If you’re experiencing a sore throat and cough, amoxicillin may be a suitable option for treatment, especially if a bacterial infection is suspected. This antibiotic works by targeting specific bacteria, effectively reducing inflammation and alleviating symptoms. Consulting a healthcare professional remains essential to determine if this medication is appropriate for your condition.
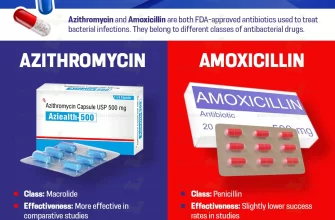
Amoxicillin belongs to the penicillin group of antibiotics, making it a go-to choice for various infections, including those affecting the respiratory system. It’s crucial to use this medication only when prescribed, as misuse can lead to antibiotic resistance. Keep in mind that symptoms lasting longer than a week or severe manifestations require prompt medical attention to rule out complications or other underlying health issues.
Dosage typically varies based on the patient’s age, weight, and the severity of the infection. Standard recommendations suggest taking amoxicillin three times a day for a week. Maintaining a consistent schedule ensures optimal effectiveness. Be aware of potential side effects, including gastrointestinal upset or allergic reactions, and report any unusual symptoms to your doctor.
Combining amoxicillin with supportive measures, such as hydration, throat lozenges, and rest, can enhance recovery. Stay informed about your health and seek guidance whenever symptoms arise, ensuring a swift return to wellness.
- Amoxicillin for Sore Throat and Cough
- Dosage and Administration
- Side Effects and Precautions
- Understanding the Role of Amoxicillin in Treating Throat Infections
- When Is Amoxicillin Prescribed?
- Dosage and Administration
- When is Amoxicillin Prescribed for Cough and Sore Throat?
- Diagnosis Confirmation
- Guidelines for Use
- Dosage Guidelines for Amoxicillin in Throat Infections
- Duration of Treatment
- Special Considerations
- Possible Side Effects of Amoxicillin Use for Cough
- Allergic Reactions
- Other Possible Side Effects
- How Amoxicillin Works Against Bacterial Infections
- Alternatives to Amoxicillin for Sore Throat Management
- Home Remedies
- Throat Lozenges and Sprays
- Factors to Consider Before Taking Amoxicillin
- Consulting a Healthcare Provider: Key Questions to Ask
Amoxicillin for Sore Throat and Cough
Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for sore throats caused by bacterial infections, particularly streptococcal pharyngitis. For effective treatment, consult with a healthcare provider to determine if your throat infection is bacterial, as amoxicillin is ineffective against viral infections.
Dosage and Administration
The typical dosage for adults and children over 40 kg is 500 mg every 12 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours, depending on the severity of the infection. Always complete the full course, even if symptoms improve, to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Side Effects and Precautions
While generally well-tolerated, amoxicillin can cause side effects like nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. Notify your doctor of any past allergic reactions to penicillin or cephalosporin antibiotics. Ensure your doctor is aware of all medications and conditions you have to avoid interactions.
Understanding the Role of Amoxicillin in Treating Throat Infections
Amoxicillin targets bacterial infections in the throat, providing relief from symptoms like pain and inflammation associated with strep throat. This antibiotic disrupts the growth of bacteria, making it a key choice for healthcare providers when a bacterial cause is confirmed or strongly suspected.
When Is Amoxicillin Prescribed?
Healthcare providers recommend Amoxicillin specifically for bacterial throat infections, such as streptococcal pharyngitis. If you experience a sore throat accompanied by high fever, swollen lymph nodes, or white patches on the tonsils, your doctor may perform a rapid strep test. A positive result indicates that Amoxicillin can help expedite your recovery process.
Dosage and Administration
Patients typically receive Amoxicillin in either tablet or liquid form, with dosages depending on age, weight, and severity of the infection. It’s essential to adhere to the prescribed schedule to maintain consistent medication levels in the bloodstream. Skipping doses can lead to decreased effectiveness and potential resistance. Complete the entire course of medication, even if symptoms improve, to fully eradicate the infection.
Stay hydrated and consider using throat lozenges to soothe irritation while on the medication. Always discuss any allergies or other medications with your healthcare provider to avoid interactions.
Amoxicillin offers significant support in managing bacterial throat infections, facilitating a quicker return to health when used appropriately.
When is Amoxicillin Prescribed for Cough and Sore Throat?
Amoxicillin is prescribed for cough and sore throat primarily when a bacterial infection is suspected. If a healthcare provider identifies streptococcal pharyngitis, commonly known as strep throat, treatment with Amoxicillin may be initiated. Symptoms of strep throat include severe sore throat, fever, swollen lymph nodes, and absence of cough.
Diagnosis Confirmation
Before prescribing Amoxicillin, clinicians often perform a rapid strep test or throat culture to confirm the presence of Streptococcus bacteria. If the test results are positive, the prescription of Amoxicillin helps combat the infection effectively.
Guidelines for Use
For adults and children able to swallow, Amoxicillin is commonly administered as an oral suspension or tablet. It is crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. This practice ensures complete elimination of the bacteria and reduces the risk of resistance.
Amoxicillin is not effective against viral infections, which are common causes of cough and sore throats. If a viral cause is suspected, supportive treatments may be recommended instead. Always consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
Dosage Guidelines for Amoxicillin in Throat Infections
The standard dosage of amoxicillin for adults with bacterial throat infections, such as strep throat, is typically 500 mg every 12 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours for more severe cases. For children, the recommended dose is usually based on their weight, with a common guideline being 20-40 mg per kg per day, divided into two or three doses.
