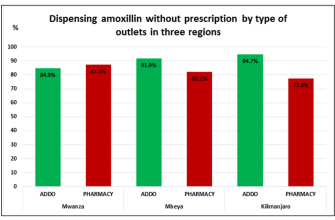
Amoxicillin is a recommended treatment for urinary tract infections (UTIs) caused by susceptible bacteria. This penicillin-type antibiotic effectively combats bacteria, helping to alleviate symptoms and promote recovery. For optimal results, it’s crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s dosage instructions and complete the full course of medication.
Typically, a healthcare professional may prescribe amoxicillin when laboratory tests indicate that the specific bacteria causing the UTI is sensitive to this antibiotic. This ensures a higher chance of cure while minimizing the risk of antibiotic resistance. Many patients report significant symptom relief within a few days of starting the treatment.
In addition to taking amoxicillin, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids can assist in flushing out the bacteria from your urinary system. Consider integrating cranberry juice into your routine, as some studies suggest that it may help prevent future UTIs. Always communicate with your healthcare provider about your symptoms and progress, especially if they do not improve within a few days of starting treatment.
- Amoxicillin Treats UTI
- Dosage and Administration
- Side Effects and Considerations
- Understanding Urinary Tract Infections
- Common Causes and Risk Factors
- Treatment Options
- How Amoxicillin Works Against Bacteria
- Mechanism of Action
- Effectiveness Against Common Bacteria
- Indications for Using Amoxicillin in UTI Treatment
- Types of UTIs Treated with Amoxicillin
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Guidelines for Amoxicillin in UTI Cases
- Potential Side Effects and Considerations
- Amoxicillin Resistance: What You Need to Know
- When to Consult a Doctor About UTI Treatment
- Recognizing Severe Symptoms
- Recurring Infections
- Special Considerations
Amoxicillin Treats UTI
Amoxicillin is often prescribed for urinary tract infections (UTIs) caused by susceptible bacteria. This antibiotic works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, effectively eliminating the infection. For optimal results, ensure accurate diagnosis and confirm that the causative bacteria are sensitive to amoxicillin.
Dosage and Administration
The typical dosage for treating UTIs with amoxicillin is 500 mg every 8 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours. Treatment usually lasts 7 to 14 days, depending on the severity of the infection. Always follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding dosage and duration.
Side Effects and Considerations
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and mild allergic reactions. If you experience severe side effects, such as difficulty breathing or swelling, seek medical attention immediately. Inform your doctor about any existing allergies or medication interactions before starting treatment.
While amoxicillin is effective for many UTIs, some cases may require alternative antibiotics due to bacterial resistance. Regular follow-ups and urine tests can help in managing recurrent infections effectively.
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) occur when harmful bacteria enter the urinary system, leading to inflammation. Symptoms typically include a frequent urge to urinate, burning sensation during urination, and cloudy urine. Maintaining proper hydration can help flush out bacteria, reducing the risk of infection.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of UTIs. Women are more susceptible due to anatomical differences, such as a shorter urethra. Sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract. Certain contraceptive methods, such as diaphragms, may also increase risk. Individuals with urinary retention or a suppressed immune system are at higher risk as well.
Treatment Options
Antibiotics, like amoxicillin, effectively treat UTIs, targeting the bacteria responsible for the infection. Completing the full course of prescribed antibiotics is crucial, even if symptoms improve early. Alongside antibiotics, using analgesics can alleviate discomfort. Always consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment tailored to individual needs.
How Amoxicillin Works Against Bacteria
Amoxicillin targets bacterial infections by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. This action disrupts the integrity of the bacterial cell wall, causing it to weaken and ultimately leading to the death of the bacteria.
Mechanism of Action
- Amoxicillin binds to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located within the bacterial cell wall.
- This binding blocks the transpeptidation enzyme, which is crucial for cross-linking the peptidoglycan layers.
- As a result, the cell wall cannot maintain its structural integrity, making the bacteria susceptible to osmotic pressure.
Effectiveness Against Common Bacteria
Amoxicillin effectively combats various pathogens responsible for urinary tract infections, including:
- Escherichia coli: The leading cause of UTIs, vulnerable to amoxicillin’s action.
- Klebsiella pneumoniae: Another common UTI pathogen, often responsive to this antibiotic.
- Proteus mirabilis: While some strains may show resistance, many are still treatable with amoxicillin.
By disrupting vital processes within these bacteria, amoxicillin helps clear infections effectively. Adhering to prescribed dosages ensures maximum impact and reduces the risk of developing antibiotic resistance.
Indications for Using Amoxicillin in UTI Treatment
Amoxicillin is recommended for treating uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) caused by susceptible organisms. Its broad-spectrum coverage makes it a suitable option for infections primarily caused by Escherichia coli and other Gram-negative bacteria.
