When faced with serious infections, choosing the right treatment is paramount. Amoxicillin IV provides a potent solution, particularly for patients unable to tolerate oral medications. This formulation allows for rapid absorption and higher bioavailability, ensuring effective combat against various bacterial pathogens.
Dosage accuracy plays a significant role in patient outcomes. Typically, healthcare professionals recommend adjusting the dose based on the infection’s severity and patient-specific factors. For adults, a common administration is 1 to 2 grams every 8 hours, while pediatric doses depend on weight and specific conditions. Monitoring for signs of effectiveness and potential side effects helps guide adjustments for optimal treatment.
Administration via IV not only enhances absorption but also rapidly achieves therapeutic levels in the bloodstream, making it particularly valuable in hospital settings. This approach may also reduce gastrointestinal side effects associated with oral antibiotics, offering a more comfortable experience for patients.
While Amoxicillin IV is generally well-tolerated, awareness of possible adverse reactions is crucial. Skin rashes, allergies, or gastrointestinal disturbances can occur, requiring medical assessment and intervention. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any treatment to ensure it aligns with individual health needs.
- Understanding Amoxicillin IV: Practical Insights
- Administration Guidelines
- Potential Side Effects
- Clinical Uses of Amoxicillin IV in Hospital Settings
- Dosage Guidelines and Administration Techniques for Amoxicillin IV
- Administration Techniques
- Special Considerations
- Monitoring and Managing Side Effects of Amoxicillin IV Treatment
Understanding Amoxicillin IV: Practical Insights
Amoxicillin IV doses typically range from 1 to 2 grams every 8 hours, depending on the severity of the infection and patient-specific factors. Monitor renal function closely, especially in cases of dose adjustments for renal impairment. Always ensure the dosage aligns with current clinical guidelines specific to the type of infection being treated.
Administration Guidelines
Administer Amoxicillin IV slowly over 30 minutes to minimize potential side effects. In cases requiring prolonged therapy, switch to oral formulations when clinically appropriate to enhance patient comfort and adherence. Check for compatibility with other intravenous medications if co-administering.
Potential Side Effects
Watch for common reactions such as gastrointestinal upset, rash, or allergic reactions. Educate patients about signs of serious side effects, including difficulty breathing or swelling of the face and throat. Immediate intervention is crucial in such cases. Regular follow-ups help identify and manage any emerging concerns effectively.
Encourage hydration to support renal clearance and reduce the risk of crystalluria. This simple measure can significantly impact patient outcomes. Maintain open communication with healthcare staff for timely updates on patient progress and any adverse reactions.
Clinical Uses of Amoxicillin IV in Hospital Settings
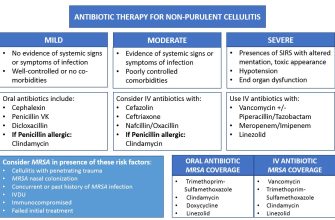
Amoxicillin IV serves as a frontline treatment for a variety of bacterial infections in hospital environments. It effectively targets pathogens like Streptococcus pneumoniae and Escherichia coli. Healthcare providers often administer it for pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and skin infections, particularly when patients cannot take oral medications.
The drug is particularly beneficial in pediatric care, addressing acute otitis media and respiratory tract infections. Its intravenous formulation allows for rapid absorption, ensuring quick therapeutic effects. In surgical settings, it plays a key role in prophylaxis to prevent postoperative infections, especially in procedures involving contaminated sites.
Monitoring drug-related allergies is vital, especially with a history of penicillin sensitivity. Providers often consider alternative options based on patient history. Dosing adjustments may be necessary in cases of renal impairment. Regular assessment of therapeutic outcomes ensures optimal dosing and minimizes the potential for resistance development.
Amoxicillin IV stands out in its ability to maintain a favorable safety profile while being generally well-tolerated by patients. Its use contributes significantly to reduced hospitalization durations and improved recovery rates. Timely intervention with this antibiotic can decrease complication risks and enhance patient outcomes.
Dosage Guidelines and Administration Techniques for Amoxicillin IV
Administer Amoxicillin IV as an infusion or bolus. The typical dosage for adults ranges from 1 to 2 grams every 8 to 12 hours, depending on infection severity. For pediatric patients, the recommended dose is typically 30 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three doses.
Administration Techniques
- Prepare the solution using sterile technique.
- For intravenous infusion, dilute the Amoxicillin IV with compatible fluids, such as Normal Saline or Dextrose 5% in Water (D5W).
- Infuse over a period of 30 minutes to 1 hour to minimize potential reactions.
- Monitor the patient closely during the first administration for allergic reactions or infusion-related side effects.
Special Considerations
- Adjust dosages for patients with renal impairment. Reduced renal function may require less frequent dosing.
- Consider the patient’s weight in pediatric dosing to ensure accurate administration.
- Avoid administering Amoxicillin IV through the same line as incompatible medications.
Always verify the dosage with updated guidelines and adjust as needed based on patient response and clinical status. Regularly assess the site of administration for signs of phlebitis or infiltration, ensuring timely intervention if complications arise.
Monitoring and Managing Side Effects of Amoxicillin IV Treatment
Regularly assess patients receiving Amoxicillin IV for any adverse reactions. Monitor vital signs, including temperature and heart rate, as these can indicate a possible allergic response or infection exacerbation. Conduct routine evaluations of renal function, particularly in those with pre-existing kidney issues, as dosage adjustments may be necessary.
Be vigilant for gastrointestinal side effects. Diarrhea is common with antibiotic therapy; advise patients to report any severe or persistent symptoms. Recommend dietary adjustments, such as increasing fluid intake and consuming bland foods, to alleviate discomfort. If diarrhea persists, consider switching to a probiotic or an alternative antibiotic.
Skin reactions, including rashes, may occur. Instruct patients to notify you immediately if a rash appears, as this may signal an allergic response. If a rash develops, evaluate its severity. Mild reactions may warrant continued observation, while severe or widespread reactions often require discontinuation of the drug and initiation of appropriate antihistamine treatment.
Educate patients about the potential for yeast infections, which can arise during and after treatment. Advise them to recognize signs such as unusual discharge or itching and report these symptoms promptly. Use antifungal treatments as needed and consider preventive measures for future courses of antibiotics.
Conduct periodic blood tests to evaluate liver function, especially in patients with a history of liver disease or those receiving prolonged therapy. Elevations in liver enzymes may necessitate a reevaluation of treatment plans.
Encourage open communication between patients and healthcare providers. This collaboration helps in identifying and addressing side effects early, promoting better outcomes and patient comfort. Tailor monitoring plans based on individual risk factors and past medical history for enhanced safety during Amoxicillin IV therapy.