Duration of Treatment
For throat infections, continue amoxicillin therapy for 10 days. Stopping the medication early may result in incomplete treatment and potential recurrence of the infection. Always ensure to complete the prescribed course, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
Special Considerations
Patients with renal impairment may require adjusted dosages due to altered clearance of the medication. Monitoring kidney function is essential in these cases. Pregnant or nursing individuals should consult their healthcare provider for tailored recommendations.
Possible Side Effects of Amoxicillin Use for Cough
Using amoxicillin for a cough can lead to several side effects that users should be aware of. Common reactions include gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. These symptoms occur as a result of the antibiotic impacting the natural balance of bacteria in the gut.
Allergic Reactions
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions, ranging from mild to severe. Signs of an allergic response include rashes, itching, or swelling, particularly in the face or throat. In rare instances, anaphylaxis can occur, requiring immediate medical attention.
Other Possible Side Effects
Less common side effects may involve changes in liver function, indicated by jaundice or dark urine. Users may also notice yeast infections or fungal infections due to the alteration in normal flora. If any unusual symptoms arise, consult a healthcare provider for guidance and possible alternatives.
How Amoxicillin Works Against Bacterial Infections
Amoxicillin targets bacteria by inhibiting their ability to form cell walls. This action disrupts the structure that protects bacterial cells, leading to their eventual death. When a bacterial infection occurs, such as in cases of sore throat, the presence of bacteria triggers an immune response. Amoxicillin assists the immune system by reducing the number of viable bacteria, allowing the body to eliminate the infection more effectively.
This antibiotic is particularly effective against specific types of bacteria, including streptococci and enterococci, which are common culprits in throat infections. By blocking the enzyme transpeptidase, which is involved in the cross-linking of peptidoglycan layers in bacterial cell walls, amoxicillin compromises the bacteria’s integrity.
It’s important to complete the full course of amoxicillin as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. Skipping doses or stopping too early can lead to antibiotic resistance, where bacteria adapt and learn to survive despite treatment.
Dosage may vary based on the severity of the infection and the individual’s health status. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and duration. Regular monitoring and follow-up can ensure that the medication is working effectively and help manage any potential side effects.
In cases where a cough accompanies a sore throat, amoxicillin can reduce the underlying infection, thereby alleviating symptoms. However, remember that antibiotics like amoxicillin are ineffective against viral infections. Always seek medical advice to confirm whether a bacterial infection is present before beginning treatment.
Alternatives to Amoxicillin for Sore Throat Management
Consider using over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to alleviate throat discomfort. These medications reduce pain and inflammation effectively.
Home Remedies
- Saltwater Gargle: Mix one teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water. Gargle several times a day to soothe irritation.
- Honey and Lemon: Combine honey with fresh lemon juice in warm water. This mixture can provide relief and has antibacterial properties.
- Herbal Teas: Drink chamomile or ginger tea. Both have soothing effects and can help reduce inflammation.
Throat Lozenges and Sprays
- Throat Lozenges: Sucking on lozenges or hard candies stimulates saliva production, which helps keep the throat moist.
- Throat Sprays: Sprays containing anesthetics can numb the throat and reduce pain temporarily.
For persistent symptoms, a healthcare provider may recommend a course of corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, especially if allergies are a factor. Always consult with a healthcare professional before trying new treatments, especially in cases of severe symptoms or underlying health conditions.
Factors to Consider Before Taking Amoxicillin
Consult your healthcare provider before using amoxicillin, especially if you have existing health conditions.
- Allergies: Inform your doctor about any allergies to penicillin or other antibiotics. A history of allergic reactions may preclude amoxicillin use.
- Pregnancy and Nursing: Discuss with your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding. Amoxicillin is generally considered safe, but medical advice is important.
- Interactions: Review current medications. Amoxicillin can interact with certain anticoagulants and other drugs, altering their effectiveness.
- Dosing: Adhere strictly to the prescribed dosage. Do not self-adjust or skip doses, as this can lead to resistance and treatment failure.
- Duration of Use: Complete the full course as directed, even if symptoms improve. Stopping early may result in a resurgence of infection.
Be mindful of side effects. Common ones include nausea, diarrhea, and skin rashes. Report any severe reactions, such as difficulty breathing or swelling, immediately.
Consider your specific symptoms. Amoxicillin may not be suitable for all throat infections, particularly those caused by viral infections like the common cold.
Keep an open line of communication with your healthcare provider. Share your progress and any concerns during treatment for optimal care.
Consulting a Healthcare Provider: Key Questions to Ask
Ask your healthcare provider about the specific cause of your sore throat and cough. Understanding whether it’s viral or bacterial will guide effective treatment options.
Inquire about the appropriateness of amoxicillin for your condition. Mention any symptoms, such as fever or severe pain, that can help determine if antibiotics are necessary.
Discuss potential side effects of amoxicillin. Knowing the common reactions helps you monitor your health effectively while on the medication.
Consider asking how long you should expect to take amoxicillin. Clarifying the duration promotes adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen.
Request information about possible interactions with other medications you may be taking. This ensures safe and effective use of all treatments.
Seek advice on additional remedies or supportive care to alleviate your symptoms. Recommendations might include over-the-counter medications or home remedies to enhance comfort.
Confirm when to follow up if your symptoms do not improve. Knowing the timeline helps in maintaining health without unnecessary delays.
| Question | Reason |
|---|---|
| What is causing my sore throat and cough? | Identifies the appropriate treatment. |
| Is amoxicillin necessary for my condition? | Ensures antibiotics are used only when needed. |
| What are the side effects of amoxicillin? | Prepares you for monitoring your response. |
| How long will I need to take this medication? | Helps in following the treatment plan. |
| Are there any interactions with my current medications? | Ensures overall safety in your treatment. |
| What additional remedies can help? | Enhances comfort alongside medication. |
| When should I follow up if I feel no improvement? | Prevents complications and encourages timely care. |