Types of UTIs Treated with Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin effectively addresses both cystitis and pyelonephritis in patients without complicated medical histories. It is particularly beneficial for women experiencing recurrent UTIs, as well as for pregnant patients who require safe antibiotic options.
Dosage and Administration
The typical dosage for uncomplicated UTIs in adults is 500 mg every eight hours for seven days. Adjustments may be necessary based on renal function and the patient’s overall health. Adherence to the prescribed duration is crucial for minimizing recurrence and resistance development.
Dosage Guidelines for Amoxicillin in UTI Cases
For uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs), the typical dosage of amoxicillin for adults is 500 mg taken every 12 hours, or 250 mg every 8 hours. This regimen is generally prescribed for a duration of 7 to 14 days, depending on the severity of the infection and individual patient factors.
In pediatric patients, the recommended dosage varies based on weight. Generally, the dosage is calculated as 20-40 mg/kg/day divided into two or three doses. Here’s a quick reference table for pediatric dosages:
| Weight (kg) | Dosage (mg/day) | Dosing Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 10 kg | 200 – 400 mg | Every 12-8 hours |
| 20 kg | 400 – 800 mg | Every 12-8 hours |
| 30 kg | 600 – 1200 mg | Every 12-8 hours |
| 40 kg | 800 – 1600 mg | Every 12-8 hours |
Patients with renal impairment may require adjusted dosages due to decreased clearance of the drug. Always confirm the appropriate dosage adjustments with healthcare providers based on specific kidney function tests.
Monitor for signs of improvement within 48 to 72 hours. If symptoms persist, re-evaluate the case to ensure the appropriateness of amoxicillin for the specific bacteria causing the UTI, since resistance can occur.
Always consult with a healthcare professional for tailored dosages and to address any potential interactions with other medications. This ensures safe and effective treatment of the infection.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Patients using amoxicillin for urinary tract infections (UTIs) should stay informed about possible side effects. Common reactions include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These symptoms can often be mild and temporary, but if they persist, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable.
Allergic reactions can occur, manifesting as rash, itching, or difficulty breathing. If any of these symptoms arise, seek medical attention immediately as they may indicate a more serious condition.
Some individuals may experience changes in taste, headaches, or fatigue. Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet can help alleviate these effects. Probiotic supplements may also support gut health during antibiotic treatment.
Monitor for signs of superinfection, which can happen when antibiotics disrupt normal bacterial balance. Symptoms like fever or recurring infections warrant a follow-up with your doctor.
Always inform your doctor about other medications or supplements you are taking. Some interactions may reduce amoxicillin’s effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects.
Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should discuss the potential risks and benefits of using amoxicillin, as well as alternative treatments with their healthcare provider.
Adhering to the prescribed dosage and course is essential. Stopping the medication early can lead to resistance and may complicate treatment for future infections. If you have questions or concerns about your treatment, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional.
Amoxicillin Resistance: What You Need to Know
Stay informed about the rising issue of amoxicillin resistance. Bacterial infections, especially urinary tract infections (UTIs), often rely on amoxicillin for treatment. However, resistance is increasingly common. Understanding the factors that contribute to this phenomenon can help you take proactive measures.
First, misuse and overuse of antibiotics play a crucial role in developing resistance. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for dosage and duration of treatment. Avoid using antibiotics without a prescription.
In addition, consider the role of proper hygiene practices. Maintaining good personal hygiene can minimize the risk of UTIs and reduce the need for antibiotics. Staying hydrated and urinating regularly can also help flush out harmful bacteria.
Regular laboratory testing is vital in confirming the effectiveness of amoxicillin against your specific infection. Sensitivity testing can identify whether bacteria are resistant, guiding the selection of appropriate medication.
Stay updated on local resistance patterns. Collaborate with healthcare professionals to monitor changes in effectiveness over time in your community. This awareness aids in making informed decisions regarding antibiotic use.
Lastly, consider alternative treatment strategies when faced with resistance. Your healthcare provider might suggest other antibiotics, depending on the sensitivity results. Adapting treatment plans ensures that infections are effectively managed.
When to Consult a Doctor About UTI Treatment
Seek medical advice if you experience symptoms lasting longer than two days. Early intervention can prevent complications.
Recognizing Severe Symptoms
Contact a healthcare provider if you notice:
- Persistent fever over 101°F (38.3°C)
- Severe abdominal or lower back pain
- Blood in urine
- Vomiting
- Symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI) accompanied by chills or shaking
Recurring Infections
If UTIs occur more than twice within six months, it’s time to consult a doctor. Recurrent infections may indicate an underlying issue that requires further investigation.
Women who experience UTIs after sexual activity should speak with their healthcare provider about preventive measures.
Special Considerations
Pregnant women and individuals with diabetes or compromised immune systems should seek prompt medical attention at the first sign of UTI symptoms. These populations face higher risks for complications.
Lastly, if over-the-counter treatments are not providing relief, don’t hesitate to reach out to your doctor for prescription options like amoxicillin or other suitable antibiotics.